Abstract
Background
A stroke is an acute damage to a certain area of a nerve tissue of the brain. In developed countries, it ranks second among the most often causes of death and is also the leading cause of disability. Recent findings emphasize the significant neuroprotective effect of conditioning on the course and rate of recovery after ischemic attack; however the molecular mechanism of ischemic tolerance induced by conditioning is still not completely explored.
Methods and results
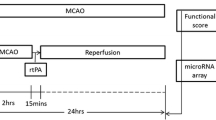
The purpose of this study is an identification of changes in gene expression induced by stimulation of reaction cascades after activation of the neuroprotective mechanism using an experimental rat model of global ischemia. The induction of neuroprotective cascades was stimulated by the application of early and delayed form of remote ischemic postconditioning. The quantitative qRT-PCR method was used to assess the rate of change in ADM, BDNF, CDKN1A, CREB, GADD45G, IL6, nNOS, and TM4SF1 gene expression levels 72 h after ischemic attack. The detected results confirm the neuroprotective effect of both forms of postconditioning. Participation of neuroprotection-related gene expression changes was observed once as an early one (CREB, GADD45G), once as a delayed one (ADM, IL6), or both (BDNF, CDKN1A, nNOS, TM4SF1) postconditioning forms, depending on the particular gene.
Conclusions
Our results characterize impact of ischemic tolerance on the molecular level. We predict ischemic tolerance to be consisted of complex combination of early and delayed remote postconditioning.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Doeppner TR, Zechmeister B, Kaltwasser B, Jin F, Zheng X, Majid A, Venkataramani V, Bahr M, Hermann DM (2018) Very delayed remote ischemic post-conditioning induces sustained neurological recovery by mechanisms involving enhanced angioneurogenesis and peripheral immunosuppression reversal. Front Cell Neurosci 12:383
Shi C-X, Ding Y-B, Jin FYJ, Li T, Ma J-H, Qiao L-Y, Pan W-Z, Li K-Z (2018) Effects of sevoflurane post-conditioning in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury via TLR4/NF-κB pathway in rats. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 22:1770–1775
Doeppner TR, Doehring M, Kaltwasser B, Majid A, Lin F, Bahr M, Kilic E, Hermann DM (2017) Ischemic post-conditioning induces post-stroke neuroprotection via Hsp70-mediated proteasome inhibition and facilitates neural progenitor cell transplantation. Mol Neurobiol 54:6061–6073
Howard DPJ, Gaziano L, Rothwell PM, Oxford Vascular S (2021) Risk of stroke in relation to degree of asymptomatic carotid stenosis: a population-based cohort study, systematic review, and meta-analysis. Lancet Neurol 20:193–202
Kisrieva YS, Petushkova NA, Samenkova NF, Kuznetsova GP, Larina OV, Teryaeva NB, Zgoda VG, Karuzina II, Usachev DU, Belyaev AY (2018) Analysis of blood plasma protein composition in patients with cerebral ischemia. Bull Exp Biol Med 165:22–26
Rothstein L, Jickling GC (2013) Ischemic stroke biomarkers in blood. Biomark Med 7:37–47
Swyngedouw NE, Jickling GC (2017) RNA as a stroke biomarker. Future Neurol 12:71–78
Barr TL, Conley Y, Ding J, Dillman A, Warach S, Singleton A, Matarin M (2010) Genomic biomarkers and cellular pathways of ischemic stroke by RNA gene expression profiling. Neurology 75:1009–1014
Moore DF, Li H, Jeffries N, Wright V, Cooper RA Jr, Elkahloun A, Gelderman MP, Zudaire E, Blevins G, Yu H, Goldin E, Baird AE (2005) Using peripheral blood mononuclear cells to determine a gene expression profile of acute ischemic stroke: a pilot investigation. Circulation 111:212–221
