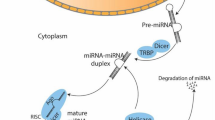
Abstract
Along with evolution, a considerable number of signaling cascades have evolved within cells to meet their multifaceted needs. Among transmitting molecules, phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K), Akt, and mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) have teamed up to build a signaling axis that effectively regulates various cellular processes including cell proliferation and migration. Given the extensive output of the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling axis, its aberrancy could subsequently lead to the formation of a wide range of human cancers spanning from hematologic malignancies to different types of solid tumors. Despite the high frequency of the PI3K pathway over-activation in most malignancies, mutations in the DNA sequence are not equally common. Such incompatibility sheds light on the possible effects of post-translational modification mechanisms that may take control of this pathway, some of the most important ones of which are through microRNAs (miRNAs or miRs). The present review is designed to take off the veil from the regulatory role of these small non-coding RNAs on the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling axis in carcinogenesis.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
Code availability
Not applicable.
Abbreviations
- ALL:
-
Acute lymphoblastic leukemia
- AML:
-
Acute myeloid leukemia
- APL:
-
Acute promyelocytic leukemia
- BC:
-
Bladder cancer
- BrC:
-
Breast cancer
- CLL:
-
Chronic lymphoid leukemia
- CML:
-
Chronic myeloid leukemia
- CRC:
-
Colorectal cancer
- CREB:
-
CAMP-response element binding protein
- DLBCL:
-
Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
- EC:
-
Endometrial cancer
- EGFR:
-
Epidermal growth factor receptor
- EMT:
-
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition
- FOXO1:
-
Forkhead box protein O1
- GC:
-
Gastric cancer
- GPCRs:
-
G protein-coupled receptors
- GSK-3B:
-
Glycogen-synthesis kinase-3B
- HCC:
-
Hepatocellular carcinoma
- HER2:
-
Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2
- HM:
-
Hematologic malignancies
- HNSCC:
-
Head and neck squamous carcinoma
- KRAS:
-
Kirsten rat sarcoma
- MAPK:
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinase
- MDM2:
-
Mouse double minute 2 homolog
- miR:
-
MicroRNA
- miRNA:
-
MicroRNA
- miRISC:
-
MiRNA-induced silencing complex
- MM:
-
Multiple myeloma
- mTOR:
-
Mammalian target of rapamycin
- NF-κB:
-
Nuclear factor kappa B
- NSCLS:
-
Non-small cell lung cancer
- OC:
-
Ovarian cancer
- PC:
-
Prostate cancer
- PDAC:
-
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
- PDCD4:
-
Programmed cell death 4 protein
- PI3K:
-
Phosphoinositide 3-kinase
- PIP2:
-
Phosphatidylinositol-4,5-diphosphate
- PKB:
-
Protein kinase B
- PTEN:
-
Phosphatase and tensin homolog
- RNAi:
-
RNA interference
- RTKs:
-
Tyrosine kinase receptors
- TSC2:
-
Tuberous sclerosis complex 2
- UTR:
-
Untranslated region
- VEGF:
-
Vascular endothelial growth factor
References
Osaki M, Oshimura M, Ito H (2004) PI3K-Akt pathway: its functions and alterations in human cancer. Apoptosis 9(6):667–676
Soung YH et al (2006) Mutational analysis of AKT1, AKT2 and AKT3 genes in common human carcinomas. Oncology 70(4):285–289
Goh JN et al (2016) microRNAs in breast cancer: regulatory roles governing the hallmarks of cancer. Biol Rev 91(2):409–428
Svoronos AA, Engelman DM, Slack FJ (2016) OncomiR or tumor suppressor? The duplicity of microRNAs in cancer. Cancer Res 76(13):3666–3670
Hu M et al (2019) MicroRNAs and the PTEN/PI3K/Akt pathway in gastric cancer. Oncol Rep 41(3):1439–1454
Noorolyai S et al (2019) The relation between PI3K/AKT signalling pathway and cancer. Gene 698:120–128
Porta C, Paglino C, Mosca A (2014) Targeting PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling in cancer. Front Oncol 4:64
Carnero A et al (2008) The PTEN/PI3K/AKT signalling pathway in cancer, therapeutic implications. Curr Cancer Drug Targets 8(3):187–198
Vara JÁF et al (2004) PI3K/Akt signalling pathway and cancer. Cancer Treat Rev 30(2):193–204
