Abstract
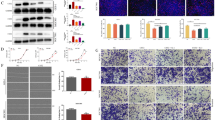
Tachykinins such as Substance P (SP) are a group of neuropeptides that are involved in cancer development. Neurokinin-1 receptor (NK-1R) is the main tachykinin receptor mediating the effects of SP, which is overexpressed in human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) and other malignant tissues. However, the effects of SP/NK-1R system on the migration of esophageal cancer cells and angiogenesis is not clear yet. This study seeks to obtain data to address these research gaps. In order to assess the effects of the FDA-approved aprepitant drug, a commercially available NK-1R antagonist, on the viability of KYSE-30 ESCC cells, resazurin assay was performed. The influence of SP/NK-1R system on the migration potential of these cells was examined using scratch assay. The effects of this system on the expression levels of metastatic factors were also examined by RT-PCR and western blot analyses. The half-maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) value for KYSE-30 cells treated with aprepitant found to be 29.88 μM. Treatment with SP significantly promoted KYSE-30 esophageal cancer cell migration, and aprepitant blocked this effect. In addition, SP significantly induced the expression of matrix metalloproteinase-2 (MMP-2), MMP-9, vascular endothelial growth factor-A (VEGF-A), and VEGF receptor1 (VEGFR1) in the cells, whereas aprepitant inhibited the up-regulation effects caused by SP. SP plays important roles in the development of human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by promoting cancer cell invasion and enhancing the expression of factors involved in cellular migration and angiogenesis, which can be blocked by the NK-1R antagonist, aprepitant.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pennathur A, Gibson MK, Jobe BA, Luketich JD (2013) Oesophageal carcinoma. Lancet (London, England) 381(9864):400–412
Thrumurthy SG, Chaudry MA, Thrumurthy SS, Mughal M (2019) Oesophageal cancer: risks, prevention, and diagnosis. BMJ. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.l4373
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A (2018) Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA: Cancer J Clin. 68(6):394–424
Demeester SR (2009) Epidemiology and biology of esophageal cancer. Gastroint Cancer Res 3(2 Suppl):S2–5
Enzinger PC, Mayer RJ (2003) Esophageal cancer. N Engl J Med 349(23):2241–2252
Gonzalez N, Moody TW, Igarashi H, Ito T, Jensen RT (2008) Bombesin-related peptides and their receptors: recent advances in their role in physiology and disease states. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes 15(1):58
Martinez-Fong D, Trédaniel J, Forgez P (2013) Neurotensin and its high affinity receptor 1 as a potential pharmacological target in cancer therapy. Front Endocrinol 3:184
Steinhoff MS, von Mentzer B, Geppetti P, Pothoulakis C, Bunnett NW (2014) Tachykinins and their receptors: contributions to physiological control and the mechanisms of disease. Physiol Rev 94(1):265–301
Stewart JM, Gera L, Chan DC, Bunn PA Jr, York EJ, Simkeviciene V et al (2002) Bradykinin-related compounds as new drugs for cancer and inflammation. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 80(4):275–280
Ghasemi A, Hashemy SI, Aghaei M, Panjehpour M (2017) RhoA/ROCK pathway mediates leptin-induced uPA expression to promote cell invasion in ovarian cancer cells. Cell Signal 32:104–114
Ghasemi A, Hashemy SI, Aghaei M, Panjehpour M (2018) Leptin induces matrix metalloproteinase 7 expression to promote ovarian cancer cell invasion by activating ERK and JNK pathways. J Cell Biochem 119(2):2333–2344
Ghasemi A, Saeidi J, Azimi-Nejad M, Hashemy SI (2019) Leptin-induced signaling pathways in cancer cell migration and invasion. Cell Oncol 42:243
Ghasemi A, Saeidi J, Mohtashami M, Hashemy SI (2019) Estrogen-independent role of ERα in ovarian cancer progression induced by leptin/Ob-Rb axis. Mol Cell Biochem 458(1–2):207–217
Lorestani S, Ghahremanloo A, Jangjoo A, Abedi M, Hashemy SI (2020) Evaluation of serum level of substance P and tissue distribution of NK-1 receptor in colorectal cancer. Mol Biol Rep
Hashemian P, Javid H, Tadayyon Tabrizi A, Hashemy SI (2020) The role of tachykinins in the initiation and progression of gastrointestinal cancers: a review. Int J Cancer Manag 13(5):e100717