Stamova B, Xu H, Jickling G, Bushnell C, Tian Y, Ander BP, Zhan X, Liu D, Turner R, Adamczyk P, Khoury JC, Pancioli A, Jauch E, Broderick JP, Sharp FR (2010) Gene expression profiling of blood for the prediction of ischemic stroke. Stroke 41:2171–2177
Tang Y, Xu H, Du X, Lit L, Walker W, Lu A, Ran R, Gregg JP, Reilly M, Pancioli A, Khoury JC, Sauerbeck LR, Carrozzella JA, Spilker J, Clark J, Wagner KR, Jauch EC, Chang DJ, Verro P, Broderick JP, Sharp FR (2006) Gene expression in blood changes rapidly in neutrophils and monocytes after ischemic stroke in humans: a microarray study. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 26:1089–1102
Jickling GC, Stamova B, Ander BP, Zhan X, Liu D, Sison SM, Verro P, Sharp FR (2012) Prediction of cardioembolic, arterial, and lacunar causes of cryptogenic stroke by gene expression and infarct location. Stroke 43:2036–2041
Jickling GC, Stamova B, Ander BP, Zhan X, Tian Y, Liu D, Xu H, Johnston SC, Verro P, Sharp FR (2011) Profiles of lacunar and nonlacunar stroke. Ann Neurol 70:477–485
Jickling GC, Xu H, Stamova B, Ander BP, Zhan X, Tian Y, Liu D, Turner RJ, Mesias M, Verro P, Khoury J, Jauch EC, Pancioli A, Broderick JP, Sharp FR (2010) Signatures of cardioembolic and large-vessel ischemic stroke. Ann Neurol 68:681–692
Jickling GC, Zhan X, Stamova B, Ander BP, Tian Y, Liu D, Sison SM, Verro P, Johnston SC, Sharp FR (2012) Ischemic transient neurological events identified by immune response to cerebral ischemia. Stroke 43:1006–1012
Ramsay L, Quille ML, Orset C, de la Grange P, Rousselet E, Ferec C, Le Gac G, Genin E, Timsit S (2019) Blood transcriptomic biomarker as a surrogate of ischemic brain gene expression. Ann Clin Transl Neurol 6:1681–1695
Pulsinelli WA, Brierley JB (1979) A new model of bilateral hemispheric ischemia in the unanesthetized rat. Stroke 10:267–272
Schmidt-Kastner R, Paschen W, Ophoff BG, Hossmann KA (1989) A modified four-vessel occlusion model for inducing incomplete forebrain ischemia in rats. Stroke 20:938–946
Nemethova M, Talian I, Danielisova V, Tkacikova S, Bonova P, Bober P, Matiasova M, Sabo J, Burda J (2016) Delayed bradykinin postconditioning modulates intrinsic neuroprotective enzyme expression in the rat CA1 region after cerebral ischemia: a proteomic study. Metab Brain Dis 31:1391–1403
Bonova P, Nemethova M, Matiasova M, Bona M, Gottlieb M (2016) Blood cells serve as a source of factor-inducing rapid ischemic tolerance in brain. Eur J Neurosci 44:2958–2965
Ayers JD, Rota PA, Collins ML, Drew CP (2012) Alternatives to retroorbital blood collection in hispid cotton rats (Sigmodon hispidus). J Am Assoc Lab Anim Sci 51:239–245
Kang Y, Wu Z, Cai LuB (2018) Evaluation of reference genes for gene expression studies in mouse and N2a cell ischemic stroke models using quantitative real-time PCR. BMC Neurosci 19:3
Yuan J (2009) Neuroprotective strategies targeting apoptotic and necrotic cell death for stroke. Apoptosis 14:469–477
Chen J, Graham SH, Zhu RL, Simon RP (1996) Stress proteins and tolerance to focal cerebral ischemia. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 16:566–577
Kirino T, Tsujita Y, Tamura A (1991) Induced tolerance to ischemia in gerbil hippocampal neurons. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 11:299–307
Kitagawa K, Matsumoto M, Tagaya M, Hata R, Ueda H, Niinobe M, Handa N, Fukunaga R, Kimura K, Mikoshiba K et al (1990) “Ischemic tolerance” phenomenon found in the brain. Brain Res 528:21–24
Yunoki M, Kanda T, Suzuki K, Uneda A, Hirashita K, Yoshino K (2017) Ischemic tolerance of the brain and spinal cord: a review. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 57:590–600
Kakimoto M, Kawaguchi M, Sakamoto T, Inoue S, Furuya H, Nakamura M, Konishi N (2003) Evaluation of rapid ischemic preconditioning in a rabbit model of spinal cord ischemia. Anesthesiology 99:1112–1117
