Abstract
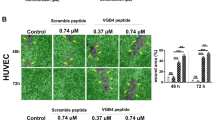
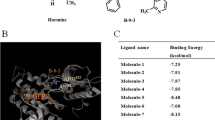
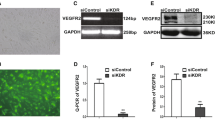
There is ample evidence to suggest that vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) is a potent mitogen factor in vasculogenesis and angiogenesis and that blockade of VEGF-mediated signals can also prevent tumor growth via enforcing cell apoptosis. In the current study, we assessed the suppressing effect of VGB4, a VEGF antagonist peptide with the binding ability to both VEGF receptor1 and VEGF receptor2, on VEGF-induced proliferation and migration of the human lung adenocarcinoma cell line A549 and the human colon adenocarcinoma cell line HT29 using MTT assay, colony formation assay, and Scratch-wound assay. To evaluate the apoptotic inductive effect of VGB4 on A549 and HT29 cells, apoptosis analysis was carried out by flow cytometry and TUNEL assay. Likewise, p53 and PTEN expression level was examined by immunofluorescence microscopy. In addition, the level of proteins involved in VEGF signaling pathways related to apoptosis was investigated using western blot analysis. Our results indicated that VGB4 markedly inhibited VEGF-induced proliferation and migration, and induced apoptosis of A549 and HT29 cells dose dependently. Encouragingly, significant downregulation of B-cell lymphoma 2 (Bcl2), X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis, Procaspase9, and procaspase3, as well as upregulation of PTEN and P53 tumor suppressors, BCL2 associated X, Cytochrome c, cleaved caspase9, and cleaved caspase3 in VGB4-treated A549 and HT29 cells, further confirmed the profound inductive influence of VGB4 on apoptotic pathways. These findings along with the results from our previous studies show that VGB4 may be considerable for cancer therapy.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this article.
References
Gerl R, Vaux DL (2005) Apoptosis in the development and treatment of cancer. Carcinogenesis 26(2):263–270. https://doi.org/10.1093/carcin/bgh283
Hanahan D, Weinberg RA (2011) Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell 144(5):646–674. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2011.02.013
Reed JC (1999) Dysregulation of apoptosis in cancer. J Clin Oncol 17(9):2941–2941. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.1999.17.9.2941
Sharma A, Boise LH, Shanmugam M (2019) Cancer metabolism and the evasion of apoptotic cell death. Cancers 11(8):1144. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11081144
Fernald K, Kurokawa M (2013) Evading apoptosis in cancer. Trends Cell Biol 23(12):620–633. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tcb.2013.07.006
Singh R, Letai A, Sarosiek K (2019) Regulation of apoptosis in health and disease: the balancing act of BCL-2 family proteins. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 20(3):175–193. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41580-018-0089-8
Lee C, Tien H, Hu C, Chou W, Lin L (2007) Marrow angiogenesis-associated factors as prognostic biomarkers in patients with acute myelogenous leukaemia. Br J Cancer 97(7):877–882. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bjc.6603966
Madlambayan GJ, Meacham AM, Hosaka K, Mir S, Jorgensen M, Scott EW, Siemann DW, Cogle CR (2010) Leukemia regression by vascular disruption and antiangiogenic therapy. Blood 116(9):1539–1547. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2009-06-230474
Pidgeon GP, Barr MP, Harmey JH, Foley DA, Bouchier-Hayes DJ (2001) Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) upregulates BCL-2 and inhibits apoptosis in human and murine mammary adenocarcinoma cells. Br J Cancer 85(2):273–278. https://doi.org/10.1054/bjoc.2001.1876
Gerber H-P, Dixit V, Ferrara N (1998) Vascular endothelial growth factor induces expression of the antiapoptotic proteins Bcl-2 and A1 in vascular endothelial cells. J Biol Chem 273(21):13313–13316. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.273.21.13313
Gerber H-P, McMurtrey A, Kowalski J, Yan M, Keyt BA, Dixit V, Ferrara N (1998) Vascular endothelial growth factor regulates endothelial cell survival through the phosphatidylinositol 3′-kinase/Akt signal transduction pathway: requirement for Flk-1/KDR activation. J Biol Chem 273(46):30336–30343. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.273.46.30336
