Abstract
Background
Aberrant activation of the Wnt signaling pathway is observed in most colorectal cancers (CRC). OCC-1D is a splice variant of OCC-1 gene which is considered as a long noncoding RNA (lncRNA) due to lacking the translational initiation codon of the gene. Here, we sought supporting evidence for the effects of OCC-1D on the Wnt pathway and cell cycle progression in CRC.
Methods and results
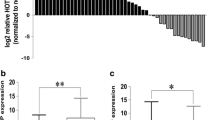
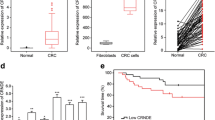
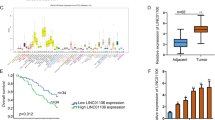
TOP/FOPflash assay and qRT-PCR indicated that expression alterations of OCC-1D could change Wnt signaling activity in colon cancer cells. Consistently, immunocytochemistry results showed the effect of OCC-1D overexpression on nuclear localization of β-catenin proteins in SW480 cells. Flow cytometry, wound healing and MTT assay confirmed the cell cycle stimulatory effects of OCC-1D in CRC-originated cell lines (SW480 and HCT116). qRT-PCR revealed a positive correlation between the expression level of OCC-1D and its neighboring gene, APPL2. Two distinct tests, downregulation of APPL2 mRNA by using shRNA and Wnt signaling inhibition by using small molecule, along with OCC-1D overexpression confirmed that OCC-1D lncRNA exerts its effect on Wnt signaling pathway through expression modulation of APPL2 gene.
Conclusions
Collectively, we suggested the putative regulatory effects of OCC-1D lncRNA on cell cycle progression and Wnt signaling activation through enhancing the APPL2 gene transcription.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CRC:
-
Colorectal cancer
- OCC-1 :
-
Overexpressed in Colorectal Carcinoma-1
- lncRNA:
-
Long non-coding RNA
- ICC:
-
Immunocytochemistry assay
- APPL2 :
-
Adaptor Protein, Phosphotyrosine Interacting With PH Domain And Leucine Zipper 2
- HDAC :
-
Histone deacetylase complex
- GSK -3 β :
-
Glycogen synthase kinase3β
- TCF :
-
Transcription Factor
- shRNA:
-
Small hairpin RNA
References
Atkin WS et al (2010) Once-only flexible sigmoidoscopy screening in prevention of colorectal cancer: a multicentre randomised controlled trial. The Lancet 375(9726):1624–1633
Jemal A et al (2011) Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin 61(2):69–90
Houlston RS (2012) COGENT (COlorectal cancer GENeTics) revisited. Mutagenesis 27(2):143–151
Lubbe S et al (2012) The 14q22. 2 colorectal cancer variant rs4444235 shows cis-acting regulation of BMP4. Oncogene 31(33):3777–3784
Pittman AM et al (2009) The colorectal cancer risk at 18q21 is caused by a novel variant altering SMAD7 expression. Genome Res 19(6):987–993
Zampetaki A, Albrecht A, Steinhofel K (2018) Long non-coding RNA structure and function: is there a link? Front Physiol 9:1201
Kung JT, Colognori D, Lee JT (2013) Long noncoding RNAs: past, present, and future. Genetics 193(3):651–669
Xu M-D, Qi P, Du X (2014) Long non-coding RNAs in colorectal cancer: implications for pathogenesis and clinical application. Mod Pathol 27(10):1310–1320
Pibouin L et al (2002) Cloning of the mRNA of overexpression in colon carcinoma-1: a sequence overexpressed in a subset of colon carcinomas. Cancer Genet Cytogenet 133(1):55–60
Kikuchi K et al (2009) Transcripts of unknown function in multiple-signaling pathways involved in human stem cell differentiation. Nucleic Acids Res 37(15):4987–5000
Najafi H et al (2017) Alternative splicing of the OCC-1 gene generates three splice variants and a novel exonic microRNA, which regulate the Wnt signaling pathway. RNA 23(1):70–85
Rashid S et al (2009) Endosomal adaptor proteins APPL1 and APPL2 are novel activators of β-catenin/TCF-mediated transcription. J Biol Chem 284(27):18115–18128
Behrens J et al (1996) Functional interaction of β-catenin with the transcription factor LEF-1. Nature 382(6592):638–642
Van de Wetering M et al (1997) Armadillo coactivates transcription driven by the product of the Drosophila segment polarity gene dTCF. Cell 88(6):789–799
Morgan RG et al (2019) LEF-1 drives aberrant β-catenin nuclear localization in myeloid leukemia cells. Haematologica 104(7):1365
Schenck A et al (2008) The endosomal protein Appl1 mediates Akt substrate specificity and cell survival in vertebrate development. Cell 133(3):486–497
Segditsas S, Tomlinson I (2006) Colorectal cancer and genetic alterations in the Wnt pathway. Oncogene 25(57):7531–7537
