Abstract
Background
Lung cancer (LC) is the most common types of cancer worldwide and is marked by high mortality rate. LC is classified into two major types due to their molecular and histological properties; non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) A549 and small cell lung cancer (SCLC). Currently, surgery, chemotherapy and radiation therapy are the most common treatment options of LC. However, the survival rate of LC is still very poor. Therefore, new treatment strategies are urgently needed. Erufosine (ErPC3) is a novel alkylphosphocholine and inhibits the translocation of Akt to the plasma membrane.
Methods and results
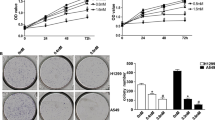
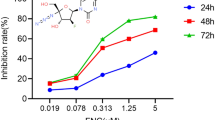
In the current study, the effects of ErPC3 in NSCLC cell line A549 and SCLC cell line DMS 114 in terms of cell viability, induction of apoptosis, cell cycle phase distribution, gene and protein expression levels, and migration capacity were investigated. 25 µM ErPC3 exhibited dose-dependent cytotoxicity against in both cancer cells. However, DMS 114 was more sensitive to ErPC3 than A549. Similarly, ErPC3 induced apoptotic cell ratio in DMS114 was significantly greater than A549. 25 µM ErPC3 caused the accumulation of both cell in G2/M phase. The levels of BCL-2 were downregulated and CASPASE 3–7 and BAX were upregulated while p-Akt levels were reduced in A549 and DMS 114 cells treated with 25 µM ErPC3. Besides, ErPC3 displayed anti-migratory effect on A549 and DMS 114.
Conclusion
These findings suggest that ErPC3 may be a promising novel therapeutic candidate for treatment of LC. ErPC3 treatment merits further investigation as potential agent against LC.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL et al (2021) Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 71:209–249
Travis WD, Brambilla E, Burke AP et al (2015) Introduction to the 2015 World Health Organization classification of tumors of the lung, pleura, thymus, and heart. J Thorac Oncol 10:1240–1242
Hecht SS (2003) Tobacco carcinogens, their biomarkers and tobacco-induced cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 3:733–744
Yu C-J (2018) Letter from Taiwan. Respirology 23:535–537
Ji X, Bossé Y, Landi MT et al (2018) Identification of susceptibility pathways for the role of chromosome 15q25. 1 in modifying lung cancer risk. Nat Commun 9:1–15
Eckel SP, Cockburn M, Shu Y-H et al (2016) Air pollution affects lung cancer survival. Thorax 71:891–898
Gelsomino F, Rossi G, Tiseo M (2014) MET and small-cell lung cancer Cancers (Basel) 6:2100–2115
Yan Y, Su C, Hang M et al (2017) Recombinant Newcastle disease virus rL-RVG enhances the apoptosis and inhibits the migration of A549 lung adenocarcinoma cells via regulating alpha 7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in vitro. Virol J 14:190. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12985-017-0852-z
McLean AEB, Barnes DJ, Troy LK (2018) Diagnosing lung cancer: the complexities of obtaining a tissue diagnosis in the era of minimally invasive and personalised medicine. J Clin Med. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm7070163
Deveraux QL, Schendel SL, Reed JC (2001) Antiapoptotic proteins. The bcl-2 and inhibitor of apoptosis protein families. Cardiol Clin 19:57–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0733-8651(05)70195-8
Cheng H, Shcherba M, Pendurti G et al (2014) Targeting the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway: potential for lung cancer treatment. Lung Cancer Manag 3:67–75
Vivanco I, Sawyers CL (2002) The phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase–AKT pathway in human cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 2:489–501
Tsao AS, McDonnell T, Lam S et al (2003) Increased phospho-AKT (Ser473) expression in bronchial dysplasia: implications for lung cancer prevention studies. Cancer Epidemiol Prev Biomarkers 12:660–664
Balsara BR, Pei J, Mitsuuchi Y et al (2004) Frequent activation of AKT in non-small cell lung carcinomas and preneoplastic bronchial lesions. Carcinogenesis 25:2053–2059. https://doi.org/10.1093/carcin/bgh226
