Abstract
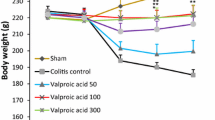
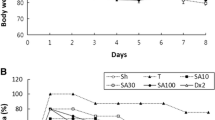
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is considered a chronic inflammatory gastrointestinal disease with treatment options which exhibit low efficacies and lead to considerable side effects. Hence, the challenge to alleviate IBD complications is remained to be resolved. The purpose of this study is evaluating anti-inflammatory impacts of gabapentin on acetic acid-induced colitis in rats. Colitis was induced by the instillation of 2 mL of 3% acetic acid solution into rat’s colons. Rats were randomly allocated into six groups including normal group, colitis control group, gabapentin-treated groups (25, 50, and 100 mg/kg; i.p.), and dexamethasone-treated group (1 mg/kg; i.p.). Based on the macroscopic assessment besides histological and biochemical findings [myeloperoxidase (MPO), pro-inflammatory cytokines], the efficacy of gabapentin was investigated. Gabapentin (50 and 100 mg/kg), and dexamethasone considerably reduced macroscopic and microscopic colonic lesions induced by acetic acid in rats in comparison with colitis control group. These results were confirmed by reduced levels of MPO activity and colonic concentrations of interleukin-6, interleukin-1 beta, and tumor necrosis factor-alpha, in inflamed colon tissue. Our data demonstrated that gabapentin exerts profitable impacts in experimental colitis that might be ascribed to its anti-inflammatory features and thus can be a potential therapeutic agent for IBD treatment.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and analyzed in the current study are available.
References
Zhang YZ, Li YY (2014) Inflammatory bowel disease: pathogenesis. World J Gastroenterol 20(1):91. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i1.91
Podolsky DK (1991) Inflammatory bowel disease. N Engl J Med 325(13):928–937
Braus NA, Elliott DE (2009) Advances in the pathogenesis and treatment of IBD. Clin Immunol 132(1):1–9
Cho JH, Abraham C (2007) Inflammatory bowel disease genetics: Nod2. Annu Rev Med 58:401–416
Warner W, Sanchez R, Dawoodian A, Li E, Momand J (2013) Pro-inflammatory cytokines in the pathogenesis of IBD. NIH Public Access 80(4):631–637
Baumgart DC, Sandborn WJ (2007) Inflammatory bowel disease: clinical aspects and established and evolving therapies. Lancet 369(9573):1641–1657
Ma X, Sun Q, Sun X, Chen D, Wei C, Yu X, Liu C, Li Y, Li J (2018) Activation of GABAA receptors in colon epithelium exacerbates acute colitis. Front Immunol 9:987
Zizzo MG, Serio R (2017) Therapeutic potential of the gabaergic system in ulcerative colitis: current status and perspectives. Dig Dis Sci 62(10):2780
Barragan A, Weidner JM, Jin Z, Korpi E, Birnir B (2015) GABA ergic signalling in the immune system. Acta Physiol 213(4):819–827
Aggarwal S, Ahuja V, Paul J (2017) Attenuated GABAergic signaling in intestinal epithelium contributes to pathogenesis of ulcerative colitis. Dig Dis Sci 62(10):2768–2779
Backonja M, Beydoun A, Edwards KR, Schwartz SL, Fonseca V, Hes M, LaMoreaux L, Garofalo E, Gabapentin Diabetic Neuropathy Study Group (1998) Gabapentin for the symptomatic treatment of painful neuropathy in patients with diabetes mellitus: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 280(21):1831–1836
Singh D, Kennedy DH (2003) The use of gabapentin for the treatment of postherpetic neuralgia. Clin Ther 25(3):852–889
Poellmann W, Feneberg W (2008) Current management of pain associated with multiple sclerosis. CNS Drugs 22(4):291–324
Gur A, Oktayoglu P (2009) Advances in diagnostic and treatment options in patients with fibromyalgia syndrome. Open Access Rheumatol 1:193