Behelgardi MF, Zahri S, Mashayekhi F, Mansouri K, Asghari SM (2018) A peptide mimicking the binding sites of VEGF-A and VEGF-B inhibits VEGFR-1/-2 driven angiogenesis, tumor growth and metastasis. Sci Rep 8(1):1–13. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-36394-0
Behelgardi MF, Zahri S, Shahvir ZG, Mashayekhi F, Mirzanejad L, Asghari SM (2020) Targeting signaling pathways of VEGFR1 and VEGFR2 as a potential target in the treatment of breast cancer. Mol Biol Rep 47(3):2061–2071. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-020-05306-9
Ellis LM, Hicklin DJ (2008) VEGF-targeted therapy: mechanisms of anti-tumour activity. Nat Rev Cancer 8(8):579–591. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc2403
Jiang N, Dai Q, Su X, Fu J, Feng X, Peng J (2020) Role of PI3K/AKT pathway in cancer: the framework of malignant behavior. Mol Biol Rep 47(6):4587–4629. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-020-05435-1
Inai T, Mancuso M, Hashizume H, Baffert F, Haskell A, Baluk P, Hu-Lowe DD, Shalinsky DR, Thurston G, Yancopoulos GD (2004) Inhibition of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) signaling in cancer causes loss of endothelial fenestrations, regression of tumor vessels, and appearance of basement membrane ghosts. Am J Pathol 165(1):35–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0002-9440(10)63273-7
Mancuso MR, Davis R, Norberg SM, O’Brien S, Sennino B, Nakahara T, Yao VJ, Inai T, Brooks P, Freimark B (2006) Rapid vascular regrowth in tumors after reversal of VEGF inhibition. J Clin Investig 116(10):2610–2621. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI24612
Fallah A, Sadeghinia A, Kahroba H, Samadi A, Heidari HR, Bradaran B, Zeinali S, Molavi O (2019) Therapeutic targeting of angiogenesis molecular pathways in angiogenesis-dependent diseases. Biomed Pharmacother 110:775–785. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2018.12.022
Assareh E, Mehrnejad F, Mansouri K, Esmaeili Rastaghi AR, Naderi-Manesh H, Asghari SM (2019) A cyclic peptide reproducing the α1 helix of VEGF-B binds to VEGFR-1 and VEGFR-2 and inhibits angiogenesis and tumor growth. Biochem J 476(4):645–663. https://doi.org/10.1042/BCJ20180823
Sadremomtaz A, Kobarfard F, Mansouri K, Mirzanejad L, Asghari SM (2018) Suppression of migratory and metastatic pathways via blocking VEGFR1 and VEGFR2. J Recept Signal Transduct 38(5–6):432–441. https://doi.org/10.1080/10799893.2019.1567785
Gille J, Heidenreich R, Pinter A, Schmitz J, Boehme B, Hicklin DJ, Henschler R, Breier G (2007) Simultaneous blockade of VEGFR-1 and VEGFR-2 activation is necessary to efficiently inhibit experimental melanoma growth and metastasis formation. Int J Cancer 120(9):1899–1908. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.22531
Sadremomtaz A, Mansouri K, Alemzadeh G, Safa M, Rastaghi AE, Asghari SM (2018) Dual blockade of VEGFR1 and VEGFR2 by a novel peptide abrogates VEGF-driven angiogenesis, tumor growth, and metastasis through PI3K/AKT and MAPK/ERK1/2 pathway. Biochim Biophys Acta 1862(12):2688–2700. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbagen.2018.08.013
Fan F, Wey JS, McCarty MF, Belcheva A, Liu W, Bauer TW, Somcio RJ, Wu Y, Hooper A, Hicklin DJ (2005) Expression and function of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-1 on human colorectal cancer cells. Oncogene 24(16):2647–2653. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1208246
Decaussin M, Sartelet H, Robert C, Moro D, Claraz C, Brambilla C, Brambilla E (1999) Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and its two receptors (VEGF-R1-Flt1 and VEGF-R2-Flk1/KDR) in non-small cell lung carcinomas (NSCLCs): correlation with angiogenesis and survival. J Pathol 188(4):369–377. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1096-9896(199908)188:4%3c369::AID-PATH381%3e3.0.CO;2-X
Holzer TR, Fulford AD, Nedderman DM, Umberger TS, Hozak RR, Joshi A, Melemed SA, Benjamin LE, Plowman GD, Schade AE (2013) Tumor cell expression of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 is an adverse prognostic factor in patients with squamous cell carcinoma of the lung. PLoS ONE 8(11):e80292. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0080292
