Abstract
Background
Hypomagnesemia has been associated with development of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) and its complications. Irisin has beneficial effects on glucose uptake and improves hepatic glucose and lipid metabolism. In this study, we aimed to evaluate the effects of long-term treatment of MgSO4 and insulin on insulin resistance, dyslipidemia, serum and hepatic irisin levels, skeletal muscle gene expression of fibronectin type III domain-containing protein 5 (FNDC5), mitochondrial transcription factor A (TFAM) and mitochondrial uncoupling protein 3 (UCP3) in T2DM rats.
Methods and Results
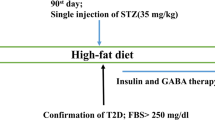
Twenty-four rats were divided into four groups: Control group, diabetic control (DC) using a high-fat diet + streptozotocin, insulin-treated diabetic group (DC + Ins), MgSO4-treated diabetic group (DC + Mg). At the end of therapies, serum concentrations of FBG, TG, insulin, Ox-LDL, along with serum and hepatic irisin levels were measured. FNDC5, TFAM, and UCP3 mRNA expressions were measured in the skeletal muscle by Real-time PCR. In comparison with DC group, MgSO4 therapy resulted in decreased FBG, TG, Ox-LDL, improved serum insulin and irisin levels, and increased mRNA expressions of FNDC5, UCP3 and TFAM. Insulin therapy significantly decreased FBG, Ox-LDL, FNDC5 and serum irisin levels compared with the control group. While, insulin therapy markedly increased TFAM and UCP3 compared with the DC group.
Conclusions
In conclusion, MgSO4 can improve insulin resistance and hyperlipidemia partly through decreasing Ox-LDL, increasing serum irisin levels as well as increasing FNDC5, TFAM, and UCP3 mRNA expressions in T2DM rats. These findings can be considered in the management of diabetes treatment.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Derived data supporting the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author on request.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Belete TM (2020) A recent achievement in the discovery and development of novel targets for the treatment of type-2 diabetes mellitus. J Exp Pharmacol 12:1–15
Ciaraldi TP, Ryan AJ, Mudaliar SR, Henry RR (2016) Altered myokine secretion is an intrinsic property of skeletal muscle in type 2 diabetes. PLoS ONE 11(7):e0158209
Boström P, Wu J, Jedrychowski MP, Korde A, Ye L, Lo JC, Rasbach KA, Boström EA, Choi JH, Long JZ, Kajimura S (2012) A PGC1-α-dependent myokine that drives brown-fat-like development of white fat and thermogenesis. Nature 481(7382):463–468
Gizaw M, Anandakumar P, Debela T (2017) A review on the role of irisin in insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Pharmacopuncture 20(4):235–242
Højlund K, Boström P (2013) Irisin in obesity and type 2 diabetes. J Diabetes Complicat 27(4):303–304
Martinez Munoz IY, Camarillo Romero EdS, Garduno Garcia JD (2018) Irisin a novel metabolic biomarker: present knowledge and future directions. Int J Endocrinol
Nakhjavani M, Khalilzadeh O, Khajeali L, Esteghamati A, Morteza A, Jamali A et al (2010) Serum oxidized-LDL is associated with diabetes duration independent of maintaining optimized levels of LDL-cholesterol. Lipids 45(4):321–327
Zhang M, Xu Y, Jiang L (2019) Irisin attenuates oxidized low-density lipoprotein impaired angiogenesis through AKT/mTOR/S6K1/Nrf2 pathway. J Cell Physiol 234(10):18951–18962
Meex RC, Blaak EE, van Loon LJ (2019) Lipotoxicity plays a key role in the development of both insulin resistance and muscle atrophy in patients with type 2 diabetes. Obes Rev 20(9):1205–12017
Ngo HB, Lovely GA, Phillips R, Chan DC (2014) Distinct structural features of TFAM drive mitochondrial DNA packaging versus transcriptional activation. Nat Commun 5(1):1–12
Lee K, Jin H, Chei S, Oh H-J, Lee J-Y, Lee B-Y (2020) Effect of dietary silk peptide on obesity, hyperglycemia, and skeletal muscle regeneration in high-fat diet-fed mice. Cells 9(2):377
Rizwan H, Pal S, Sabnam S, Pal A (2020) High glucose augments ROS generation regulates mitochondrial dysfunction and apoptosis via stress signalling cascades in keratinocytes. Life Sci 241:117148
Busiello RA, Savarese S, Lombardi A (2015) Mitochondrial uncoupling proteins and energy metabolism. Front Physiol 6:36