Ebrahimi S, Javid H, Alaei A, Hashemy SI (2020) New insight into the role of substance P/Neurokinin-1 receptor system in breast cancer progression and its crosstalk with microRNAs. Clin Genet
Morgat C, Mishra AK, Varshney R, Allard M, Fernandez P, Hindié E (2014) Targeting neuropeptide receptors for cancer imaging and therapy: perspectives with bombesin, neurotensin, and neuropeptide-Y receptors. J Nucl Med 55(10):1650–1657
Liu L, Burcher E (2005) Tachykinin peptides and receptors: putting amphibians into perspective. Peptides 26(8):1369–1382
Bossaller C, Reither K, Hehlert-Friedrich C, Auch-Schwelk W, Graf K, Gräfe M et al (1992) In vivo measurement of endothelium-dependent vasodilation with substance P in man. Herz 17(5):284–290
De Felipe C, Herrero JF, O'Brien JA, Palmer JA, Doyle CA, Smith AJ et al (1998) Altered nociception, analgesia and aggression in mice lacking the receptor for substance P. Nature 392(6674):394–397
Ebner K, Singewald N (2006) The role of substance P in stress and anxiety responses. Amino Acids 31(3):251–272
Palma C, Manzini S (1998) Substance P induces secretion of immunomodulatory cytokines by human astrocytoma cells. J Neuroimmunol 81(1–2):127–137
Khorasani S, Boroumand N, Lavi Arab F, Hashemy SI (2020) The immunomodulatory effects of tachykinins and their receptors. J Cell Biochem 121:3031
Fadaee J, Khoshkhui M, Emadzadeh M, Hashemy SI, Hosseini RF, Azad FJ et al (2020) Evaluation of serum substance P level in chronic urticaria and correlation with disease severity. Iran J Allergy Asthma Immunol 19:18–26
Davoodian M, Boroumand N, Bahar MM, Jafarian AH, Asadi M, Hashemy SI (2019) Evaluation of serum level of substance P and tissue distribution of NK-1 receptor in breast cancer. Mol Biol Rep 46(1):1285–1293
Dong J, Feng F, Xu G, Zhang H, Hong L, Yang J (2015) Elevated SP/NK-1R in esophageal carcinoma promotes esophageal carcinoma cell proliferation and migration. Gene 560(2):205–210
Gharaee N, Pourali L, Jafarian AH, Hashemy SI (2018) Evaluation of serum level of substance P and tissue distribution of NK-1 receptor in endometrial cancer. Mol Biol Rep 45(6):2257–2262
Javid H, Mohammadi F, Zahiri E, Hashemy SI (2019) The emerging role of substance P/neurokinin-1 receptor signaling pathways in growth and development of tumor cells. J Physiol Biochem 75:415
Munoz M, Covenas R (2013) Involvement of substance P and the NK-1 receptor in cancer progression. Peptides 48:1–9
Wang F, Liu S, Liu J, Feng F, Guo Y, Zhang W et al (2019) SP promotes cell proliferation in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma through the NK1R/Hes1 axis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 514(4):1210–1216
Javid H, Asadi J, Zahedi Avval F, Afshari AR, Hashemy SI (2020) The role of substance P/neurokinin 1 receptor in the pathogenesis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma through constitutively active PI3K/Akt/NF-kappaB signal transduction pathways. Mol Biol Rep 47:2253
Jin Z, Olaru A, Yang J, Sato F, Cheng Y, Kan T et al (2007) Hypermethylation of tachykinin-1 is a potential biomarker in human esophageal cancer. Clin Cancer Res 13(21):6293–6300
Jiang WG, Sanders AJ, Katoh M, Ungefroren H, Gieseler F, Prince M et al (2015) Tissue invasion and metastasis: molecular, biological and clinical perspectives. Sem Cancer Biol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcancer.2015.03.008
Kai F, Drain AP, Weaver VM (2019) The extracellular matrix modulates the metastatic journey. Dev Cell 49(3):332–346
Shay G, Lynch CC, Fingleton B (2015) Moving targets: emerging roles for MMPs in cancer progression and metastasis. Matrix Biol 44–46:200–206
Juchniewicz A, Kowalczuk O, Milewski R, Laudanski W, Dziegielewski P, Kozlowski M et al (2017) MMP-10, MMP-7, TIMP-1 and TIMP-2 mRNA expression in esophageal cancer. Acta Biochim Pol 64(2):295–299
Wu F, Gao X, Wang Y, Lu F, Qiao X, Dong Z (2008) Pilot research of the expression of MMP-2 gene and survivin gene in primary esophageal cancer and subclinical microscopic tumor. Chin J Radiat Oncol 17(4):269–273
Amirchaghmaghi M, Hashemy SI, Alirezaei B, Keyhani FJ, Kargozar S, Vasigh S et al (2016) Evaluation of plasma isoprostane in patients with oral lichen planus. J Dent 17(1):21
