Abstract
Background
New onset diabetes mellitus demonstrates a roughly correlation with pancreatic cancer (PaC), which is unique in PaC and was named as PaC-induced DM, but the inner mechanism remains unclear. Exosomes mediate intercellular communication and bearing microRNAs might be direct constituent of effect in target cells.
Methods and results
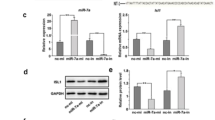
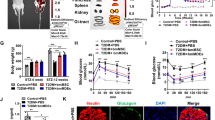
The isolated exosomes from PaC cells were used to treat pancreatic β cells or the primary mice islets, and the glucose stimulated insulin secretions were measured. We validated the exosomal miR-19a from PaC cells to be an important mediator in the down regulation of insulin secretion by targeting Neurod1, the validated gene involved in insulin secretion, by using the quantitative real-time PCR, western blot, and promoter luciferase activity. The relative insulin, cAMP and Ca2+ expressions were also assayed to verify the inverse correlation between cancerous miR-19a and pancreatic islets Neurod1.
Conclusions
Our study indicated that signal changes between cancer cells and β cells via exosomes might be important in the pathogenesis of PaC-induced DM and supplemented the pathogenesis of PaC-induced DM and provide a possible access of PaC screening strategy.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aggarwal G, Kamada P, Chari ST (2013) Prevalence of diabetes mellitus in pancreatic cancer compared to common cancers. Pancreas 42(2):198–201
Pannala R et al (2008) Prevalence and clinical profile of pancreatic cancer-associated diabetes mellitus. Gastroenterology 134(4):981–987
Singhi AD et al (2019) Early detection of pancreatic cancer: opportunities and challenges. Gastroenterology 156(7):2024–2040
Yoon BH et al (2021) Pancreatic cancer-associated diabetes is clinically distinguishable from conventional diabetes. J Surg Res 261:215–225
Pereira SP et al (2020) Early detection of pancreatic cancer. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol 5(7):698–710
Chen W et al (2021) Validation of the enriching new-onset diabetes for pancreatic cancer model in a diverse and integrated healthcare setting. Dig Dis Sci 66(1):78–87
Xia T, Chen XY, Zhang YN (2021) MicroRNAs as biomarkers and perspectives in the therapy of pancreatic cancer. Mol Cell Biochem. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-021-04233-y
Wang X et al (2021) Effects of CAF-derived microRNA on tumor biology and clinical applications. Cancers (Basel) 13(13):3160
Dai X et al (2015) Altered profile of serum microRNAs in pancreatic cancer associated new-onset diabetes mellitus. J Diabetes 8:422
Thakur A et al (2021) The mini player with diverse functions: extracellular vesicles in cell biology, disease, and therapeutics. Protein Cell. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13238-021-00863-6
Zhao Z et al (2021) The significance of exosomal RNAs in the development, diagnosis, and treatment of pancreatic cancer. Cancer Cell Int 21(1):364
Pang W et al (2021) Pancreatic cancer-derived exosomal microRNA-19a induces beta-cell dysfunction by targeting ADCY1 and EPAC2. Int J Biol Sci 17(13):3622–3633
Chen X et al (2009) Role of miR-143 targeting KRAS in colorectal tumorigenesis. Oncogene 28(10):1385–1392
Lewis BP et al (2003) Prediction of mammalian microRNA targets. Cell 115(7):787–798
Krek A et al (2005) Combinatorial microRNA target predictions. Nat Genet 37(5):495–500
John B et al (2004) Human microRNA targets. PLoS Biol 2(11):e363
Rehmsmeier M et al (2004) Fast and effective prediction of microRNA/target duplexes. RNA 10(10):1507–1517
Zhang Y et al (2010) Secreted monocytic miR-150 enhances targeted endothelial cell migration. Mol Cell 39(1):133–144
Aggarwal G et al (2012) Adrenomedullin is up-regulated in patients with pancreatic cancer and causes insulin resistance in beta cells and mice. Gastroenterology 143(6):1510–15171
Hart PA et al (2021) Distinguishing diabetes secondary to pancreatic diseases from type 2 diabetes mellitus. Curr Opin Gastroenterol 37(5):520–525
Nakanishi N et al (2009) The up-regulation of microRNA-335 is associated with lipid metabolism in liver and white adipose tissue of genetically obese mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 385(4):492–496
Chae JH, Stein GH, Lee JE (2004) NeuroD: the predicted and the surprising. Mol Cells 18(3):271–288
Aramata S et al (2005) Synergistic activation of the insulin gene promoter by the beta-cell enriched transcription factors MafA, Beta2, and Pdx1. Biochim Biophys Acta 1730(1):41–46
Ono Y, Kataoka K (2021) MafA, NeuroD1, and HNF1beta synergistically activate the Slc2a2 (Glut2) gene in beta-cells. J Mol Endocrinol 67(3):71–82
Zhang ZW et al (2011) MicroRNA-19b downregulates insulin 1 through targeting transcription factor NeuroD1. FEBS Lett 585(16):2592–2598
Horikawa Y, Enya M (2019) Genetic dissection and clinical features of MODY6 (NEUROD1-MODY). Curr Diabetes Rep 19(3):12
Yin Y et al (2014) Tumor-secreted miR-214 induces regulatory T cells: a major link between immune evasion and tumor growth. Cell Res 24(10):1164–1180
Wang Y et al (2021) Decreased inhibition of exosomal miRNAs on SARS-CoV-2 replication underlies poor outcomes in elderly people and diabetic patients. Signal Transduct Target Ther 6(1):300
Zhou LK et al (2020) Absorbed plant MIR2911 in honeysuckle decoction inhibits SARS-CoV-2 replication and accelerates the negative conversion of infected patients. Cell Discov 6:54
Chen Q et al (2020) SIDT1-dependent absorption in the stomach mediates host uptake of dietary and orally administered microRNAs. Cell Res 31:247
Funding
This work was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81802304/H1617).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Su, J., Pang, W., Zhang, A. et al. Exosomal miR-19a decreases insulin production by targeting Neurod1 in pancreatic cancer associated diabetes. Mol Biol Rep 49, 1711–1720 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-021-06980-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-021-06980-z