Jensen AA, Mosbacher J, Elg S, Lingenhoehl K, Lohmann T, Johansen TN, Abrahamsen B, Mattsson JP, Lehmann A, Bettler B, Bräuner-Osborne H (2002) The anticonvulsant gabapentin (Neurontin) does not act through γ-aminobutyric acid-B receptors. Mol Pharmacol 61(6):1377–1384
Maneuf YP, Luo ZD, Lee K (2006) alpha2delta and the mechanism of action of gabapentin in the treatment of pain. Semin Cell Dev Biol 17(5):565–570
Taylor CP, Gee NS, Su TZ, Kocsis JD, Welty DF, Brown JP, Dooley DJ, Boden P, Singh L (1998) A summary of mechanistic hypotheses of gabapentin pharmacology. Epilepsy Res 29(3):233–249
Cai K, Nanga RP, Lamprou L, Schinstine C, Elliott M, Hariharan H, Reddy R, Epperson CN (2012) The impact of gabapentin administration on brain GABA and glutamate concentrations: a 7T 1 H-MRS study. Neuropsychopharmacol Rep 37(13):2764–2771
Lee B-S, Jun I-G, Kim S-H, Park JY (2013) Intrathecal gabapentin increases interleukin-10 expression and inhibits pro-inflammatory cytokine in a rat model of neuropathic pain. J Korean Med Sci 28(2):308–314
Dias JM, de Brito TV, de Aguiar MD, da Silva Santos PW, Batista JA, do Nascimento Dias EG, Barros Fernandes H, Damasceno SR, Silva RO, Aragão KS, Souza MH (2014) Gabapentin, a synthetic analogue of gamma aminobutyric acid, reverses systemic acute inflammation and oxidative stress in mice. Inflammation 37(5):1826–1836
Yu J, Wang DS, Bonin RP, Penna A, Alavian-Ghavanini A, Zurek AA, Rauw G, Baker GB, Orser BA (2019) Gabapentin increases expression of δ subunit-containing GABA(A) receptors. EBioMedicine 42:203–213
Taylor CP (1997) Mechanisms of action of gabapentin. Revue Neurologique 153:S39-45
Abdel-Salam OM, Sleem AA (2009) Study of the analgesic, anti-inflammatory, and gastric effects of gabapentin. Drug Discov Ther 3(1):18–26
Badawy GM, Atallah MN, Sakr SA (2019) Effect of gabapentin on fetal rat brain and its amelioration by ginger. Heliyon 5(9):e02387
Motavallian A, Minaiyan M, Rabbani M, Andalib S, Mahzouni P (2013) Involvement of 5HT3 receptors in anti-inflammatory effects of tropisetron on experimental TNBS-induced colitis in rat. BioImpacts 3(4):169
Karmeli F, Cohen P, Rachmilewitz D (2000) Cyclo-oxygenase-2 inhibitors ameliorate the severity of experimental colitis in rats. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 12(2):223–231
Motavallian-Naeini A, Minaiyan M, Rabbani M (2012) Anti-inflammatory effect of ondansetron through 5-HT3 receptors on TNBS-induced colitis in rat. EXCLI J 11:30–44
Abràmoff MD, Magalhães PJ, Ram SJ (2004) Image processing with ImageJ. Biophotonics Int 11(7):36–42
Bradley P, Priebat DA, Christensen RD, Rothstein G (1982) Measurement of cutaneous inflammation: estimation of neutrophil content with an enzyme marker. J Invest Dermatol 78:206–209
Sanei MH, Hadizadeh F, Adibi P, Alavi SA (2014) Inflammatory cells’ role in acetic acid-induced colitis. Adv Biomed Res 3(1):193
Osafo N, Obiri DD, Danquah KO, Essel LB, Antwi AO (2019) Potential effects of xylopic acid on acetic acid-induced ulcerative colitis in rats. Turk J Gastroenterol 30(8):732
Owusu G, Obiri DD, Ainooson GK, Osafo N, Antwi AO, Duduyemi BM, Ansah C (2020) Acetic acid-induced ulcerative colitis in sprague dawley rats is suppressed by hydroethanolic extract of cordia vignei leaves through reduced serum levels of TNF-α and IL-6. Int J Chronic Dis. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/8785497
Yang XL, Guo TK, Wang YH, Huang YH, Liu X, Wang XX, Li W, Zhao X, Wang LP, Yan S, Wu D (2012) Ginsenoside Rd attenuates the inflammatory response via modulating p38 and JNK signaling pathways in rats with TNBS-induced relapsing colitis. Int Immunopharmacol 12(2):408–414