Guo J, Wang M, Liu X (2015) MicroRNA-195 suppresses tumor cell proliferation and metastasis by directly targeting BCOX1 in prostate carcinoma. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 34(1):1
Ismail R et al (2016) Combination of VP3 and CD147-knockdown enhance apoptosis and tumor growth delay index in colorectal tumor allograft. BMC Cancer 16(1):1
Ma H et al (2014) Pol III promoters to express small RNAs: delineation of transcription initiation. Mol Ther-Nucleic Acids 3:e161
Aiyar A, Xiang Y, Leis J (1996) Site-directed mutagenesis using overlap extension PCR. In vitro mutagenesis protocols. Springer, pp 177–191
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2− ΔΔCT method. Methods 25(4):402–408
Najdi R et al (2012) A uniform human Wnt expression library reveals a shared secretory pathway and unique signaling activities. Differentiation 84(2):203–213
Shtutman M et al (1999) The cyclin D1 gene is a target of the β-catenin/LEF-1 pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci 96(10):5522–5527
Zhang S et al (2012) Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway upregulates c-Myc expression to promote cell proliferation of P19 teratocarcinoma cells. Anat Rec 295(12):2104–2113
Albanese C et al (2003) IKKα regulates mitogenic signaling through transcriptional induction of cyclin D1 via Tcf. Mol Biol Cell 14(2):585–599
Bienz M, Clevers H (2000) Linking colorectal cancer to Wnt signaling. Cell 103(2):311–320
Morin PJ et al (1997) Activation of β-catenin-Tcf signaling in colon cancer by mutations in β-catenin or APC. Science 275(5307):1787–1790
Tetsu O, McCormick F (1999) β-Catenin regulates expression of cyclin D1 in colon carcinoma cells. Nature 398(6726):422–426
Athineos D, Sansom O (2010) Myc heterozygosity attenuates the phenotypes of APC deficiency in the small intestine. Oncogene 29(17):2585–2590
He T-C et al (1998) Identification of c-MYC as a target of the APC pathway. Science 281(5382):1509–1512
Lavergne E et al (2011) Blocking Wnt signaling by SFRP-like molecules inhibits in vivo cell proliferation and tumor growth in cells carrying active β-catenin. Oncogene 30(4):423–433
Feng Z et al (2017) miR-590-3p promotes colon cancer cell proliferation via Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway by inhibiting WIF1 and DKK1. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 21(21):4844–4852
Datler C, Grimm S (2013) Reconstitution of CKMT1 expression fails to rescue cells from mitochondrial membrane potential dissipation: Implications for controlling RNAi experiments. Biochim Biophys Acta (BBA) 1833(12):2844–2855
Wu X et al (2016) Tankyrase 1 inhibitior XAV939 increases chemosensitivity in colon cancer cell lines via inhibition of the Wnt signaling pathway. Int J Oncol 48(4):1333–1340
Chial HJ et al (2008) Membrane targeting by APPL1 and APPL2: dynamic scaffolds that oligomerize and bind phosphoinositides. Traffic 9(2):215–229
Ørom UA et al (2010) Long noncoding RNAs with enhancer-like function in human cells. Cell 143(1):46–58
Hung T, Chang HY (2010) Long noncoding RNA in genome regulation: prospects and mechanisms. RNA Biol 7(5):582–585
Wang KC, Chang HY (2011) Molecular mechanisms of long noncoding RNAs. Mol Cell 43(6):904–914
Zhang X et al (2009) Maternally expressed gene 3 (MEG3) noncoding ribonucleic acid: isoform structure, expression, and functions. Endocrinology 151(3):939–947
Schatoff EM, Leach BI, Dow LE (2017) Wnt signaling and colorectal cancer. Curr Colorectal Cancer Rep 13(2):101–110
Acknowledgements
Authors thank Dr. Sadat Dokanehiifard, Zahra Shabaninejad, and Dr. Fahimeh sadat Hosseini aghdaee for their kind advices and help during performing the experiments.
Funding
This work was supported by Tarbiat Modares University (TMU) financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
FY made the conception and design. BS participated in the development of methodology. FY performed the experiments. FY analyzed the data. FY and HN wrote the manuscript. BS reviewed and/or revised the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yousefi, F., Najafi, H., Behmanesh, M. et al. OCC-1D regulates Wnt signaling pathway: potential role of long noncoding RNA in colorectal cancer. Mol Biol Rep 49, 3377–3387 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-021-07110-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-021-07110-5