Abstract
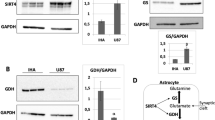
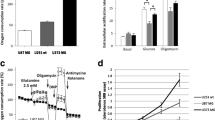
Glioblastoma multiform is a primary brain tumor derived from glial cells. The aim of this study is to investigate how glutamate metabolism is regulated by glutamate transporter 1 (GLT-1) degradation pathway in glioblastoma and glial cell lines. The protein expression levels of GLT-1, total ubiquitin, protein kinase C (PKC) proteins involved in the GLT-1 degradation pathway were measured by the western blot technique. Additionally, in glial and glioblastoma cells, the level of glutamate accumulated in the medium and the lysates was measured with the glutamate assay. GLT-1 protein expression was increased significantly in glioblastoma cells. The expression levels of the PKC protein and total ubiquitin were found to be decreased in glioblastoma cells although not significantly. The glutamate accumulated in the medium and lysates of glioblastoma cells is reduced compared to glial cells. Further research regarding excitotoxicity in glioblastoma focusing on GLT-1 degradation or activation pathway may create new opportunities of drug and treatment development.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ohgaki H, Kleihues P (2012) The definition of primary and secondary gliobalstoma. Clin Cancer Res 19(4):764–772
Sontheimer H (2008) A role for glutamate in growth and invasion of primary brain tumors. J Neurochem 105(2):287–295
Sheldon AL, Gonzalez MI, Krizman-Genda EN, Susarla BTS, Robinson MB (2008) Ubiquitination-mediated internalization and degradation of the astroglial glutamate transporter, GLT-1. Neurochem Int 53(6–8):296–308
Danbolt NC (2001) Glutamate uptake. Prog Neurobiol 65:1–105
Ezza HSA, Khadrawyb YA (2014) Glutamate excitotoxicity and neurodegeneration. J Mol Genet Med 8:4
Ye ZC, Sontheimer H (1999) Glioma cells release excitotoxic concentrations of glutamate. Cancer Res 59:4383–4391
Lin CLG, Kong Q, Cuny GD, Glicksman MA (2012) Glutamate transporter EAAT2: a new target for the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases. Future Med Chem 4(13):1689–1700
Karaca M, Frigerio F, Maechler P (2011) From pancreatic islets to central nervous system, the importance of glutamate dehydrogenase for the control of energy homeostasis. Neurochem Int 59:510–517
Rothstein JD, Martin L, Levey AI, Dykes-Hoberg M, Jin L, Wu D, Nash N, Kuncl RW (1994) Localization of neuronal and glial glutamate transporters. Neuron 13:713–725
Magi S, Piccirillo S, Amoroso S, Lariccia V (2019) Excitatory amino acid transporters (EAATs): glutamate transport and beyond. Int J Mol Sci 20(22):5674
Parkin GM, Udawela M, Gibbons A, Dean B (2018) Glutamate transporters, EAAT1 and EAAT2, are potentially important in the pathophysiology and treatment of schizophrenia and affective disorders. World J Psychiatry 8(2):51–63
Kanai Y, Smith CP, Hediger MA (1993) The elusive transporters with a high affinity for glutamate. Trends Neurosci 16:365–370
Zhang Y, He X, Meng X, Wu X, Tong H, Zhang X, Qu S (2017) Regulation of glutamate transporter trafficking by Nedd4-2 in a Parkinson’s disease model. Cell Death Dis 8:e2574
Susarla BTS, Robinson MB (2008) Internalization and degradation of the glutamate transporter GLT-1 in response to phorbol ester. Neurochem Int 52(4–5):709–722
Peterson AR, Binder DK (2019) Post-translational regulation of GLT-1 in neurological diseases and its potential as an effective therapeutic target. Front Mol Neurosci 12:164
Donmez G (2012) The neurobiology of sirtuins and their role in neurodegeneration. TIPS 33(9):494
Shih J, Liu L, Mason A, Higashimori H, Donmez G (2014) Loss of SIRT4 decreases GLT-1-dependent glutamate uptake and increases sensitivity to kainic acid. J Neurochem 131(5):573–581
Haigis MC, Mostoslavsky R, Haigis KM et al (2006) SIRT4 inhibits glutamate dehydrogenase and opposes the effects of calorie restriction in pancreatic beta cells. Cell 126(5):941–954
Dönmez-Yalçın G, Çolak M (2020) SIRT4 prevents excitotoxicity via modulating glutamate metabolism in glioma cells. Hum Exp Toxicol 39(7):938–947
Turcan S, Rohle D, Goenka A, Walsh LA, Fang F, Yilmaz E, Campos C, Fabius AW, Lu C, Ward PS, Thompson CB, Kaufman A, Guryanova O, Levine R, Heguy A, Viale A, Morris LG, Huse JT, Mellinghoff IK, Chan TA (2012) IDH1 mutation is sufficient to establish the glioma hypermethylator phenotype. Nature 483(7390):479–483
