Abstract
Purpose
Cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) are major components of tumor microenvironment that stimulate ESCC and GC progression. The LncRNA-CAF, FLJ22447, is located in the vicinity of HIF1A, while their association remains unclear. This study aims to assess the FLJ22447 expression in the ESCC and GC patients and evaluate its association with the HIF1A gene.
Methods
Fresh ESCC and GC tumor samples and their adjacent non-tumor tissues were collected from patients who underwent surgery in Imam Khomeini Hospital, Tehran, Iran. The expression of FLJ22447, HIF1A, and VEGF was evaluated using qRT-PCR test. The association of their expression with tumor clinicopathological features in ESCC patients was assessed. System biology tools were then applied for the possible biological subsequences of the FLJ22447.
Results
A significant reduction in FLJ22447 expression was observed in ESCC and GC tissues than adjacent non-tumor tissues, while, the expression of HIF1A and VEGF were increased. Low expression of FLJ22447 was significantly correlated with HIF1A (P = 2.4e–73, R = 0.63) and VEGF (P = 0.00019, R = 0.15) expression. A significant relationship was detected between the high expression of HIF1A and tumor stages (I–II) and it was related to the reduced survival of ESCC patients. Conversely, increased VEGF expression was linked to the advanced stages (III–IV) and metastasis in ESCC. The analysis of FLJ22447-interacted proteins showed that MYC, JUN, SMRCA4, PPARG, AR, FOS, and CEBPA are the hub genes. These proteins were implicated in the cancer related pathways. Among them, SPI1, E2F1, TCF7L2, and STAT1 were significantly expressed in esophageal and gastric cancers that were functionally involved in the proliferation, apoptosis, and angiogenesis pathways in cancer.
Conclusion
The results suggested that FLJ22447 may have a regulatory function on the HIF1A expression. We identified the FLJ22447-interacted proteins and their molecular function in cancer pathogenesis. Further research emphasis is to realize the association of FLJ22447 with its protein partners in progression of cancer. These may provide an insight into the FLJ22447 activity that could introduce it as a potential value in tumor gene therapy.


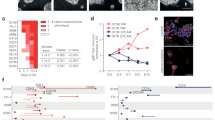
adopted from GEPIA resources. Log2 (TPM + 1) was used for log-scale. ESCA esophageal carcinoma; TPM Transcripts per million




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data will be available while editor requested.
References
Plavetić D, Plavetić ND, Barić MB, Bradić LB, Kulić A, Pleština S (2014) Hypoxia in solid tumors: biological responses to hypoxia and implications on therapy and prognosis. Period Biol 116(4):361–364
Banys-Paluchowski M, Witzel I, Riethdorf S, Pantel K, Rack B, Janni W, Fasching PA, Aktas B, Kasimir-Bauer S, Hartkopf A (2018) The clinical relevance of serum vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in correlation to circulating tumor cells and other serum biomarkers in patients with metastatic breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 172(1):93–104
Spirina L, Usynin Y, Yurmazov Z, Slonimskaya E, Kolegova E, Kondakova I (2017) Transcription factors NF-kB, HIF-1, HIF-2, growth factor VEGF, VEGFR2 and carboanhydrase IX mRNA and protein level in the development of kidney cancer metastasis. Mol Biol 51(2):328–332
Bahramian S, Shamsabadi F, Fazel A, Delshad E, Amini A, Memari F, Shafiee M (2020) Evaluation of Arylsulfatase D (ARSD) and long noncoding RNA ARSD-AS1 gene expression in breast cancer patients and their association with oncogenic transcription factors. J BUON 25:1805–1813
Muz B, de la Puente P, Azab F, Azab AK (2015) The role of hypoxia in cancer progression, angiogenesis, metastasis, and resistance to therapy. Hypoxia 3:83
Ivan M, Kaelin WG Jr (2017) The EGLN-HIF O(2)-sensing system: multiple inputs and feedbacks. Mol Cell 66(6):772–779
Hashimoto T, Shibasaki F (2015) Hypoxia-inducible factor as an angiogenic master switch. Front Pediatr 3:33–33
AM Roberts, IR Watson, AJ Evans, DA Foster, MS Irwin, M Ohh (2009) Suppression of hypoxia-inducible factor 2α restores p53 activity via Hdm2 and reverses chemoresistance of renal carcinoma cells. Cancer Res 0008-5472. CAN-09-1770.
