Abstract
Background
Adipose tissue (AT) is a passive reservoir for energy storage and an active endocrine organ responsible for synthesizing bioactive molecules called adipokines. Omentin is known as an anti-inflammatory adipokine that can modulate insulin sensitivity. The present study aimed to investigate the relationship between omentin mRNA expression and glucose homeostasis of visceral adipose tissue (VAT) and subcutaneous adipose tissue (SAT) in non-diabetic adults.
Methods
VAT and SAT adipose tissues were collected from 137 adults aged ≥ 18 years hospitalized for abdominal surgery. Before surgery, preoperative blood samples were taken from the participants to measure fasting plasma glucose, insulin, and triglyceride. BMI, HOMA-IR, HOMA-B, and QUICKI were calculated. Insulin levels were measured with Mercodia kits using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). In order to obtain omentin mRNA expression, real-time PCR was performed.
Results
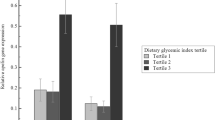
Overall, 91 (66.4%) subjects were healthy [without insulin resistance (IR)], and 46 (33.6%) participants were with IR. In healthy and IR subjects, omentin gene expression was 1.04 and 2.32, respectively in VAT, and 3.06 and 1.30, respectively, in SAT (P > 0.05). After controlling for age and BMI, linear regression analysis indicated a significant positive association of SAT omentin expression with insulin concentration (β = 0.048; 95% CI 0.009, 0.088, P = 0.017) and HOMA-IR (β = 0.173; 95% CI 0.023, 0.323, P = 0.014). Moreover, a negative association of SAT omentin expression with HOMA-B (β = − 0.001; 95% CI 0.002, − 0.001, P < 0.001) was observed.
Conclusion
This study's finding confirms a direct association between IR with omentin mRNA levels in SAT. Besides, the indicator of insulin sensitivity had an inverse association with omentin gene expression in SAT. This aspect of research suggests that omentin secretion from SAT has a strong link with insulin regulation.

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AT:
-
Adipose tissue
- VAT:
-
Visceral adipose tissue
- SAT:
-
Subcutaneous adipose tissue
- WAT:
-
White adipose tissue
- BAT:
-
Brown adipose tissue
- BMI:
-
Body mass index
- PCR:
-
Polymerase chain reaction
- CT:
-
Threshold cycle
- NF-κB:
-
Nuclear factor-Kb
- IR:
-
Insulin resistance
- T2DM:
-
Type 2 diabetes mellitus
- IGR:
-
Impaired glucose regulation
- NGT:
-
Normal glucose tolerance
- FPG:
-
Fasting plasma glucose
- TGs:
-
Triglycerides
- QUICKI:
-
Quantitative insulin sensitivity check index insulin sensitivity
- HOMA-IR:
-
The evaluation of the homeostatic model of IR
- HOMA-B:
-
Homeostasis model assessment B cell function
- STZβ:
-
Standardized β
- ELISA:
-
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
References
Wozniak SE, Gee LL, Wachtel MS, Frezza EE (2009) Adipose tissue: the new endocrine organ? A review article. Dig Dis Sci 54:1847–1856
Lago F, Gómez R, Gómez-Reino JJ, Dieguez C, Gualillo O (2009) Adipokines as novel modulators of lipid metabolism. Trends Biochem Sci 34:500–510
Seale P, Conroe HM, Estall J, Kajimura S, Frontini A, Ishibashi J, Cohen P, Cinti S, Spiegelman BM (2011) Prdm16 determines the thermogenic program of subcutaneous white adipose tissue in mice. J Clin Invest 121:96–105
McGown C, Birerdinc A, Younossi ZM (2014) Adipose tissue as an endocrine organ. Clin Liver Dis 18:41–58
Tan BK, Adya R, Randeva HS (2010) Omentin: a novel link between inflammation, diabesity, and cardiovascular disease. Trends Cardiovasc Med 20:143–148
Rabe K, Lehrke M, Parhofer KG, Broedl UC (2008) Adipokines and insulin resistance. Mol Med 14:741–751
Després J-P, Lemieux I, Bergeron J, Pibarot P, Mathieu P, Larose E, Rodés-Cabau J, Bertrand OF, Poirier P (2008) Abdominal obesity and the metabolic syndrome: contribution to global cardiometabolic risk. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 28:1039–1049
Zhong X, Zhang H-y, Tan H, Zhou Y, Liu F-l, F-q C, Shang D-y (2011) Association of serum omentin-1 levels with coronary artery disease. Acta Pharmacol Sin 32:873–878
Shah A, Mehta N, Reilly MP (2008) Adipose inflammation, insulin resistance, and cardiovascular disease. J Parenter Enter Nutr 32:638–644
Kershaw EE, Flier JS (2004) Adipose tissue as an endocrine organ. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 89:2548–2556