Tang J-M, He Q-Y, Guo R-X, Chang X-J (2006) Phosphorylated Akt overexpression and loss of PTEN expression in non-small cell lung cancer confers poor prognosis. Lung Cancer 51:181–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lungcan.2005.10.003
Scrima M, De Marco C, Fabiani F et al (2012) Signaling networks associated with AKT activation in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC): new insights on the role of phosphatydil-inositol-3 kinase. PLoS ONE 7:e30427. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0030427
Papadimitrakopoulou V, Adjei AA (2006) The Akt/mTOR and mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways in lung cancer therapy. J Thorac Oncol Off Publ Int Assoc Study Lung Cancer 1:749–751
Tripathi SC, Fahrmann JF, Celiktas M et al (2017) MCAM mediates chemoresistance in small-cell lung cancer via the PI3K/AKT/SOX2 signaling pathway. Cancer Res 77:4414–4425
Chometon G, Cappuccini F, Raducanu A et al (2014) The membrane-targeted alkylphosphocholine erufosine interferes with survival signals from the extracellular matrix. Anti-Cancer Agents Med Chem (Formerly Curr Med Chem Agents) 14:578–591
van Blitterswijk WJ, Verheij M (2013) Anticancer mechanisms and clinical application of alkylphospholipids. Biochim Biophys Acta 1831:663–674
Yosifov DY, Konstantinov SM, Berger MR, Erucylphospho-N N (2009) N-trimethylpropylammonium shows substantial cytotoxicity in multiple myeloma cells. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1171:350
Rudner J, Ruiner C-E, Handrick R et al (2010) The Akt-inhibitor Erufosine induces apoptotic cell death in prostate cancer cells and increases the short term effects of ionizing radiation. Radiat Oncol 5:1–12
Martelli AM, Papa V, Tazzari PL et al (2010) Erucylphosphohomocholine, the first intravenously applicable alkylphosphocholine, is cytotoxic to acute myelogenous leukemia cells through JNK-and PP2A-dependent mechanisms. Leukemia 24:687–698
Kaleagasioglu F, Berger MR (2014) Differential effects of erufosine on proliferation, wound healing and apoptosis in colorectal cancer cell lines. Oncol Rep 31:1407–1416
Dineva IK, Zaharieva MM, Konstantinov SM et al (2012) Erufosine suppresses breast cancer in vitro and in vivo for its activity on PI3K, c-Raf and Akt proteins. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 138:1909–1917
Veenman L, Alten J, Linnemannstöns K et al (2010) Potential involvement of F 0 F 1-ATP (synth) ASE and reactive oxygen species in apoptosis induction by the antineoplastic agent erucylphosphohomocholine in glioblastoma cell lines. Apoptosis 15:753–768
Ansari SS, Sharma AK, Soni H et al (2018) Induction of ER and mitochondrial stress by the alkylphosphocholine erufosine in oral squamous cell carcinoma cells. Cell Death Dis 9:1–15
Königs SK, Pallasch CP, Lindner LH et al (2010) Erufosine, a novel alkylphosphocholine, induces apoptosis in CLL through a caspase-dependent pathway. Leuk Res 34:1064–1069
Avsar Abdik E, Kaleagasioglu F, Abdik H et al (2019) ABT-737 and erufosine combination against castration-resistant prostate cancer: a promising but cell-type specific response associated with the modulation of anti-apoptotic signaling. Anticancer Drugs 30:383–393
Bade BC, Dela Cruz CS (2020) Lung cancer 2020: epidemiology, etiology, and prevention. Clin Chest Med 41:1–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccm.2019.10.001
Subramanian J, Regenbogen T, Nagaraj G et al (2013) Review of ongoing clinical trials in non-small-cell lung cancer: a status report for 2012 from the ClinicalTrials.gov Web site. J Thorac Oncol Off Publ Int Assoc Study Lung Cancer 8:860–865. https://doi.org/10.1097/JTO.0b013e318287c562
Semenova E, Böttger F, Song JY et al (2018) PO-338 Tumour heterogeneity underlies differential cisplatin sensitivity in mouse models of SCLC. ESMO Open 3:A360–A361
Sarvi S, Mackinnon AC, Avlonitis N et al (2014) CD133+ cancer stem-like cells in small cell lung cancer are highly tumorigenic and chemoresistant but sensitive to a novel neuropeptide antagonist. Cancer Res 74:1554–1565
Thomas A, Chen Y, Yu T et al (2015) Trends and characteristics of young non-small cell lung cancer patients in the United States. Front Oncol 5:113. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2015.00113
