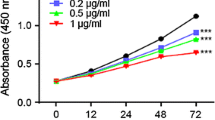
Abstract
Diclofenac is a preferential cyclooxygenase 2 inhibitor (COX-2) and member of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Inflammation is one of the main reason of poor prognosis of colon cancer cases; thereby NSAIDs are potential therapeutic agents in colon cancer therapy. In this study, our aim to understand the potential molecular targets of diclofenac, which may propose new therapeutic targets in HCT 116 (wt p53) and SW480 (mutant p53R273H) colon cancer cells. For this purpose, we identified different response against diclofenac treatment through expression profiles of PI3K/Akt/MAPK signaling axis. Our hypothesis was diclofenac-mediated apoptosis is associated with inhibition of PI3K/Akt/MAPK signaling axis. We found that sub-cytotoxic concentration of diclofenac (400 µM) promoted further apoptosis in HCT 116 cells compared to SW480 colon cancer cells. Diclofenac triggered dephosphorylation of PTEN, PDK, Akt, which led to inhibition of PI3K/Akt survival axis in HCT 116 colon cancer cells. However, diclofenac showed lesser effect in SW480 colon cancer cells. In addition, diclofenac further activated p44/42, p38 and SAPK/JNK in HCT 116 cells compared to SW480 cells.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adamson DJ, Frew D, Tatoud R, Wolf CR, Palmer CN (2002) Diclofenac antagonizes peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma signaling. Mol Pharmacol 61(1):7–12
Ahmed AY, Gad AM, El-Raouf OMA (2017) Curcumin ameliorates diclofenac sodium-induced nephrotoxicity in male albino rats. J Biochem Mol Toxicol 31(10):e21951
Al-Nimer MS, Hameed HG, Mahmood MM (2015) Antiproliferative effects of aspirin and diclofenac against the growth of cancer and fibroblast cells: in vitro comparative study. Saudi Pharm J 23(5):483–486
Arico S, Pattingre S, Bauvy C, Gane P, Barbat A, Codogno P, Ogier-Denis E (2002) Celecoxib induces apoptosis by inhibiting 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase-1 activity in the human colon cancer HT-29 cell line. J Biol Chem 277(31):27613–27621
Assandri A, Canali S, Giachetti C (1993) Local tolerability and pharmacokinetic profile of a new transdermal delivery system, diclofenac hydroxyethylpyrrolidine plaster. Drugs Exp Clin Res 19(3):89–95
Awara WM, El-Sisi AE, El-Sayad ME, Goda AE (2004) The potential role of cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors in the treatment of experimentally-induced mammary tumour: does celecoxib enhance the anti-tumour activity of doxorubicin? Pharmacol Res 50(5):487–498
Baba Y, Nosho K, Shima K, Hayashi M, Meyerhardt JA, Chan AT, Giovannucci E, Fuchs CS, Ogino S (2011) Phosphorylated AKT expression is associated with PIK3CA mutation, low stage, and favorable outcome in 717 colorectal cancers. Cancer 117(7):1399–1408
Boldt S, Weidle UH, Kolch W (2002) The role of MAPK pathways in the action of chemotherapeutic drugs. Carcinogenesis 23(11):1831–1838
Bowen KA, Doan HQ, Zhou BP, Wang Q, Zhou Y, Rychahou PG, Evers BM (2009) PTEN loss induces epithelial–mesenchymal transition in human colon cancer cells. Anticancer Res 29(11):4439–4449
Chakraborti AK, Garg SK, Kumar R, Motiwala HF, Jadhavar PS (2010) Progress in COX-2 inhibitors: a journey so far. Curr Med Chem 17(15):1563–1593
Chen JC, Chen Y, Su YH, Tseng SH (2007) Celecoxib increased expression of 14-3-3sigma and induced apoptosis of glioma cells. Anticancer Res 27(4B):2547–2554
Cho M, Gwak J, Park S, Won J, Kim DE, Yea SS, Cha IJ, Kim TK, Shin JG, Oh S (2005) Diclofenac attenuates Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in colon cancer cells by activation of NF-kappaB. FEBS Lett 579(20):4213–4218
Cronin-Fenton DP, Heide-Jorgensen U, Ahern TP, Lash TL, Christiansen P, Ejlertsen B, Sorensen HT (2016) Low-dose aspirin, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, selective COX-2 inhibitors and breast cancer recurrence. Epidemiology 27(4):586–593
Din FV, Valanciute A, Houde VP, Zibrova D, Green KA, Sakamoto K, Alessi DR, Dunlop MG (2012) Aspirin inhibits mTOR signaling, activates AMP-activated protein kinase, and induces autophagy in colorectal cancer cells. Gastroenterology 142(7):1504–1515 e1503
Ding JH, Yuan LY, Huang RB, Chen GA (2014) Aspirin inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis of multiple myeloma cells through regulation of Bcl-2 and Bax and suppression of VEGF. Eur J Haematol 93(4):329–339