Nagao A, Kobayashi M, Koyasu S, Chow CCT, Harada H (2019) HIF-1-dependent reprogramming of glucose metabolic pathway of cancer cells and its therapeutic significance. Int J Mol Sci 20(2):238
Ladeira K, Macedo F, Longatto-Filho A, Martins SF (2018) Angiogenic factors: role in esophageal cancer, a brief review. Esophagus 15(2):53–58
Jin X, Dai L, Ma Y, Wang J, Liu Z (2020) Implications of HIF-1α in the tumorigenesis and progression of pancreatic cancer. Cancer Cell Int 20(1):1–11
Zhao X, Gao S, Ren H, Sun W, Zhang H, Sun J, Yang S, Hao J (2014) Hypoxia-inducible factor-1 promotes pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma invasion and metastasis by activating transcription of the actin-bundling protein fascin. Cancer Res 74(9):2455–2464
Jin F, Brockmeier U, Otterbach F, Metzen E (2012) New insight into the SDF-1/CXCR4 axis in a breast carcinoma model: hypoxia-induced endothelial SDF-1 and tumor cell CXCR4 are required for tumor cell intravasation. Mol Cancer Res 10(8):1021
Viallard C, Larrivée B (2017) Tumor angiogenesis and vascular normalization: alternative therapeutic targets. Angiogenesis 20(4):409–426
Bramhachari PV, Prathyusha A, Reddy DRS (2017) Overview of transcription factors in esophagus cancer, role of transcription factors in gastrointestinal malignancies. Springer, Singapore, pp 31–42
Becker S, Wang H, Simmons AB, Suwanmanee T, Stoddard GJ, Kafri T, Hartnett ME (2018) Targeted knockdown of overexpressed VEGFA or VEGF164 in Müller cells maintains retinal function by triggering different signaling mechanisms. Sci Rep 8(1):2003
Gutschner T, Diederichs S (2012) The hallmarks of cancer: a long non-coding RNA point of view. RNA Biol 9(6):703–719
Ahn Y-H, Kim JS (2020) Long non-coding RNAs as regulators of interactions between cancer-associated fibroblasts and cancer cells in the tumor microenvironment. Int J Mol Sci 21(20):7484
Ding L, Ren J, Zhang D, Li Y, Huang X, Hu Q, Wang H, Song Y, Ni Y, Hou Y (2018) A novel stromal lncRNA signature reprograms fibroblasts to promote the growth of oral squamous cell carcinoma via LncRNA-CAF/interleukin-33. Carcinogenesis 39(3):397–406
Schmitt AM, Chang HY (2016) Long noncoding RNAs in cancer pathways. Cancer Cell 29(4):452–463
Rupaimoole R, Slack FJ (2017) MicroRNA therapeutics: towards a new era for the management of cancer and other diseases. Nat Rev Drug Discov 16(3):203
Tang Z, Li C, Kang B, Gao G, Li C, Zhang Z (2017) GEPIA: a web server for cancer and normal gene expression profiling and interactive analyses. Nucleic Acids Res 45(W1):W98–W102
Fang Z, Xu J, Zhang B, Wang W, Liu J, Liang C, Hua J, Meng Q, Yu X, Shi S (2020) The promising role of noncoding RNAs in cancer-associated fibroblasts: an overview of current status and future perspectives. J Hematol Oncol 13(1):1–21
Du X, Xu Q, Pan D, Xu D, Niu B, Hong W, Zhang R, Li X, Chen S (2019) HIC-5 in cancer-associated fibroblasts contributes to esophageal squamous cell carcinoma progression. Cell Death Dis 10(12):1–16
Zhou L, Zhu Y, Sun D, Zhang Q (2020) Emerging roles of long non-coding RNAs in the tumor microenvironment. Int J Biol Sci 16(12):2094
Lambert M, Jambon S, Depauw S, David-Cordonnier M-H (2018) Targeting transcription factors for cancer treatment. Molecules 23(6):1479
Kimura S, Kitadai Y, Tanaka S, Kuwai T, Hihara J, Yoshida K, Toge T, Chayama K (2004) Expression of hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1α is associated with vascular endothelial growth factor expression and tumour angiogenesis in human oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Eur J Cancer 40(12):1904–1912
Takala H, Saarnio J, Wiik H, Ohtonen P, Soini Y (2011) HIF-1α and VEGF are associated with disease progression in esophageal carcinoma. J Surg Res 167(1):41–48
Tzao C, Lee S-C, Tung H-J, Hsu H-S, Hsu W-H, Sun G-H, Yu C-P, Jin J-S, Cheng Y-L (2008) Expression of hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1α and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-D as outcome predictors in resected esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Dis Markers 25(3):141–148
Kaelin WG Jr, Ratcliffe PJ, Semenza GL (2019) Out of breath: molecular description of cellular responses to hypoxia–2019 Nobel prize for physiology or medicine. Curr Sci 117(9):1418
Wei B, Tai Y, Tong H, Wen S-L, Tang S-H, Huan H, Huang Z-Y, Liu R, Tang Y-M, Yang J-H (2017) Correlations between VEGF-A expression and prognosis in patients with gastric adenocarcinoma. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 10(8):8461
Ham I-H, Lee D, Hur H (2019) Role of cancer-associated fibroblast in gastric cancer progression and resistance to treatments. J Oncol 2019:1–11
Ma Z, Chen M, Yang X, Xu B, Song Z, Zhou B, Yang T (2018) The role of cancer-associated fibroblasts in tumorigenesis of gastric cancer. Curr Pharm Des 24(28):3297–3302
Sewell-Loftin MK, Bayer SVH, Crist E, Hughes T, Joison SM, Longmore GD, George SC (2017) Cancer-associated fibroblasts support vascular growth through mechanical force. Sci Rep 7(1):1–12
Dales JP, Garcia S, Meunier-Carpentier S, Andrac-Meyer L, Haddad O, Lavaut MN, Allasia C, Bonnier P, Charpin C (2005) Overexpression of hypoxia-inducible factor HIF-1α predicts early relapse in breast cancer: Retrospective study in a series of 745 patients. Int J Cancer 116(5):734–739
Acknowledgements
We gratefully acknowledge all persons who helped us in this study in Molecular Genetic lab which was supported by Golestan University of Medical Sciences, Gorgan, Iran.
Funding
This research was supported in part by Golestan University of Medical sciences (Project Grant No. 960704177). The study sponsor had no role in the study design, collection, analysis and interpretation of the data or the writing of the report.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed.
Ethical approval
This research was approved in Ethics Committee of by IR.GOUMS.REC.1397.006.
Consent for publication
Not Applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bahramian, S., Sahebi, R., Roohinejad, Z. et al. Low expression of LncRNA-CAF attributed to the high expression of HIF1A in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and gastric cancer patients. Mol Biol Rep 49, 895–905 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-021-06882-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-021-06882-0