Abstract
Background
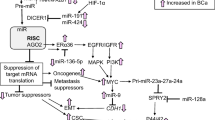
The ErbB signaling pathway plays important role in the pathogenesis of lung cancer. We explored the role of miRNA-377 as a tumor suppressor in NSCLC through silencing of some genes in the ErbB pathway.
Methods and Results
The targeting effect of miRNA-377 on EGFR, MAPK1, ABL2, and PAK2 was evaluated. The expression levels of these genes and miRNA-377 were surveyed in NSCLC and normal human tissues, Calu-6, and A549 cells. Real-time PCR was used to figure out whether miRNA-377 could decrease the target genes mRNAs in transfected lung cancer cell lines. The effects of miRNA-377 on apoptosis cell and proliferation were analyzed. We showed that miRNA-377 targets EGFR, MAPK1, and PAK2 mRNAs in in-silico and luciferase reporter assay. The expression of miRNA-377 was significantly downregulated in human NSCLC tissues, Calu-6 and A549 cells compared to their controls. We observed a negative correlation between EGFR, MAPK1, PAK2, and miRNA-377 expression in human NSCLC tissues. A significant reduction in EGFR, MAPK1, and PAK2 mRNA levels was detected, following miRNA-377 transfection in Calu-6 and A549 cells. The higher levels of miRNA-377 in Calu-6, and A549 cells induced apoptosis and reduced proliferation, significantly.
Conclusions
All these data reveal that miRNA-377 functions as a tumor suppressor in NSCLC and may serve as a potential therapeutic target for the treatment of NSCLC.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The authors confirm that the data supporting the findings of this study are available.
References
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A (2018) Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 68(6):394–424
Sekine I, Yamamoto N, Nishio K, Saijo N (2008) Emerging ethnic differences in lung cancer therapy. Br J Cancer 99(11):1757–1762
Götz R (2008) Inter-cellular adhesion disruption and the RAS/RAF and beta-catenin signalling in lung cancer progression. Cancer Cell Int 8(1):1–4
Su VY, Yang KY, Huang TY, Hsu CC, Chen YM, Yen JC, Chou YC, Chang YL, He CH (2020) The efficacy of first-line tyrosine kinase inhibitors combined with co-medications in Asian patients with EGFR mutation non-small cell lung cancer. Sci Rep 10(1):1–4
Giancotti FG (2014) Deregulation of cell signaling in cancer. FEBS Lett 588(16):2558–2570
Jiang N, Dai Q, Su X, Fu J, Feng X, Peng J (2020) Role of PI3K/AKT pathway in cancer: the framework of malignant behavior. Mol Biol Rep 47(6):4587–4629
Ramaiah, M. J., & Kumar, K. R (2021) mTOR-Rictor-EGFR axis in oncogenesis and diagnosis of glioblastoma multiforme. Mol Biol Rep 1–23
Obradovic J, Todosijevic J, Jurisic V (2021) Application of the conventional and novel methods in testing EGFR variants for NSCLC patients in the last 10 years through different regions: a systematic review. Mol Biol Rep 1–12
Hynes NE, MacDonald G (2009) ErbB receptors and signaling pathways in cancer. Curr Opin Cell Biol 21(2):177–184
Engelman JA, Jänne PA, Mermel C, Pearlberg J, Mukohara T, Fleet C, Cichowski K, Johnson BE, Cantley LC (2005) ErbB-3 mediates phosphoinositide 3-kinase activity in gefitinib-sensitive non-small cell lung cancer cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci 102(10):3788–3793
Torigoe H, Yamamoto H, Sakaguchi M, Youyi C, Namba K, Sato H, Shien K, Soh J, Suzawa K, Tomida S, Tsukuda K (2018) Tumor-suppressive effect of LRIG1, a negative regulator of ErbB, in non-small cell lung cancer harboring mutant EGFR. Carcinogenesis 39(5):719–727
Deng Q, Fang Q, Sun H, Singh AP, Alexander M, Li S, Cheng H, Zhou S (2020) Detection of plasma EGFR mutations for personalized treatment of lung cancer patients without pathologic diagnosis. Cancer Med 9(6):2085–2095