Goel HL, Mercurio AM (2013) VEGF targets the tumour cell. Nat Rev Cancer 13(12):871–882. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc3627
Seto T, Higashiyama M, Funai H, Imamura F, Uematsu K, Seki N, Eguchi K, Yamanaka T, Ichinose Y (2006) Prognostic value of expression of vascular endothelial growth factor and its flt-1 and KDR receptors in stage I non-small-cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 53(1):91–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lungcan.2006.02.009
Duff SE, Jeziorska M, Rosa DD, Kumar S, Haboubi N, Sherlock D, O’Dwyer ST, Jayson GC (2006) Vascular endothelial growth factors and receptors in colorectal cancer: implications for anti-angiogenic therapy. Eur J Cancer 42(1):112–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejca.2005.09.018
Berns K, Horlings HM, Hennessy BT, Madiredjo M, Hijmans EM, Beelen K, Linn SC, Gonzalez-Angulo AM, Stemke-Hale K, Hauptmann M (2007) A functional genetic approach identifies the PI3K pathway as a major determinant of trastuzumab resistance in breast cancer. Cancer Cell 12(4):395–402. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2007.08.030
Will M, Qin ACR, Toy W, Yao Z, Rodrik-Outmezguine V, Schneider C, Huang X, Monian P, Jiang X, De Stanchina E (2014) Rapid induction of apoptosis by PI3K inhibitors is dependent upon their transient inhibition of RAS–ERK signaling. Cancer Discov 4(3):334–347. https://doi.org/10.1158/2159-8290
Chang F, Lee J, Navolanic P, Steelman L, Shelton J, Blalock W, Franklin R, McCubrey J (2003) Involvement of PI3K/Akt pathway in cell cycle progression, apoptosis, and neoplastic transformation: a target for cancer chemotherapy. Leukemia 17(3):590–603. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2402824
Liu R, Chen Y, Liu G, Li C, Song Y, Cao Z, Li W, Hu J, Lu C, Liu Y (2020) PI3K/AKT pathway as a key link modulates the multidrug resistance of cancers. Cell Death Dis 11(9):1–12. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-020-02998-6
Bishnupuri KS, Alvarado DM, Khouri AN, Shabsovich M, Chen B, Dieckgraefe BK, Ciorba MA (2019) IDO1 and kynurenine pathway metabolites activate PI3K-Akt signaling in the neoplastic colon epithelium to promote cancer cell proliferation and inhibit apoptosis. Can Res 79(6):1138–1150. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472
Li L, Wang F, Zhang J, Wang K, De X, Li L, Zhang Y (2021) Typical phthalic acid esters induce apoptosis by regulating the PI3K/Akt/Bcl-2 signaling pathway in rat insulinoma cells. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 208:111461. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.111461
Fan Y, Yang F, Cao X, Chen C, Zhang X, Zhang X, Lin W, Wang X, Liang C (2016) Gab1 regulates SDF-1-induced progression via inhibition of apoptosis pathway induced by PI3K/AKT/Bcl-2/BAX pathway in human chondrosarcoma. Tumor Biol 37(1):1141–1149. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-3815-2
Chaudhary AK, Yadav N, Bhat TA, O’Malley J, Kumar S, Chandra D (2016) A potential role of X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein in mitochondrial membrane permeabilization and its implication in cancer therapy. Drug Discov Today 21(1):38–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.drudis.2015.07.014
Funding
No funding was received for conducting this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection, and the analyses were performed by MFB, ZGS and SMA. The manuscript was written by MFB and all authors read and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This study includes only laboratory studies on stable established cell lines. No ethical or institutional approval is required.
Research involving human participants
No humans were used in this study.
Consent to publish
Authors approve for submitting the publication.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Farzaneh Behelgardi, M., Gholami Shahvir, Z. & Asghari, S.M. Apoptosis induction in human lung and colon cancer cells via impeding VEGF signaling pathways. Mol Biol Rep 49, 3637–3647 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-022-07203-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-022-07203-9