Tang W, Tang S, Wang H, Ge Z, Zhu D, Bi Y (2017) Insulin restores UCP3 activity and decreases energy surfeit to alleviate lipotoxicity in skeletal muscle. Int J Mol Med 40(6):2000–2010
Koh J-H, Johnson ML, Dasari S, LeBrasseur NK, Vuckovic I, Henderson GC, Cooper SA, Manjunatha S, Ruegsegger GN, Shulman GI, Lanza IR (2019) TFAM enhances fat oxidation and attenuates high-fat diet-induced insulin resistance in skeletal muscle. Diabetes 68(8):1552–1564
Ye X, Shen Y, Ni C, Ye J, Xin Y, Zhang W, Ren Y (2019) Irisin reverses insulin resistance in C2C12 cells via the p38-MAPK-PGC-1α pathway. Peptides 119:170120
Pilchova I, Klacanova K, Tatarkova Z, Kaplan P, Racay P (2017) The involvement of Mg2+ in regulation of cellular and mitochondrial functions. Oxid Med Cell Longev
Ramadass S, Basu S, Srinivasan A (2015) SERUM magnesium levels as an indicator of status of diabetes mellitus type 2. Diabetes Metab Syndr 9(1):42–45
Xu LHR, Maalouf NM (2017) Effect of acute hyperinsulinemia on magnesium homeostasis in humans. Diabetes Metab Res Rev 33(2):e2844
Guerrero-Romero F, Rodrı́guez-Morán M (2000) Hypomagnesemia is linked to low serum HDL-cholesterol irrespective of serum glucose values. J Diabetes Complicat 14(5):272–276
Liu M, Jeong E-M, Liu H, Xie A, So EY, Shi G, Jeong GE, Zhou A, Dudley SC Jr (2019) Magnesium supplementation improves diabetic mitochondrial and cardiac diastolic function. JCI Insight 4(1):768–770
Zhang Y, Zhou B, Wen M, Hu M, Peng J-G, Wang Y, Fan LL, Tang L (2020) ZG02 improved hepatic glucose metabolism and insulin sensitivity via activation of AMPK/Sirt1 signaling pathways in a high-fat diet/streptozotocin-induced Type 2 Diabetes model. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes 13:4333–4339
Srinivasan K, Viswanad B, Asrat L, Kaul C, Ramarao P (2005) Combination of high-fat diet-fed and low-dose streptozotocin-treated rat: a model for type 2 diabetes and pharmacological screening. Pharmacol Res 52(4):313–320
Rezaee Z, Marandi SM, Alaei H, Esfarjani F (2019) The effect of preventive exercise on the neuroprotection in 6-hydroxydopamine-lesioned rat brain. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab 44(12):1267–1275
Pezeshki A, Zapata RC, Singh A, Yee NJ, Chelikani PK (2016) Low protein diets produce divergent effects on energy balance. Sci Rep 6(1):1–13
Jiang L, Zhang F, He Y, Fan W, Zheng M, Kang J, Huang F, He HW (2019) Melatonin regulates mitochondrial function and biogenesis during rat dental papilla cell differentiation. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 23(13):5967–5979
Gao H, Guan T, Li C, Zuo G, Yamahara J, Wang J, Li Y (2012) Treatment with ginger ameliorates fructose-induced Fatty liver and hypertriglyceridemia in rats: modulation of the hepatic carbohydrate response element-binding protein-mediated pathway. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med
Najafi A, Pourfarzam M, Zadhoush F (2021) Oxidant/antioxidant status in Type-2 diabetes mellitus patients with metabolic syndrome. J Res Med Sci 26:6
Kamran M, Kharazmi F, Malekzadeh K, Talebi A, Khosravi F, Soltani N (2019) Effect of long-term administration of oral magnesium sulfate and insulin to reduce streptozotocin-induced hyperglycemia in rats: the role of Akt2 and IRS1 gene expressions. Biol Trace Elem Res 190(2):396–404
Sales CH, dos Santos AR, Cintra DEC, Colli C (2014) Magnesium-deficient high-fat diet: effects on adiposity, lipid profile and insulin sensitivity in growing rats. Clin Nutr 33(5):879–888
Solaimani H, Soltani N, MaleKzadeh K, Sohrabipour S, Zhang N, Nasri S, Wang Q (2014) Modulation of GLUT4 expression by oral administration of Mg2+ to control sugar levels in STZ-induced diabetic rats. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 92(6):438–444
Haile K, Timerga A (2020) Dyslipidemia and its associated risk factors among adult Type-2 Diabetic Patients at Jimma University Medical Center, Jimma, Southwest Ethiopia. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes 13:4589–4597
Shahwan MJ, Jairoun AA, Farajallah A, Shanabli S (2019) Prevalence of dyslipidemia and factors affecting lipid profile in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Metab Syndr 13(4):2387–2392