Milella M et al (2015) PTEN: multiple functions in human malignant tumors. Front Oncol 5:24
Vivanco I, Sawyers CL (2002) The phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase–AKT pathway in human cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 2(7):489–501
Purow B (2009) MicroRNAs in the central nervous system and potential roles of RNA interference in brain tumors. CNS cancer. Humana Press, Totowa, pp 651–677
Lewis BP et al (2003) Prediction of mammalian microRNA targets. Cell 115(7):787–798
Krol J, Loedige I, Filipowicz W (2010) The widespread regulation of microRNA biogenesis, function and decay. Nat Rev Genet 11(9):597–610
Fabian MR, Sonenberg N (2012) The mechanics of miRNA-mediated gene silencing: a look under the hood of miRISC. Nat Struct Mol Biol 19(6):586–593
Santhekadur PK et al (2012) Multifunction protein staphylococcal nuclease domain containing 1 (SND1) promotes tumor angiogenesis in human hepatocellular carcinoma through novel pathway that involves nuclear factor κB and miR-221. J Biol Chem 287(17):13952–13958
Yoo BK et al (2011) Increased RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC) activity contributes to hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 53(5):1538–1548
Pink RC et al (2011) Pseudogenes: pseudo-functional or key regulators in health and disease? RNA 17(5):792–798
Kashani B et al (2019) You are what you eat: Sequence analysis reveals how plant microRNAs may regulate the human genome. Comput Biol Med 106:106–113
Chakraborty C, Sharma AR, Sharma G (2020) Therapeutic advances of miRNAs: a preclinical and clinical update. J Adv Res 28:127–138
Park S et al (2010) Role of the PI3K/AKT and mTOR signaling pathways in acute myeloid leukemia. Haematologica 95(5):819–828
Bertacchini J et al (2015) Targeting PI3K/AKT/mTOR network for treatment of leukemia. Cell Mol Life Sci 72(12):2337–2347
Jia CY et al (2011) MiR-223 suppresses cell proliferation by targeting IGF-1R. PloS One 6(11):e27008
Chen L et al (2019) microRNA-628 inhibits the proliferation of acute myeloid leukemia cells by directly targeting IGF-1R. Onco Targets Ther 12:907
Zhou J-D et al (2019) MicroRNA-335/ID4 dysregulation predicts clinical outcome and facilitates leukemogenesis by activating PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in acute myeloid leukemia. Aging (Albany NY) 11(10):3376
Li Y et al (2013) Epigenetic silencing of microRNA-193a contributes to leukemogenesis in t (8; 21) acute myeloid leukemia by activating the PTEN/PI3K signal pathway. Blood J Am Soc Hematol 121(3):499–509
Bai H et al (2011) Involvement of miR-21 in resistance to daunorubicin by regulating PTEN expression in the leukaemia K562 cell line. FEBS Lett 585(2):402–408
Li Z, Luo J (2018) Epigenetic regulation of HOTAIR in advanced chronic myeloid leukemia. Cancer Manage Res 10:5349
Palacios F et al (2015) Activation of the PI3K/AKT pathway by microRNA-22 results in CLL B-cell proliferation. Leukemia 29(1):115–125
Olive V et al (2009) miR-19 is a key oncogenic component of mir-17-92. Genes Dev 23(24):2839–2849
Go H et al (2015) MicroRNA-21 plays an oncogenic role by targeting FOXO1 and activating the PI3K/AKT pathway in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Oncotarget 6(17):15035
Han B, Wang S, Zhao H (2020) MicroRNA-21 and microRNA-155 promote the progression of Burkitt’s lymphoma by the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 13(1):89
Roccaro AM et al (2009) MicroRNAs 15a and 16 regulate tumor proliferation in multiple myeloma. Blood J Am Soc Hematol 113(26):6669–6680
Jiang Y, Chang H, Chen G (2018) Effects of microRNA-20a on the proliferation, migration and apoptosis of multiple myeloma via the PTEN/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Oncol Lett 15(6):10001–10007
Tokunaga E et al (2006) Activation of PI3K/Akt signaling and hormone resistance in breast cancer. Breast Cancer 13(2):137–144
Rask L et al (2011) High expression of miR-21 in tumor stroma correlates with increased cancer cell proliferation in human breast cancer. APMIS 119(10):663–673
Li N et al (2017) MiR-106b and miR-93 regulate cell progression by suppression of PTEN via PI3K/Akt pathway in breast cancer. Cell Death Dis 8(5):e2796–e2796
