Abstract
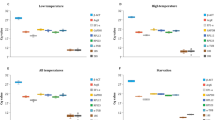
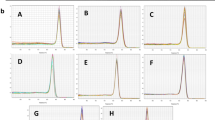
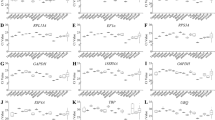
The relative quantification of gene expression is mainly realized through reverse transcription-quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR). However, the accuracy of this technique is deeply influenced by the expression stability of the reference genes used for data normalization. Therefore, the selection of suitable reference genes for a given experimental condition is a prerequisite in gene expression studies. Dichelops melacanthus (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae) is an important phloem sap-sucking insect pest of soybean, wheat, and maize in Brazil. Most of the genetic and molecular biology studies require gene expression analysis. Nevertheless, there are no reports about reference genes for RT-qPCR data normalization in D. melacanthus. In this study, we evaluated the expression stability of nine candidate reference genes (nadh, sdhb, gapdh, fau, ef1a, rpl9, ube4a, gus and rps23) in different developmental stages, body parts, sex, starvation-induced stress and dsRNA exposure by RefFinder software that integrates the statistical algorithms geNorm, NormFinder, BestKeeper, and ΔCt method. Our results showed that ef1a and nadh are the most stable reference genes for developmental stages, fau and rps23 for sex, ube4a and rps23 for body parts, rpl9 and fau for starvation stress, and nadh and sdhb for dsRNA exposure treatment. The reference genes selected in this work will be useful for further RT-qPCR analyses on D. melacanthus, facilitating future gene expression studies that can provide a better understanding of the developmental, physiological, and molecular processes of this important insect pest. Moreover, the knowledge gained from these studies can be helpful to design effective and sustainable pest management strategies.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The expression datasets generated during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request. All other data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article and its Supplementary Information file.
References
Silva JJ, Ventura MU, Silva FAC, Panizzi AR (2013) Population dynamics of Dichelops melacanthus (Dallas) (Heteroptera: Pentatomidae) on host plants. Neotrop Entomol 42:141–145. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13744-012-0104-2
Chocorosqui VR, Panizzi AR (2004) Impact of cultivation systems on Dichelops melacanthus (Dallas) (Heteroptera: Pentatomidae) population and damage and its chemical control on wheat. Neotrop Entomol 33:487–492. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1519-566X2004000400014
Depieri RA, Panizzi AR (2011) Duration of feeding and superficial and in-depth damage to soybean seed by selected species of stink bugs (Heteroptera: Pentatomidae). Neotrop Entomol 40:197–203. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1519-566X2011000200007
Panizzi AR, Lucini T (2019) Body position of the stink bug Dichelops melacanthus (Dallas) during feeding from stems of maize seedlings. Braz J Biol 79:304–310
Gomes EC, Hayashida R, de Freitas BA (2020) Dichelops melacanthus and Euschistus heros injury on maize: basis for re-evaluating stink bug thresholds for IPM decisions. Crop Prot 130:105050. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cropro.2019.105050
Ávila CJ, Duarte MM (2012) Eficiência de inseticidas, aplicados nas sementes e em pulverização, no controle do percevejo barriga-verde Dichelops melacanthus (Dallas) (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae), na cultura do milho. BioAssay 7:1–6
Farias LR, Schimmelpfeng PHC, Togawa RC et al (2015) Transcriptome-based identification of highly similar odorant-binding proteins among neotropical stink bugs and their egg parasitoid. PLoS ONE 10:e0132286. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0132286
Sparks ME, Shelby KS, Kuhar D, Gundersen-Rindal DE (2014) Transcriptome of the invasive brown marmorated stink bug, Halyomorpha halys (Stål) (Heteroptera: Pentatomidae). PLoS ONE 9:e111646. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0111646
Ioannidis P, Lu Y, Kumar N et al (2014) Rapid transcriptome sequencing of an invasive pest, the brown marmorated stink bug Halyomorpha halys. BMC Genomics 15:1–22. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-15-738