Kidwai SS, Nageen A, Bashir F, Ara J (2020) HbA1c–A predictor of dyslipidemia in type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Pak J Med Sci 36(6):1339–1343
Kostov K, Halacheva L (2018) Role of magnesium deficiency in promoting atherosclerosis, endothelial dysfunction, and arterial stiffening as risk factors for hypertension. Int J Mol Sci 19(6):1724–1747
Fazlali M, Kharazmi F, Kamran M, Malekzadeh K, Talebi A, Khosravi F, Soltani N (2019) Effect of oral magnesium sulfate administration on lectin-like oxidized low-density lipoprotein receptor-1 gene expression to prevent atherosclerosis in diabetic rat vessels. J Diabetes Investig 10(3):650–658
Xuan X, Lin J, Zhang Y, Zhou L, Xu L, Jia J, Zhao B, Lin Z, Zhu Q, Li L, Wu T (2020) Serum irisin levels and clinical implication in elderly patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Clin Med Res 12(9):612–617
Varela-Rodríguez BM, Pena-Bello L, Juiz-Valiña P, Vidal-Bretal B, Cordido F, Sangiao-Alvarellos S (2016) FNDC5 expression and circulating irisin levels are modified by diet and hormonal conditions in hypothalamus, adipose tissue and muscle. Sci Rep 6(1):1–13
Al-Ghazali M, Hanaa AA, Al-Rufaie MM, Rawaa AA (2019) The correlation of irisin levels and some trace element as a potential mark diagnosis of gestational diabetes mellitus. Acta Med Iran 57(1):42–50
Chen S-Q, Ding L-N, Zeng N-X, Liu H-M, Zheng S-H, Xu J-W, Li RM (2019) Icariin induces irisin/FNDC5 expression in C2C12 cells via the AMPK pathway. Biomed Pharmacother 115:108930
Li Q, Jia S, Xu L, Li B, Chen N (2019) Metformin-induced autophagy and irisin improves INS-1 cell function and survival in high-glucose environment via AMPK/SIRT1/PGC-1α signal pathway. Food Sci Nutr 7(5):1695–1703
Liu Y, Xu F, Jiang P (2020) Effect of sitagliptin on expression of skeletal muscle peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ coactivator-1 α and irisin in a rat model of type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Int Med Res 48(5):0300060519885569
Ha BG, Moon D-S, Kim HJ, Shon YH (2016) Magnesium and calcium-enriched deep-sea water promotes mitochondrial biogenesis by AMPK-activated signals pathway in 3T3-L1 preadipocytes. Biomed Pharmacother 83:477–484
Schrauwen P, Hesselink M (2002) UCP2 and UCP3 in muscle controlling body metabolism. J Exp Biol 205(15):2275–2285
Vaughan R, Gannon N, Barberena M, Garcia-Smith R, Bisoffi M, Mermier C, Conn CA, Trujillo KA (2014) Characterization of the metabolic effects of irisin on skeletal muscle in vitro. Diabetes Obes Metab 16(8):711–718
Shao Q, Meng L, Lee S, Tse G, Gong M, Zhang Z, Zhao J, Zhao Y, Li G, Liu T (2019) Empagliflozin, a sodium glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitor, alleviates atrial remodeling and improves mitochondrial function in high-fat diet/streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Cardiovasc Diabetol 18(1):1–14
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by Isfahan University of Medical Sciences.
Funding
The current research was funded by Isfahan University of Medical Science (Grant: 198246).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Dr. FZ participated in hypothesis generation, study design and manuscript development (revision, editing and finalizing). Ms. FY conducted experiments, participated in statistical analysis, data interpretation and manuscript development (draft and revision). Dr. MA contributed to experimental procedure, data interpretation, and manuscript editing. Dr. NS and Dr. HR participated in preparation of diabetic rat model and treatment and Dr. MG participated in data interpretation and manuscript development (revision and editing). All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
Approval no: IR.MUI.MED.REC.1398.120.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
All authors consent to the publication of the manuscript in molecular biology reports.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yazdanimoghaddam, F., Aghaei, M., Ghasemi, M. et al. Beneficial effects of MgSO4 on TFAM, UPC3 and FNDC5 mRNA expressions in skeletal muscle of type 2 diabetic rats: a possible mechanism to improve insulin resistance. Mol Biol Rep 49, 2795–2803 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-021-07091-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-021-07091-5