Fukuhara A, Matsuda M, Nishizawa M, Segawa K, Tanaka M, Kishimoto K, Matsuki Y, Murakami M, Ichisaka T, Murakami H (2005) Visfatin: a protein secreted by visceral fat that mimics the effects of insulin. Science 307:426–430
Yang R-Z, Lee M-J, Hu H, Pray J, Wu H-B, Hansen BC, Shuldiner AR, Fried SK, McLenithan JC, Gong D-W (2006) Identification of omentin as a novel depot-specific adipokine in human adipose tissue: possible role in modulating insulin action. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 290:E1253–E1261
Rostami H, Samadi M, Yuzbashian E, Zarkesh M, Asghari G, Hedayati M, Daneshafrooz A, Mirmiran P, Khalaj A (2017) Habitual dietary intake of fatty acids are associated with leptin gene expression in subcutaneous and visceral adipose tissue of patients without diabetes. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids 126:49–54
Yuzbashian E, Zarkesh M, Asghari G, Hedayati M, Safarian M, Mirmiran P, Khalaj A (2018) Is apelin gene expression and concentration affected by dietary intakes? A systematic review. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 58:680–688
de Souza Batista CM, Yang R-Z, Lee M-J, Glynn NM, Yu D-Z, Pray J, Ndubuizu K, Patil S, Schwartz A, Kligman M (2007) Omentin plasma levels and gene expression are decreased in obesity. Diabetes 56:1655–1661
Thörne A, Lönnqvist F, Apelman J, Hellers G, Arner P (2002) A pilot study of long-term effects of a novel obesity treatment: omentectomy in connection with adjustable gastric banding. Int J Obes 26:193–199
Shibata R, Ouchi N, Takahashi R, Terakura Y, Ohashi K, Ikeda N, Higuchi A, Terasaki H, Kihara S, Murohara T (2012) Omentin as a novel biomarker of metabolic risk factors. Diabetol Metab Syndr 4:1–4
Auguet T, Quintero Y, Riesco D, Morancho B, Terra X, Crescenti A, Broch M, Aguilar C, Olona M, Porras JA (2011) New adipokines vaspin and omentin. Circulating levels and gene expression in adipose tissue from morbidly obese women. BMC Med Genet 12:1–8
Pan H-Y, Guo L, Li Q (2010) Changes of serum omentin-1 levels in normal subjects and in patients with impaired glucose regulation and with newly diagnosed and untreated type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 88:29–33
Tan BK, Adya R, Farhatullah S, Lewandowski KC, O’Hare P, Lehnert H, Randeva HS (2008) Omentin-1, a novel adipokine, is decreased in overweight insulin-resistant women with polycystic ovary syndrome: ex vivo and in vivo regulation of omentin-1 by insulin and glucose. Diabetes 57:801–808
El-Mesallamy H, El-Derany M, Hamdy N (2011) Serum omentin-1 and chemerin levels are interrelated in patients with Type 2 diabetes mellitus with or without ischaemic heart disease. Diabet Med 28:1194–1200
Cai R, Wei L, Di J, Yu H, Bao Y, Jia W (2009) Expression of omentin in adipose tissues in obese and type 2 diabetic patients. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi 89:381–384
Nosrati-Oskouie M, Yuzbashian E, Zarkesh M, Sadat Aghili-Moghadam N, Hedayati M, Safarian M, Asghari G, Khalaj A, Mirmiran P (2020) Association of plasma fatty acids pattern with omentin gene expression in human adipose tissues: a cross-sectional study. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis 31(3):894–901
Yuzbashian E, Asghari G, Hedayati M, Zarkesh M, Mirmiran P, Khalaj A (2019) Determinants of vitamin D receptor gene expression in visceral and subcutaneous adipose tissue in non-obese, obese, and morbidly obese subjects. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 187:82–87
Nosrati-Oskouie M, Yuzbashian E, Zarkesh M, Aghili-Moghadam N, Hedayati M, Safarian M, Asghari G, Khalaj A, Mirmiran P (2021) Association of plasma fatty acids pattern with omentin gene expression in human adipose tissues: a cross-sectional study. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis 31:894–901
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods 25:402–408
Bustin SA, Benes V, Garson JA, Hellemans J, Huggett J, Kubista M, Mueller R, Nolan T, Pfaffl MW, Shipley GL (2009) The MIQE Guidelines: M inimum I nformation for Publication of Q uantitative Real-Time PCR E xperiments. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Yamawaki H, Tsubaki N, Mukohda M, Okada M, Hara Y (2010) Omentin, a novel adipokine, induces vasodilation in rat isolated blood vessels. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 393:668–672
Reinehr T, Roth CL (2018) Inflammation markers in type 2 diabetes and the metabolic syndrome in the pediatric population. Curr DiabRep 18:131