Hirsch FR, Varella-Garcia M, Cappuzzo F (2009) Predictive value of EGFR and HER2 overexpression in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. Oncogene 28(1):S32–S37
Zhang B, Chen J, Ren Z, Chen Y, Li J, Miao X, Song Y, Zhao T, Li Y, Shi Y, Ren D (2013) A specific miRNA signature promotes radioresistance of human cervical cancer cells. Cancer Cell Int 13(1):1–8
Anastasiadou E, Jacob L, Slack FJ (2018) Non-coding RNA networks in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 18(1):5–18
Wang WT, Han C, Sun YM, Chen TQ, Chen YQ (2019) Noncoding RNAs in cancer therapy resistance and targeted drug development. J Hematol Oncol 12(1):1–15
Shi ZM, Wang L, Shen H, Jiang CF, Ge X, Li DM, Wen YY, Sun HR, Pan MH, Li W, Shu YQ (2017) Downregulation of miR-218 contributes to epithelial–mesenchymal transition and tumor metastasis in lung cancer by targeting Slug/ZEB2 signaling. Oncogene 36(18):2577–2588
Cao S, Jiang L, Shen L, Xiong Z (2019) Role of microRNA-92a in metastasis of osteosarcoma cells in vivo and in vitro by inhibiting expression of TCF21 with the transmission of bone marrow derived mesenchymal stem cells. Cancer Cell Int 19(1):1–7
Bischoff A, Bayerlová M, Strotbek M, Schmid S, Beissbarth T, Olayioye MA (2015) A global microRNA screen identifies regulators of the ErbB receptor signaling network. Cell Commun Signal 13(1):1–5
Soliman SES, Abdelaleem AH, Alhanafy AM, Ibrahem RAL, Elhaded ASA, Assar MF (2021) Circulating miR-21-5p and miR-126-3p: diagnostic, prognostic value, and multivariate analysis in non-small-cell lung cancer. Mol Biol Rep 48(3):2543–2552
Kawana S, Saito R, Miki Y, Kimura Y, Abe J, Sato I, Endo M, Sugawara S, Sasano H (2021) Suppression of tumor immune microenvironment via microRNA-1 after epidermal growth factor receptor-tyrosine kinase inhibitor resistance acquirement in lung adenocarcinoma. Cancer Med 10(2):718–727
Amri J, Molaee N, Karami H, Baazm M (2021) Combination of two miRNAs has a stronger effect on stimulating apoptosis, inhibiting cell growth and increasing erlotinib sensitivity relative to single miRNA in A549 lung cancer cells. Biotechnol Appl Biochem
Sherf BA, Navarro SL, Hannah RR, Wood KV (1996) Dual-luciferase reporter assay: an advanced co-reporter technology integrating firefly and Renilla luciferase assays. Promega Notes 57(2):2–8
Chen C, Ridzon DA, Broomer AJ, Zhou Z, Lee DH, Nguyen JT, Barbisin M, Xu NL, Mahuvakar VR, Andersen MR, Lao KQ (2005) Real-time quantification of microRNAs by stemloop RT–PCR. Nucleic Acids Res 33(20):e179
Mohammadi-Yeganeh S, Paryan M, Samiee SM, Soleimani M, Arefian E, Azadmanesh K, Mostafavi E, Mahdian R, Karimipoor M (2013) Development of a robust, low cost stem-loop real-time quantification PCR technique for miRNA expression analysis. Mol Biol Rep 40(5):3665–3674
Liu XG, Xu J, Li F, Li MJ, Hu T (2018) Down-regulation of miR-377 contributes to cisplatin resistance by targeting XIAP in osteosarcoma. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 22(5):1249–1257
Barta JA, Powell CA, Wisnivesky JP (2019) Global epidemiology of lung cancer. Ann Global Health. https://doi.org/10.5334/aogh.2419
Zou X, Wei J, Huang Z, Zhou X, Lu Z, Zhu W, Miao Y (2019) Identification of a six-miRNA panel in serum benefiting pancreatic cancer diagnosis. Cancer Med 8:2810–2822
Wu J, Shen Z (2020) Exosomal miRNAs as biomarkers for diagnostic and prognostic in lung cancer. Cancer Med 9(19):6909–6922
Chang W, Liu M, Xu J, Fu H, Zhou B, Yuan T, Chen P (2016) MiR-377 inhibits the proliferation of pancreatic cancer by targeting Pim-3. Tumor Biol 37(11):14813–14824
Zehavi L, Schayek H, Jacob-Hirsch J, Sidi Y, Leibowitz-Amit R, Avni D (2015) MiR-377 targets E2F3 and alters the NF-kB signaling pathway through MAP3K7 in malignant melanoma. Mol Cancer 14(1):1–6