Satzinger G (1994) Antiepileptics from gamma-aminobutyric acid. Arzneimittelforschung 44(3):261–266
Rose M, Kam P (2002) Gabapentin: pharmacology and its use in pain management. Anaesthesia 57(5):451–462
Yamaguchi K, Kumakura S, Someya A, Iseki M, Inada E, Nagaoka I (2017) Anti-inflammatory actions of gabapentin and pregabalin on the substance P-induced mitogen-activated protein kinase activation in U373 MG human glioblastoma astrocytoma cells. Mol Med Rep 16(5):6109–6115
Stadnicki A, Pastucha E, Nowaczyk G, Mazurek U, Plewka D, Machnik G, Wilczok T, Colman RW (2005) Immunolocalization and expression of kinin B1R and B2R receptors in human inflammatory bowel disease. Am J Physiol Gastrointest 289(2):G361–G366
Ter Beek W, Biemond I, Muller E, Van den Berg M, Lamers C (2007) Substance P receptor expression in patients with inflammatory bowel disease: determination by three different techniques, ie, storage phosphor autoradiography, RT-PCR and immunohistochemistry. Neuropeptides 41(5):301–306
Hegazy SK, El-Bedewy MM (2010) Effect of probiotics on pro-inflammatory cytokines and NF-κB activation in ulcerative colitis. World J Gastroenterol 16(33):4145
Zhang Y, Cardell LO, Edvinsson L, Xu CB (2013) MAPK/NF-κB-dependent upregulation of kinin receptors mediates airway hyperreactivity: a new perspective for the treatment. Pharmacol Res 71:9–18
de Brito TV, Júnior GJ, da Cruz Júnior JS, Silva RO, da Silva Monteiro CE, Franco AX, Vasconcelos DF, de Oliveira JS, da Silva Costa DV, Carneiro TB, Duarte AS (2020) Gabapentin attenuates intestinal inflammation: role of PPAR-gamma receptor. Eur J Pharmacol 873:172974. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2020.172974
Esmaily H, Hosseini-Tabatabaei A, Rahimian R, Khorasani R, Baeeri M, Barazesh-Morgani A, Yasa N, Khademi Y, Abdollahi M (2009) On the benefits of silymarin in murine colitis by improving balance of destructive cytokines and reduction of toxic stress in the bowel cells. Open Life Sci 4(2):204–213
Elson CO, Sartor RB, Tennyson GS, Riddell RH (1995) Experimental models of inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology 109(4):1344–1367
Chang CY, Challa CK, Shah J, Eloy JD (2014) Gabapentin in acute postoperative pain management. Biomed Res Int. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/631756
Acknowledgements
The research was supported by the Vice Chancellery of Research of Guilan University of Medical Sciences, Rasht, Iran.
Funding
The research was financially supported by the Vice Chancellery of Research of Guilan University of Medical Sciences, Rasht, Iran (Contract Number: 546-41).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AM contributed to data collection, data analyses, and drafting the manuscript; SB and FAT contributed to data collection and drafting the manuscript; EZ and SD contributed to statistical analysis and drafting the manuscript; PK and MM contributed to data collection and drafting the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict interest.
Research involving human and animal rights
This study involved animals and was approved by Ethics Committee of Guilan University of Medical Sciences in accordance with National Institute of Health Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals (Ethics No: IR.GUMS.REC.1398.020).
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Motavallian, A., Bouzari, S., Zamani, E. et al. An investigation of the anti-inflammatory effects of gabapentin on acetic acid-induced colitis in rats. Mol Biol Rep 48, 3423–3430 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-021-06357-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-021-06357-2