Stetler RA, Leak RK, Gan Y, Li P, Zhang F, Hu X, Jing Z, Chen J, Zigmond MJ, Gao Y (2014) Preconditioning provides neuroprotection in models of CNS disease: paradigms and clinical significance. Prog Neurobiol 114:58–83
Han D, Wang J, Wen L, Sun M, Liu H, Gao Y (2021) Remote limb ischemic postconditioning protects against ischemic stroke via modulating microglia/macrophage polarization in mice. J Immunol Res 2021:6688053
McDonald MW, Dykes A, Jeffers MS, Carter A, Nevins R, Ripley A, Silasi G, Corbett D (2021) Remote ischemic conditioning and stroke recovery. Neurorehabil Neural Repair 35:545–549
Seifert-Held T, Pekar T, Gattringer T, Simmet NE, Scharnagl H, Bocksrucker C, Lampl C, Storch MK, Stojakovic T, Fazekas F (2013) Plasma midregional pro-adrenomedullin improves prediction of functional outcome in ischemic stroke. PLoS One 8:e68768
Wu H, Yang SF, Dai J, Qiu YM, Miao YF, Zhang XH (2015) Combination of early and delayed ischemic postconditioning enhances brain-derived neurotrophic factor production by upregulating the ERK-CREB pathway in rats with focal ischemia. Mol Med Rep 12:6427–6434
Bejot Y, Mossiat C, Giroud M, Prigent-Tessier A, Marie C (2011) Circulating and brain BDNF levels in stroke rats Relevance to clinical studies. PLoS One 6:e29405
Caracciolo L, Marosi M, Mazzitelli J, Latifi S, Sano Y, Galvan L, Kawaguchi R, Holley S, Levine MS, Coppola G, Portera-Cailliau C, Silva AJ, Carmichael ST (2018) CREB controls cortical circuit plasticity and functional recovery after stroke. Nat Commun 9:2250
Zhang S, Wang J, Qu MJ, Wang K, Ma AJ, Pan XD, Zhu XY (2021) Novel insights into the potential diagnostic value of circulating exosomal IncRNA-related networks in large artery atherosclerotic stroke. Front Mol Biosci 8:682769
Gertz K, Kronenberg G, Kalin RE, Baldinger T, Werner C, Balkaya M, Eom GD, Hellmann-Regen J, Krober J, Miller KR, Lindauer U, Laufs U, Dirnagl U, Heppner FL, Endres M (2012) Essential role of interleukin-6 in post-stroke angiogenesis. Brain 135:1964–1980
Chen ZQ, Mou RT, Feng DX, Wang Z, Chen G (2017) The role of nitric oxide in stroke. Med Gas Res 7:194–203
Lu XC, Williams AJ, Yao C, Berti R, Hartings JA, Whipple R, Vahey MT, Polavarapu RG, Woller KL, Tortella FC, Dave JR (2004) Microarray analysis of acute and delayed gene expression profile in rats after focal ischemic brain injury and reperfusion. J Neurosci Res 77:843–857
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by SK-VEGA 2/0054/20 Grant from Slovak Academy of Sciences.
Funding
This study was supported by the grant from the Slovak Scientific Grant Agency VEGA 2/0054/20.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MF: Investigation, Formal analysis, Writing—Original Draft, Validation, Visualization. MN: Methodology, Investigation, Writing—Review & Editing. LM: Investigation, VS: Investigation, Methodology, Resources, Project administration, Writing—Review & Editing. PB: Resources, Writing—Review & Editing. IK: Resources, Writing—Review & Editing. MV: Resources, RM: Conceptualization, Methodology, Validation, Resources, Data Curation, Writing—Review and Editing, Supervision, Funding acquisition, Project administration.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Ethical approval
All experiments were approved by the Institutional Ethical Committee in accordance with current national legislation and EU Directive 2010/63/EU guidelines for animal experiments.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Furman, M., Nemethova, M., Macakova, L. et al. Modifications of gene expression detected in peripheral blood after brain ischemia treated with remote postconditioning. Mol Biol Rep 49, 477–485 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-021-06899-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-021-06899-5