Formosa A, Markert EK, Lena AM, Italiano D, Finazzi-Agro E, Levine AJ, Bernardini S, Garabadgiu AV, Melino G, Candi E (2014) MicroRNAs, miR-154, miR-299-5p, miR-376a, miR-376c, miR-377, miR-381, miR-487b, miR-485-3p, miR-495 and miR-654-3p, mapped to the 14q32. 31 locus, regulate proliferation, apoptosis, migration and invasion in metastatic prostate cancer cells. Oncogene 33(44):5173–5182
Chen G, Lu L, Liu C, Shan L, Yuan D (2015) MicroRNA-377 suppresses cell proliferation and invasion by inhibiting TIAM1 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma. PloS one 10(3):e0117714
Wang L, Shao J, Zhang X, Xu M, Zhao J (2015) microRNA-377 suppresses the proliferation of human osteosarcoma MG-63 cells by targeting CDK6. Tumor Biol 36(5):3911–3917
Wang R, Ma Y, Yu D, Zhao J, Ma P (2015) miR-377 functions as a tumor suppressor in human clear cell renal cell carcinoma by targeting ETS1. Biomed Pharmacother 70:64–71
Zhang R et al (2014) MicroRNA-377 inhibited proliferation and invasion of human glioblastoma cells by directly targeting specificity protein 1. Neuro Oncol 16:1510–1522
Yu R, Cai L, Chi Y, Ding X, Wu X (2018) miR-377 targets CUL4A and regulates metastatic capability in ovarian cancer. Int J Mol Med 41(6):3147–3156
Al-Harbi S, Choudhary GS, Ebron JS, Hill BT, Vivekanathan N, Ting AH, Radivoyevitch T, Smith MR, Shukla GC, Almasan A (2015) miR-377-dependent BCL-xL regulation drives chemotherapeutic resistance in B-cell lymphoid malignancies. Mol Cancer 14(1):1–7
Liu WY, Yang Z, Sun Q, Yang X, Hu Y, Xie H, Gao HJ, Guo LM, Yi JY, Liu M, Tang H (2018) miR-377-3p drives malignancy characteristics via upregulating GSK-3β expression and activating NF-κB pathway in hCRC cells. J Cell Biochem 119(2):2124–2134
Azizi M, Fard-Esfahani P, Mahmoodzadeh H, Fazeli MS, Azadmanesh K, Zeinali S, Teimoori-Toolabi L (2017) MiR-377 reverses cancerous phenotypes of pancreatic cells via suppressing DNMT1 and demethylating tumor suppressor genes. Epigenomics 9(8):1059–1075
Meng F, Zhang L, Shao Y, Ma Q, Lv H (2015) MicroRNA-377 inhibits non-small-cell lung cancer through targeting AEG-1. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 8(11):13853
Zhang J, Zhao M, Xue ZQ, Liu Y, Wang YX (2016) miR-377 inhibited tumorous behaviors of non-small cell lung cancer through directly targeting CDK6. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 20(21):4494–4499
Acknowledgements
We thank the patients and clinicians contributing to this study. In addition, we thank Virology Department staffs for providing us the equipment. This work was supported by the Pasteur Institute of Iran. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MA and SZ designed the study. NY, SH, FRJ, MK and MHR carried out the experiments. MA, FRJ, SH, NY and RM collected and analyzed the data. SH and MA wrote the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
The present study was conducted under the instructions accepted by the Ethics Committee of Pasteur Institute of Iran, written informed consent to participate, and consent to publish forms was obtained from all participants involved in the present study. This material is the authors' own original work, which has not been previously published elsewhere. The paper is not currently being considered for publication elsewhere. The paper reflects the authors' own research and analysis in a truthful and complete manner.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hashemi, S., Yari, N., Rahimi Jamnani, F. et al. The role of miRNA-377 as a tumor suppressor in lung cancer by negative regulation of genes belonging to ErbB signaling pathway. Mol Biol Rep 49, 85–95 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-021-06844-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-021-06844-6