Dela Cruz CS, Tanoue LT, Matthay RA (2011) Lung cancer: epidemiology, etiology, and prevention. Clin Chest Med 32:605–644. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccm.2011.09.001
Islam KMM, Jiang X, Anggondowati T et al (2015) Comorbidity and survival in lung cancer patients. Cancer Epidemiol Biomark Prev 24:1079–1085. https://doi.org/10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-15-0036
Qu Q, Jiang S, Li X (2020) LncRNA TBX5-AS1 regulates the tumor progression through the PI3K/AKT pathway in non-small cell lung cancer. Onco Targets Ther 13:7949
Sabari JK, Lok BH, Laird JH et al (2017) Unravelling the biology of SCLC: implications for therapy. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 14:549–561
Fiegl M, Lindner LH, Juergens M et al (2008) Erufosine, a novel alkylphosphocholine, in acute myeloid leukemia: single activity and combination with other antileukemic drugs. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 62:321–329
Lemeshko VV, Kugler W (2007) Synergistic inhibition of mitochondrial respiration by anticancer agent erucylphosphohomocholine and cyclosporin A. J Biol Chem 282:37303–37307
Kapoor V, Zaharieva MM, Das SN, Berger MR (2012) Erufosine simultaneously induces apoptosis and autophagy by modulating the Akt–mTOR signaling pathway in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Lett 319:39–48
Pervaiz A, Akhtar MS, Mahmood S, et al (2018) Molecular basis of cell cycle arrest induced by erufosine in metastatic breast cancer cells.
Steelman LS, Navolanic PM, Sokolosky ML et al (2008) Suppression of PTEN function increases breast cancer chemotherapeutic drug resistance while conferring sensitivity to mTOR inhibitors. Oncogene 27:4086–4095
Sinnberg T, Lasithiotakis K, Niessner H et al (2009) Inhibition of PI3K-AKT-mTOR signaling sensitizes melanoma cells to cisplatin and temozolomide. J Invest Dermatol 129:1500–1515. https://doi.org/10.1038/jid.2008.379
Matsuoka T, Yashiro M (2014) The role of PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling in gastric carcinoma. Cancers (Basel) 6:1441–1463. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers6031441
Barrett D, Brown VI, Grupp SA, Teachey DT (2012) Targeting the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling axis in children with hematologic malignancies. Pediatr Drugs 14:299–316
Li X, Li C, Guo C, et al (2021) PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling orchestrates the phenotypic transition and chemoresistance of small cell lung cancer. J Genet Genomics. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jgg.2021.04.001
Wu L, Yang W, Zhang S, Lu J (2015) Alpinetin inhibits lung cancer progression and elevates sensitization drug-resistant lung cancer cells to cis-diammined dichloridoplatium. Drug Des Devel Ther 9:6119
Fulda S, Debatin K-M (2013) Caspase activation in cancer therapy. In: Madame curie bioscience database. Landes bioscience
Ansari SS, Akgün N, Berger MR (2017) Erufosine increases RhoB expression in oral squamous carcinoma cells independent of its tumor suppressive mode of action - a short report. Cell Oncol 40:89–96. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13402-016-0302-8
Acknowledgements
This study was funded by Yeditepe University. The author thanks to Prof. Fikrettin Şahin for providing laboratory facilities and Prof. Ferda Kaleagasıoglu and Prof. Martin Berger for providing Erufosine.
Funding
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HA: Investigation, Methodology, Validation, Visualization, Writing—original draft.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author declare no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
This study does not require ethical statement.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abdik, H. Antineoplastic effects of erufosine on small cell and non-small cell lung cancer cells through induction of apoptosis and cell cycle arrest. Mol Biol Rep 49, 2963–2971 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-022-07117-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-022-07117-6