Kast RE, Karpel-Massler G, Halatsch M-E (2014) CUSP9* treatment protocol for recurrent glioblastoma: aprepitant, artesunate, auranofin, captopril, celecoxib, disulfiram, itraconazole, ritonavir, sertraline augmenting continuous low dose temozolomide. Oncotarget 5(18):8052
Feistritzer C, Clausen J, Sturn DH, Djanani A, Gunsilius E, Wiedermann CJ et al (2003) Natural killer cell functions mediated by the neuropeptide substance P. Regul Pept 116(1–3):119–126
Song H, Yin W, Zeng Q, Jia H, Lin L, Liu X et al (2012) Hemokinins modulate endothelium function and promote angiogenesis through neurokinin-1 receptor. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 44(9):1410–1421
Schratzberger P, Reinisch N, Prodinger WM, Kähler CM, Sitte BA, Bellmann R et al (1997) Differential chemotactic activities of sensory neuropeptides for human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. J Immunol 158(8):3895–3901
Theoharides TC, Zhang B, Kempuraj D, Tagen M, Vasiadi M, Angelidou A et al (2010) IL-33 augments substance P-induced VEGF secretion from human mast cells and is increased in psoriatic skin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107(9):4448–4453
Borra RC, Lotufo MA, Gagioti SM, Barros Fde M, Andrade PM (2009) A simple method to measure cell viability in proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. Braz Oral Res 23(3):255–262
Ruff MR, Wahl SM, Pert CB (1985) Substance P receptor-mediated chemotaxis of human monocytes. Peptides 6:107–111
Meshki J, Douglas SD, Lai J-P, Schwartz L, Kilpatrick LE, Tuluc F (2009) Neurokinin 1 receptor mediates membrane blebbing in HEK293 cells through a Rho/Rho-associated coiled-coil kinase-dependent mechanism. J Biol Chem 284(14):9280–9289
Shay G, Lynch CC, Fingleton B (2015) Moving targets: emerging roles for MMPs in cancer progression and metastasis. Matrix Biol 44:200–206
Dalirsani Z, Pakfetrat A, Delavarian Z, Hashemy SI, Mostaan LV, Abdollahnejad M et al (2019) Comparison of matrix metalloproteinases 2 and 9 levels in saliva and serum of patients with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma and healthy subjects. Int J Cancer Manag 12(5):e90249
Kataoka M, Yamagata S, Takagi H, Thant A, Akiyama S, Iida K et al (1996) Matrix metalloproteinase 2 and 9 in esophageal cancer. Int J Oncol 8(4):773–779
Chen X, Chen G, Liu J, Yang J, Yu D, Lin D et al (2009) Genetic polymorphisms in STK15 and MMP-2 associated susceptibility to esophageal cancer in Mongolian population. Zhonghua yu fang yi xue za zhi [Chin J Prev Med] 43(7):559–564
Yu C, Zhou Y, Miao X, Xiong P, Tan W, Lin D (2004) Functional haplotypes in the promoter of matrix metalloproteinase-2 predict risk of the occurrence and metastasis of esophageal cancer. Can Res 64(20):7622–7628
Xie L, Moroi Y, Tsuji G, Liu M, Hayashida S, Takahara M et al (2010) CD10-bearing fibroblast inhibits matrigel invasive potency of interleukin-1alpha-producing squamous cell carcinoma by diminishing substance P levels in the tumor microenvironment. Cancer Sci 101(12):2570–2578
Li X, Ma G, Ma Q, Li W, Liu J, Han L et al (2013) Neurotransmitter substance P mediates pancreatic cancer perineural invasion via NK-1R in cancer cells. Mol Cancer Res 11(3):294–302
Keck PJ, Hauser SD, Krivi G, Sanzo K, Warren T, Feder J et al (1989) Vascular permeability factor, an endothelial cell mitogen related to PDGF. Science (New York, NY) 246(4935):1309–1312
Acknowledgements
This study was financially supported by the Research Council, Mashhad University of Medical Sciences, Mashhad, Iran. This manuscript is written based on the MSc thesis of Fariba Mohammadi.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare there was not any conflict of interest.
Research involving human participants and/or animals
Human participants and/or animals were not involved in this research, and informed consent was not required.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mohammadi, F., Javid, H., Afshari, A.R. et al. Substance P accelerates the progression of human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma via MMP-2, MMP-9, VEGF-A, and VEGFR1 overexpression. Mol Biol Rep 47, 4263–4272 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-020-05532-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-020-05532-1