Zhang LF et al (2020) MicroRNA-425-5p promotes breast cancer cell growth by inducing PI3K/AKT signaling. Kaohsiung J Med Sci 36(4):250–256
Bahena-Ocampo I et al (2016) miR-10b expression in breast cancer stem cells supports self-renewal through negative PTEN regulation and sustained AKT activation. EMBO Rep 17(5):648–658
Li C et al (2018) miR-19b serves as a prognostic biomarker of breast cancer and promotes tumor progression through PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Onco Targets Ther 11:4087
Gong C et al (2011) Up-regulation of miR-21 mediates resistance to trastuzumab therapy for breast cancer. J Biol Chem 286(21):19127–19137
Rahmani F et al (2020) Role of regulatory miRNAs of the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in the pathogenesis of breast cancer. Gene 737:144459
Zhang Y et al (2019) Downregulation of microRNA-1469 promotes the development of breast cancer via targeting HOXA1 and activating PTEN/PI3K/AKT and Wnt/β-catenin pathways. J Cell Biochem 120(4):5097–5107
Cui W et al (2013) micro RNA-133a regulates the cell cycle and proliferation of breast cancer cells by targeting epidermal growth factor receptor through the EGFR/A kt signaling pathway. FEBS J 280(16):3962–3974
Zhu N et al (2011) Endothelial-specific intron-derived miR-126 is down-regulated in human breast cancer and targets both VEGFA and PIK3R2. Mol Cell Biochem 351(1–2):157–164
Chen Y et al (2013) miRNA-200c increases the sensitivity of breast cancer cells to doxorubicin through the suppression of E-cadherin-mediated PTEN/Akt signaling. Mol Med Rep 7(5):1579–1584
Network CGAR (2011) Integrated genomic analyses of ovarian carcinoma. Nature 474(7353):609
Dobbin ZC, Landen CN (2013) The importance of the PI3K/AKT/MTOR pathway in the progression of ovarian cancer. Int J Mol Sci 14(4):8213–8227
Kuznetsov VA, Tang Z, Ivshina AV (2017) Identification of common oncogenic and early developmental pathways in the ovarian carcinomas controlling by distinct prognostically significant microRNA subsets. BMC Genomics 18(6):692
Polytarchou C et al (2011) Akt2 regulates all Akt isoforms and promotes resistance to hypoxia through induction of miR-21 upon oxygen deprivation. Cancer Res 71(13):4720–4731
Wang YQ et al (2013) MicroRNA-182 promotes cell growth, invasion, and chemoresistance by targeting programmed cell death 4 (PDCD4) in human ovarian carcinomas. J Cell Biochem 114(7):1464–1473
Ghafouri-Fard S, Shoorei H, Taheri M (2020) miRNA profile in ovarian cancer. Exp Mol Pathol 113:104381
Zhu L et al (2019) miR-494-3p promotes the progression of endometrial cancer by regulating the PTEN/PI3K/AKT pathway. Mol Med Rep 19(1):581–588
Myatt SS et al (2010) Definition of microRNAs that repress expression of the tumor suppressor gene FOXO1 in endometrial cancer. Cancer Res 70(1):367–377
Imam JS et al (2012) Genomic loss of tumor suppressor miRNA-204 promotes cancer cell migration and invasion by activating AKT/mTOR/Rac1 signaling and actin reorganization. PloS One 7(12):e52397
Xiang Y et al (2014) MiR-152 and miR-185 co-contribute to ovarian cancer cells cisplatin sensitivity by targeting DNMT1 directly: a novel epigenetic therapy independent of decitabine. Oncogene 33(3):378–386
Yu T et al (2018) Functions and mechanisms of microRNA-31 in human cancers. Biomed Pharmacother 108:1162–1169
Li C et al (2019) MicroRNA-936 targets FGF2 to inhibit epithelial ovarian cancer aggressiveness by deactivating the PI3K/Akt pathway. Onco Targets Ther 12:5311
Li Y et al (2016) A dual PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling inhibitor miR-99a suppresses endometrial carcinoma. Am J Transl Res 8(2):719
Kent C, Reed IG (2016) Regulation of epithelial–mesenchymal transition in endometrial cancer: connecting PI3K, estrogen signaling, and microRNAs. Clin Transl Oncol 18(11):1056–1061
Liang M et al (2015) Downregulation of miR203 induces overexpression of PIK3CA and predicts poor prognosis of gastric cancer patients. Drug Des Dev Ther 9:3607