Lavore A, Perez-Gianmarco L, Esponda-Behrens N et al (2018) Nezara viridula (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae) transcriptomic analysis and neuropeptidomics. Sci Rep 8:17244. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-35386-4
Cagliari D, Dias NP, dos Santos EÁ et al (2020) First transcriptome of the Neotropical pest Euschistus heros (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae) with dissection of its siRNA machinery. Sci Rep 10:4856. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-60078-3
Lü J, Yang C, Zhang Y, Pan H (2018) Selection of reference genes for the normalization of RT-qPCR data in gene expression studies in insects: a systematic review. Front Physiol 9:1560. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2018.01560
Huggett J, Dheda K, Bustin S, Zumla A (2005) Real-time RT-PCR normalisation; strategies and considerations. Genes Immun 6:279–284. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gene.6364190
Bustin SA, Benes V, Garson JA et al (2009) The MIQE guidelines: minimum information for publication of quantitative real-time PCR experiments. Clin Chem 55:611–622. https://doi.org/10.1373/clinchem.2008.112797
Gutierrez L, Mauriat M, Guénin S et al (2008) The lack of a systematic validation of reference genes: a serious pitfall undervalued in reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) analysis in plants. Plant Biotechnol J 6:609–618. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-7652.2008.00346.x
Hruz T, Wyss M, Docquier M et al (2011) RefGenes: identification of reliable and condition specific reference genes for RT-qPCR data normalization. BMC Genomics 12:156. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-12-156
Chapman JR, Waldenström J (2015) With reference to reference genes: a systematic review of endogenous controls in gene expression studies. PLoS ONE 10:e0141853. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0141853
Bustin SA, Benes V, Garson J et al (2013) The need for transparency and good practices in the qPCR literature. Nat Methods 10:1063–1067. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.2697
Qu C, Wang R, Che W et al (2018) Selection and evaluation of reference genes for expression analysis using quantitative real-time PCR in the asian ladybird Harmonia axyridis (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae). PLoS ONE 13:e0192521. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0192521
Wang Z, Meng Q, Zhu X et al (2019) Evaluation and validation of reference genes for quantitative Real-Time PCR in Helopeltis theivora waterhouse (Hemiptera: Miridae). Sci Rep 9:13291. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-49479-1
Rogerio LA, Galdeano DM, Arena GD et al (2019) Reference genes for gene expression studies by RT-qPCR in Brevipalpus yothersi (Acari: Tenuipalpidae), the mite vector of citrus leprosis virus. Sci Rep 9:6536. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-42993-2
Bansal R, Mittapelly P, Chen Y et al (2016) Quantitative RT-PCR gene evaluation and RNA interference in the brown marmorated stink bug. PLoS ONE 11:e0152730. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0152730
Yang C, Preisser EL, Zhang H et al (2016) Selection of reference genes for RT-qPCR analysis in Coccinella septempunctata to assess un-intended effects of RNAi transgenic plants. Front Plant Sci 7:1672. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.01672
Basu S, Pereira AE, Pinheiro DH et al (2019) Evaluation of reference genes for real-time quantitative PCR analysis in southern corn rootworm, Diabrotica undecimpunctata howardi (Barber). Sci Rep 9:10703. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-47020-y
Yang C, Pan H, Liu Y, Zhou X (2014) Selection of reference genes for expression analysis using quantitative real-time PCR in the pea aphid, Acyrthosiphon pisum (Harris) (Hemiptera, Aphidiae). PLoS ONE 9:e110454. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0110454
Fu W, Xie W, Zhang Z et al (2013) Exploring valid reference genes for quantitative real-time PCR analysis in Plutella xylostella (Lepidoptera: Plutellidae). Int J Biol Sci 9:792–802. https://doi.org/10.7150/ijbs.5862
An XK, Hou ML, Di LY (2016) Reference gene selection and evaluation for gene expression studies using qRT-PCR in the white-backed planthopper, Sogatella furcifera (Hemiptera: Delphacidae). J Econ Entomol 109:879–886. https://doi.org/10.1093/jee/tov333
Untergasser A, Nijveen H, Rao X et al (2007) Primer3Plus, an enhanced web interface to Primer3. Nucleic Acids Res 35:71–74. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkm306