Sperling M, Grzelak T, Pelczyńska M, Jasinska P, Bogdanski P, Pupek-Musialik D, Czyzewska K (2016) Concentrations of omentin and vaspin versus insulin resistance in obese individuals. Biomed Pharmacother 83:542–547
Nosrati-Oskouie M, Safarian M, Yuzbashian E, Asghari G, Zarkesh M, Aghili-Moghaddam N, Hedayati M, Mirmiran P, Khalaj A (2019) The association of omentin gene expression in visceral and subcutaneous adipose tissues with plasma fatty acids profile and dietary fatty acids. Iran J Endocrinol Metab 21(3):Pe123–Pe137
Buyukinan M, Atar M, Can U, Pirgon O, Guzelant A, Deniz I (2018) The association between serum vaspin and omentin-1 levels in obese children with metabolic syndrome. Metab Syndr Relat Disord 16:76–81
Zengi S, Zengi O, Kirankaya A, Kucuk SH, Kutanis EE, Yigit O (2019) Serum omentin-1 levels in obese children. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab 32:247–251
As Habi A, Sadeghi M, Arab A, Hajianfar H (2019) The association between omentin and diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obesity 12:1277–1286. https://doi.org/10.2147/DMSO.S206981
Hossein-Nezhad A, Mirzaei K, Alatab S, Ahmadivand Z, Najmafshar A, Peppa M, Koliaki C, Dimitriadis G, Sivakumar T, Sivakumar S (2012) Circulating omentin-1 in obesity and metabolic syndrome status compared to control subjects. Endocrinol Metab Syndr 1:008
Pessin JE, Kwon H (2013) Adipokines mediate inflammation and insulin resistance. Front Endocrinol 4:71
Šenolt L, Polanská M, Filková M, Cerezo LA, Pavelka K, Gay S, Haluzík M, Vencovský J (2010) Vaspin and omentin: new adipokines differentially regulated at the site of inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 69:1410–1411
Aliasghari F, Izadi A, Jabbari M, Imani B, Gargari BP, Asjodi F, Ebrahimi S (2018) Are vaspin and omentin-1 related to insulin resistance, blood pressure and inflammation in NAFLD patients? J Med Biochem 37:470
Yilmaz Y, Yonal O, Kurt R, Alahdab YO, Eren F, Ozdogan O, Celikel CA, Imeryuz N, Kalayci C, Avsar E (2011) Serum levels of omentin, chemerin and adipsin in patients with biopsy-proven nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Scand J Gastroenterol 46:91–97
Castro CAd, Silva KAd, Rocha MC, Sene-Fiorese M, Nonaka KO, Malavazi I, Anibal FdF, Duarte ACGdO (2019) Exercise and omentin: their role in the crosstalk between muscle and adipose tissues in type 2 diabetes mellitus rat models. Front Physiol 9:1881
Du Y, Ji Q, Cai L, Huang F, Lai Y, Liu Y, Yu J, Han B, Zhu E, Zhang J (2016) Association between omentin-1 expression in human epicardial adipose tissue and coronary atherosclerosis. Cardiovasc Diabetol 15:1–9
Razgildina N, Panteleeva A, Miroshnikova V, Pobozheva I, Polyakova E, Berkovitch O, Belyaeva O, Baranova E, Pchelina S (2018) Omentin1 gene expression in epicardial and subcutaneous adipose tissue during obesity related coronary heart disease. Atherosclerosis 275:e173–e174
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank the hospital staff, study assistants, and coordinators that took part in this research.
Funding
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
A.D., M.Z. and EY conceptualized and designed the study, analyzed and interpreted the data, prepared the manuscript and approved the final manuscript as submitted. G.A. and P.M. entered data, drafted the initial manuscript, and approved the final manuscript as submitted. R.A. and M.H. critically revised the manuscript and approved the final manuscript as submitted. S.M.F drafted the initial manuscript and approved the final manuscript as submitted. A.Kh. biopsied the patients during the abdominal surgery and approved the final manuscript as submitted.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
The study's protocol was approved by the Research Institute for Endocrine Sciences (RIES) of Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences (NO: IR.SBMU.ENDOCRINE.REC.1395.279), and the study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and RIES institutional guidelines. All participants consciously signed the written consent form approved by the committee.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Daneshafrooz, A., Yuzbashian, E., Zarkesh, M. et al. The relation of omentin gene expression and glucose homeostasis of visceral and subcutaneous adipose tissues in non-diabetic adults. Mol Biol Rep 49, 163–169 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-021-06854-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-021-06854-4