Petryszak R, Keays M, Tang AY et al (2016) Expression atlas update—an integrated database of gene and protein expression in humans, animals and plants. Nucleic Acids Res 44(D1):D746–D752
Jaworski S, Sawosz E, Grodzik M, Kutwin M, Wierzbicki M, Włodyga K, Jasik A, Michał Reichert M, Chwalibog A (2013) Comparison of tumour morphology and structure from U87 and U118 glioma cells cultured on chicken embryo chorioallantoic membrane. Bull Vet Inst Pulawy 57:593–598
Motaln H, Koren A, Gruden K, Ramšak Z, Schichor LTT (2015) Heterogeneous glioblastoma cell cross-talk promotes phenotype alterations and enhanced drug resistance. Oncotarget 6(38):40998–41017
Poteet E, Choudhury GR, Winters A, Li W, Ryou MG, Liu R, Tang L, Ghorpade A, Wen Y, Yuan F, Keir ST, Yan H, Bigner DD, Simpkins JW, Yang SH (2013) Reversing the warburg effect as a treatment for glioblastoma. JBC 288(13):9153–9164
Diao W, Tong X, Yang C, Zhang F, Bao C, Chen H, Liu L, Li M, Ye F, Fan Q, Wang J, Yang ZCO (2019) Behaviors of glioblastoma cells in in vitro microenvironments. Sci Rep 9:85
Tanaka K, Sasayama T, Nagashima H et al (2021) Glioma cells require one-carbon metabolism to survive glutamine starvation. Acta Neuropathol Commun 9:16
Dönmez-Yalçın G, Oktay E, Yalçın A, Diniz G, KahramanSolakoglu D, Senoglu M (2020) Glutamate transporter 1 expression in human glioblastomas. JBUON 25(4):2051–2058
Cluntun AA, Lukey MJ, Cerione RA, Locasale JW (2017) Glutamine metabolism in cancer: understanding the heterogeneity. Trends Cancer 3(3):169–180
Oraiopoulou ME, Tzamali E, Tzedakis G, Vakis A, Papamatheakis J, Sakkalis V (2017) In vitro/in silico study on the role of doubling time heterogeneity among primary glioblastoma cell lines. BioMed Res Int. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/8569328
Jane EP, Premkumar DR, Cavaleri JM, Sutera PA, Rajasekar T, Pollack IF (2016) Dinaciclib, a cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor promotes proteasomal degradation of Mcl-1 and enhances ABT-737–mediated cell death in malignant human glioma cell lines. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 356:354–365
Sonoda Y, Ozawa T, Hirose Y, Aldape KD, McMahon M, Berger MS, Pieper RO (2001) Formation of intracranial tumors by genetically modified human astrocytes defines four pathways critical in the development of human anaplastic astrocytoma. Cancer Res 61:4956–4960
Garg R, Benedetti LG, Abera MB, Wang HB, Abba M, Kazanietz MG (2014) Protein kinase C and cancer: what we know and what we do not. Oncogene 33(45):5225–5237
do Carmo A, Balça-Silva J, Matias D, Lopes MC (2013) PKC signaling in glioblastoma. Cancer Biol Ther 14(4):287–294
Marengo B, De Ciucis C, Ricciarelli R, Pronzato MA, Marinari UM, Domenicotti C (2011) Protein kinase C: an attractive target for cancer therapy. Cancers 3(1):531–567
Lewerenz J, Hewett SJ, Huang Y, Lambros M, Gout PW, Kalivas PW, Massie A, Smolders I, Methner A, Pergande M, Smith SB, Ganapathy V, Maher P (2013) The cystine/glutamate antiporter system xc− in health and disease: from molecular mechanisms to novel therapeutic opportunities. Antioxid Redox Signal 18(5):522–555
Lo M, Ling V, Wang Y et al (2008) The xc− cystine/glutamate antiporter: a mediator of pancreatic cancer growth with a role in drug resistance. Br J Cancer 99:464–472
Folch J, Busquets O, Ettcheto M et al (2018) Memantine for the treatment of dementia: a review on its current and future applications. J Alzheimers Dis 62(3):1223–1240
Bissaro M, Moro S (2019) Rethinking to riluzole mechanism of action: the molecular link among protein kinase CK1δ activity, TDP-43 phosphorylation, and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis pharmacological treatment. Neural Regen Res 14:2083–2085
Acknowledgements
This study was funded by Aydın Adnan Menderes University Scientific Research Projects Unit (Project number: TPF-19032).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dagdelen, D.N., Akkulak, A. & Donmez Yalcin, G. The investigation of glutamate transporter 1 (GLT-1) degradation pathway in glioblastoma cells. Mol Biol Rep 48, 3495–3502 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-021-06407-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-021-06407-9