Xie F, Xiao P, Chen D et al (2012) miRDeepFinder: A miRNA analysis tool for deep sequencing of plant small RNAs. Plant Mol Biol 80:75–84. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-012-9885-2
Vandesompele J, De Preter K, Pattyn F et al (2002) Accurate normalization of real-time quantitative RT-PCR data by geometric averaging of multiple internal control genes. Genome Biol 3:34–41. https://doi.org/10.1186/gb-2002-3-7-research0034
Andersen CL, Jensen JL, Ørntoft TF (2004) Normalization of real-time quantitative reverse transcription-PCR data: a model-based variance estimation approach to identify genes suited for normalization, applied to bladder and colon cancer data sets. Cancer Res 64:5245–5250. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-0496
Pfaffl MW, Tichopad A, Prgomet C, Neuvians TP (2004) Determination of stable housekeeping genes, differentially regulated target genes and sample integrity: BestKeeper—Excel-based tool using pair-wise correlations. Biotechnol Lett 26:509–515. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:BILE.0000019559.84305.47
Silver N, Best S, Jiang J, Thein SL (2006) Selection of housekeeping genes for gene expression studies in human reticulocytes using real-time PCR. BMC Mol Biol 7:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2199-7-33
Li H-B, Dai C-G, Zhang C-R et al (2018) Screening potential reference genes for quantitative real-time PCR analysis in the oriental armyworm Mythimna separata. PLoS ONE 13:e0195096. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0195096
Gao XK, Zhang S, Luo JY et al (2017) Identification and validation of reference genes for gene expression analysis in Aphidius gifuensis (Hymenoptera: Aphidiidae). PLoS ONE 12:e0188477. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0188477
Kozera B, Rapacz M (2013) Reference genes in real-time PCR. J Appl Genet 54:391–406. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13353-013-0173-x
Shakeel M, Rodriguez A, Bin TU, Jin F (2018) Gene expression studies of reference genes for quantitative real-time PCR: an overview in insects. Biotechnol Lett 40:227–236. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-017-2465-4
Ying W (2008) NAD+/NADH and NADP+/NADPH in cellular functions and cell death: regulation and biological consequences. Antioxidants Redox Signal 10:179–206
Rizwan M, Al Rasheed H, Tarjan G (2018) Succinate dehydrogenase complex an updated review. Arch Pathol Lab Med 142:1564–1570. https://doi.org/10.5858/arpa.2017-0285-RS
Tristan C, Shahani N, Sedlak TW, Sawa A (2011) The diverse functions of GAPDH: Views from different subcellular compartments. Cell Signal 23:317–323
Baranes-Bachar K, Levy-Barda A, Oehler J et al (2018) The ubiquitin E3/E4 ligase UBE4A adjusts protein ubiquitylation and accumulation at sites of DNA damage, facilitating double-strand break repair. Mol Cell 69:866–878. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2018.02.002
Bar S, Prasad M, Datta R (2018) Neuromuscular degeneration and locomotor deficit in a Drosophila model of mucopolysaccharidosis VII is attenuated by treatment with resveratrol. Dis Model Mech 11:dmm036954. https://doi.org/10.1242/dmm.036954
Sasikumar AN, Goss Kinzy T (2012) The many roles of the eukaryotic elongation factor 1 complex. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA 3:543–555. https://doi.org/10.1002/wrna.1118
Henras AK, Plisson-Chastang C, O’Donohue MF et al (2015) An overview of pre-ribosomal RNA processing in eukaryotes. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA 6:225–242. https://doi.org/10.1002/wrna.1269
Bin S, Pu X, Shu B et al (2018) Selection of reference genes for optimal normalization of quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction results for Diaphorina citri adults. J Econ Entomol 112:355–363. https://doi.org/10.1093/jee/toy297
Sun M, Lu M-X, Tang X-T, Du Y-Z (2015) Exploring valid reference genes for quantitative real-time PCR analysis in Sesamia inferens (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). PLoS ONE 10:e0115979. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0115979
Yang X, Pan H, Yuan L, Zhou X (2018) Reference gene selection for RT-qPCR analysis in Harmonia axyridis, a global invasive lady beetle. Sci Rep 8:2689. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-20612-w
Pinheiro DH, Siegfried BD (2020) Selection of reference genes for normalization of RT-qPCR data in gene expression studies in Anthonomus eugenii cano (Coleoptera: Curculionidae). Sci Rep 10:5070. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-61739-z