Tsukamoto Y et al (2010) MicroRNA-375 is downregulated in gastric carcinomas and regulates cell survival by targeting PDK1 and 14-3-3ζ. Cancer Res 70(6):2339–2349
Zhang H et al (2015) MicroRNA-29s could target AKT2 to inhibit gastric cancer cells invasion ability. Med Oncol 32(1):342
Xu M et al (2017) MicroRNA-379 inhibits metastasis and epithelial-mesenchymal transition via targeting FAK/AKT signaling in gastric cancer. Int J Oncol 51(3):867–876
Wu L et al (2015) MicroRNA-137 contributes to dampened tumorigenesis in human gastric cancer by targeting AKT2. PloS One 10(6):e0130124
Chun-zhi Z et al (2010) MicroRNA-221 and microRNA-222 regulate gastric carcinoma cell proliferation and radioresistance by targeting PTEN. BMC Cancer 10(1):1–10
Guo B et al (2014) miR-338-3p suppresses gastric cancer progression through a PTEN-AKT axis by targeting P-REX2a. Mol Cancer Res 12(3):313–321
Eto K et al (2014) The microRNA-21/PTEN pathway regulates the sensitivity of HER2-positive gastric cancer cells to trastuzumab. Ann Surg Oncol 21(1):343–350
Danielsen SA et al (2015) Portrait of the PI3K/AKT pathway in colorectal cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta (BBA) 1855(1):104–121
Reid JF et al (2012) miRNA profiling in colorectal cancer highlights miR-1 involvement in MET-dependent proliferation. Mol Cancer Res 10(4):504–515
Guo S et al (2013) MicroRNA-497 targets insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor and has a tumour suppressive role in human colorectal cancer. Oncogene 32(15):1910–1920
Guo C et al (2008) The noncoding RNA, miR-126, suppresses the growth of neoplastic cells by targeting phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling and is frequently lost in colon cancers. Genes Chromosom Cancer 47(11):939–946
Diosdado B et al (2009) MiR-17-92 cluster is associated with 13q gain and c-myc expression during colorectal adenoma to adenocarcinoma progression. Br J Cancer 101(4):707–714
Sarver AL, Li L, Subramanian S (2010) MicroRNA miR-183 functions as an oncogene by targeting the transcription factor EGR1 and promoting tumor cell migration. Cancer Res 70(23):9570–9580
Wu Y et al (2017) MicroRNA-21 (Mir-21) promotes cell growth and invasion by repressing tumor suppressor PTEN in colorectal cancer. Cell Physiol Biochem 43(3):945–958
Park J-K et al (2009) Antisense inhibition of microRNA-21 or-221 arrests cell cycle, induces apoptosis, and sensitizes the effects of gemcitabine in pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Pancreas 38(7):e190–e199
Liu J et al (2014) LPS induced miR-181a promotes pancreatic cancer cell migration via targeting PTEN and MAP2K4. Dig Dis Sci 59(7):1452–1460
Sarkar S et al (2013) Down-regulation of miR-221 inhibits proliferation of pancreatic cancer cells through up-regulation of PTEN, p27kip1, p57kip2, and PUMA. Am J Cancer Res 3(5):465
Yonemori K et al (2017) MicroRNA in pancreatic cancer. J Hum Genet 62(1):33–40
Fu X et al (2018) Exosomal microRNA-32-5p induces multidrug resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma via the PI3K/Akt pathway. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 37(1):52
Ohta K et al (2015) MicroRNA-93 activates c-Met/PI3K/Akt pathway activity in hepatocellular carcinoma by directly inhibiting PTEN and CDKN1A. Oncotarget 6(5):3211
Zhou Y et al (2017) Effect of microRNA-135a on cell proliferation, migration, invasion, apoptosis and tumor angiogenesis through the IGF-1/PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in non-small cell lung cancer. Cell Physiol Biochem 42(4):1431–1446
Xia H, Li Y, Lv X (2016) MicroRNA-107 inhibits tumor growth and metastasis by targeting the BDNF-mediated PI3K/AKT pathway in human non-small lung cancer. Int J Oncol 49(4):1325–1333
Zhang J-G et al (2010) MicroRNA-21 (miR-21) represses tumor suppressor PTEN and promotes growth and invasion in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Clin Chim Acta 411(11–12):846–852
Edmonds MD et al (2016) MicroRNA-31 initiates lung tumorigenesis and promotes mutant KRAS-driven lung cancer. J Clin Investig 126(1):349–364
da Silva HB et al (2013) Dissecting major signaling pathways throughout the development of prostate cancer. Prostate Cancer 2013:1–23