Koramutla MK, Aminedi R, Bhattacharya R (2016) Comprehensive evaluation of candidate reference genes for qRT-PCR studies of gene expression in mustard aphid, Lipaphis erysimi (Kalt). Sci Rep 6:25883. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep25883
Ma KS, Li F, Liang PZ et al (2016) Identication and validation of reference genes for the normalization of gene expression data in qRT-PCR analysis in Aphis gossypii (Hemiptera: Aphididae). J Insect Sci 16:17. https://doi.org/10.1093/jisesa/iew003
Wan P-J, Tang Y-H, Yuan S-Y et al (2017) Reference genes for quantitative real-time PCR analysis in symbiont Entomomyces delphacidicola of Nilaparvata lugens (Stål). Sci Rep 7:42206. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep42206
Pan H, Yang X, Siegfried BD, Zhou X (2015) A comprehensive selection of reference genes for RT-qPCR analysis in a predatory lady beetle, Hippodamia convergens (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae). PLoS ONE 10:e0125868. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0125868
Yang C, Pan H, Noland JE et al (2016) Selection of reference genes for RT-qPCR analysis in a predatory biological control agent, Coleomegilla maculata (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae). Sci Rep 5:18201. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep18201
Gu L, Knipple DC (2013) Recent advances in RNA interference research in insects: implications for future insect pest management strategies. Crop Prot 45:36–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CROPRO.2012.10.004
Scott JG, Michel K, Bartholomay LC et al (2013) Towards the elements of successful insect RNAi. J Insect Physiol 59:1212–1221. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JINSPHYS.2013.08.014
Mogilicherla K, Howell JL, Palli SR (2018) Improving RNAi in the brown marmorated stink bug: identification of target genes and reference genes for RT-qPCR. Sci Rep 8:3720. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-22035-z
Barros Rodrigues T, Khajuria C, Wang H et al (2014) Validation of reference housekeeping genes for gene expression studies in western corn rootworm (Diabrotica virgifera virgifera). PLoS ONE 9:e109825. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0109825
Yuan M, Lu Y, Zhu X et al (2014) Selection and evaluation of potential reference genes for gene expression analysis in the brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens (Hemiptera: Delphacidae) using reverse-transcription quantitative PCR. PLoS ONE 9:e86503. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0086503
Shakeel M, Zhu X, Kang T et al (2015) Selection and evaluation of reference genes for quantitative gene expression studies in cotton bollworm, Helicoverpa armigera (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). J Asia Pac Entomol 18:123–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aspen.2015.01.001
Lu Y, Yuan M, Gao X et al (2013) Identification and validation of reference genes for gene expression analysis using quantitative PCR in Spodoptera litura (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). PLoS ONE 8:e68059. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0068059
Gao Z, Deng W, Zhu F (2019) Reference gene selection for quantitative gene expression analysis in black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens). PLoS ONE 14:e0221420. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0221420
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge the funding agencies Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de Minas Gerais (FAPEMIG), Banco Nacional do Desenvolvimento (BNDES) and Embrapa Milho e Sorgo.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
DHP, ROM, BB and NPC conceived and designed the experiments. DHP, ROM, NAL and ACR performed the experiments. DHP and NAL performed the statistical analysis. DHP interpreted the data and composed the manuscript. DHP, NAL, BB, AX and NPC reviewed the manuscript. All authors approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pinheiro, D.H., Moreira, R.O., Leite, N.A. et al. Suitable reference genes for RT-qPCR analysis in Dichelops melacanthus (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae). Mol Biol Rep 47, 4989–5000 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-020-05550-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-020-05550-z