Lee K-H et al (2009) MicroRNA-330 acts as tumor suppressor and induces apoptosis of prostate cancer cells through E2F1-mediated suppression of Akt phosphorylation. Oncogene 28(38):3360–3370
Ottley E, Gold E (2014) microRNA and non-canonical TGF-β signalling: Implications for prostate cancer therapy. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 92(1):49–60
Taheri M et al (2020) Expression profile of microRNAs in bladder cancer and their application as biomarkers. Biomed Pharmacother 131:110703
Ding Z-S et al (2019) MicroRNA-34a inhibits bladder cancer cell migration and invasion, and upregulates PTEN expression. Oncol Lett 18(5):5549–5554
Ashrafizadeh M et al (2020) PTEN: what we know of the function and regulation of this onco-suppressor factor in bladder cancer? Eur J Pharmacol 881:173226
Enokida H et al (2016) The role of microRNAs in bladder cancer. Investig Clin Urol 57(Suppl 1):S60–S76
Yao Y et al (2014) MiR-330-mediated regulation of SH3GL2 expression enhances malignant behaviors of glioblastoma stem cells by activating ERK and PI3K/AKT signaling pathways. PloS One 9(4):e95060
Kefas B et al (2008) microRNA-7 inhibits the epidermal growth factor receptor and the Akt pathway and is down-regulated in glioblastoma. Cancer Res 68(10):3566–3572
Chen G et al (2010) MicroRNA-181a sensitizes human malignant glioma U87MG cells to radiation by targeting Bcl-2. Oncol Rep 23(4):997–1003
He L et al (2019) Wnt/β-catenin signaling cascade: a promising target for glioma therapy. J Cell Physiol 234(3):2217–2228
Vahabi M et al (2019) miR-96-5p targets PTEN expression affecting radio-chemosensitivity of HNSCC cells. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 38(1):1–16
Li T et al (2019) Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR/microRNA-206 sponge regulates STC2 and further influences cell biological functions in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Cell Prolif 52(5):e12651
Moradi N et al (2020) Emerging role of miR-372 and miR-101a in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Clin Lab. https://doi.org/10.7754/Clin.Lab.2019.190734
Lin P-C et al (2013) Epigenetic repression of miR-31 disrupts androgen receptor homeostasis and contributes to prostate cancer progression. Cancer Res 73(3):1232–1244
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to express their gratitude to Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences (Tehran, Iran) for supporting this study.
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
BK: Data curation, writing—original draft preparation, reviewing and editing. ZZ: data curation, writing—original draft preparation, reviewing and editing. VK: writing-reviewing and editing. AP-S: data curation, writing—original draft preparation. SHG: writing-reviewing and editing. DB: conceptualization, writing-reviewing and editing, approved the published version.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
11033_2021_6739_MOESM1_ESM.jpg
Supplementary file1 Expression profile of miRNAs associated with the regulation of the PI3K/Akt pathway in different types of human cancers. Although some miRNAs seem to be uniquely identified in a specific malignancy, others are known to play a part in various cancers. Moreover, some miRNAs are up-regulated in a cancer while being down-regulated in another; which is indicative of a possible cancer-specific or target-specific roles of miRNAs. HM hematologic malignancies; BrC breast cancer; OC ovarian cancer; BC bladder cancer; EC endometrial cancer; GC gastric cancer; CRC colorectal cancer; PDAC pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma; PC prostate cancer; HCC hepatocellular carcinoma; NSCLS non-small cell lung cancer; HNSCC head and neck squamous carcinoma (JPG 5200 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kashani, B., Zandi, Z., Kaveh, V. et al. Small molecules with huge impacts: the role of miRNA-regulated PI3K pathway in human malignancies. Mol Biol Rep 48, 8045–8059 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-021-06739-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-021-06739-6