Fang WL, Huang KH, Lan YT, Lin CH, Chang SC, Chen MH, Chao Y, Lin WC, Lo SS, Li AF, Wu CW, Chiou SH, Shyr YM (2016) Mutations in PI3K/AKT pathway genes and amplifications of PIK3CA are associated with patterns of recurrence in gastric cancers. Oncotarget 7(5):6201–6220
Fecker LF, Stockfleth E, Nindl I, Ulrich C, Forschner T, Eberle J (2007) The role of apoptosis in therapy and prophylaxis of epithelial tumours by nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Br J Dermatol 156(Suppl 3):25–33
Gomez-Lechon MJ, Ponsoda X, O’Connor E, Donato T, Castell JV, Jover R (2003) Diclofenac induces apoptosis in hepatocytes by alteration of mitochondrial function and generation of ROS. Biochem Pharmacol 66(11):2155–2167
Gomez-Lechon MJ, Ponsoda X, O’Connor E, Donato T, Jover R, Castell JV (2003) Diclofenac induces apoptosis in hepatocytes. Toxicol In Vitro 17(5–6):675–680
Gupta RA, Dubois RN (2001) Colorectal cancer prevention and treatment by inhibition of cyclooxygenase-2. Nat Rev Cancer 1(1):11–21
Han JA, Kim JI, Ongusaha PP, Hwang DH, Ballou LR, Mahale A, Aaronson SA, Lee SW (2002) P53-mediated induction of Cox-2 counteracts p53- or genotoxic stress-induced apoptosis. EMBO J 21(21):5635–5644
Hixson LJ, Alberts DS, Krutzsch M, Einsphar J, Brendel K, Gross PH, Paranka NS, Baier M, Emerson S, Pamukcu R et al (1994) Antiproliferative effect of nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs against human colon cancer cells. Cancer Epidemiol Biomark Prev 3(5):433–438
Jain S, Ghanghas P, Rana C, Sanyal SN (2017) Role of GSK-3beta in regulation of canonical Wnt/beta-catenin signaling and PI3-K/Akt oncogenic pathway in colon cancer. Cancer Invest 35(7):473–483
Malinowsky K, Nitsche U, Janssen KP, Bader FG, Spath C, Drecoll E, Keller G, Hofler H, Slotta-Huspenina J, Becker KF (2014) Activation of the PI3K/AKT pathway correlates with prognosis in stage II colon cancer. Br J Cancer 110(8):2081–2089
Meyer FA, Yaron I, Mashiah V, Yaron M (1989) Effect of diclofenac on prostaglandin E and hyaluronic acid production by human synovial fibroblasts stimulated with interleukin-1. Br J Clin Pharmacol 28(2):193–196
Minotti V, Patoia L, Roila F, Basurto C, Tonato M, Pasqualucci V, Maresca V, Del Favero A (1989) Double-blind evaluation of analgesic efficacy of orally administered diclofenac, nefopam, and acetylsalicylic acid (ASA) plus codeine in chronic cancer pain. Pain 36(2):177–183
Rana C, Piplani H, Vaish V, Nehru B, Sanyal SN (2015) Downregulation of PI3-K/Akt/PTEN pathway and activation of mitochondrial intrinsic apoptosis by Diclofenac and Curcumin in colon cancer. Mol Cell Biochem 402(1–2):225–241
Rao CV, Reddy BS (2004) NSAIDs and chemoprevention. Curr Cancer Drug Targets 4(1):29–42
Rogue A, Spire C, Brun M, Claude N, Guillouzo A (2010) Gene expression changes induced by PPAR gamma agonists in animal and human liver. PPAR Res. https://doi.org/10.1155/2010/325183
Roseweir AK, Powell AG, Bennett L, Van Wyk HC, Park J, McMillan DC, Horgan PG, Edwards J (2016) Relationship between tumour PTEN/Akt/COX-2 expression, inflammatory response and survival in patients with colorectal cancer. Oncotarget 7(43):70601–70612
Ruder EH, Laiyemo AO, Graubard BI, Hollenbeck AR, Schatzkin A, Cross AJ (2011) Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and colorectal cancer risk in a large, prospective cohort. Am J Gastroenterol 106(7):1340–1350
Singh R, Cadeddu RP, Frobel J, Wilk CM, Bruns I, Zerbini LF, Prenzel T, Hartwig S, Brunnert D, Schroeder T, Lehr S, Haas R, Czibere A (2011) The non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs Sulindac sulfide and Diclofenac induce apoptosis and differentiation in human acute myeloid leukemia cells through an AP-1 dependent pathway. Apoptosis 16(9):889–901
St-Germain ME, Gagnon V, Mathieu I, Parent S, Asselin E (2004) Akt regulates COX-2 mRNA and protein expression in mutated-PTEN human endometrial cancer cells. Int J Oncol 24(5):1311–1324
Subongkot S, Frame D, Leslie W, Drajer D (2003) Selective cyclooxygenase-2 inhibition: a target in cancer prevention and treatment. Pharmacotherapy 23(1):9–28
Trisciuoglio D, Uranchimeg B, Cardellina JH, Meragelman TL, Matsunaga S, Fusetani N, Del Bufalo D, Shoemaker RH, Melillo G (2008) Induction of apoptosis in human cancer cells by candidaspongiolide, a novel sponge polyketide. J Natl Cancer Inst 100(17):1233–1246
Wakeman C, Keenan J, Eteuati J, Hollington P, Eglinton T, Frizelle F (2017) Chemoprevention of colorectal neoplasia. ANZ J Surg 87(12):E228–E232
Warner TD, Mitchell JA (2002) Cyclooxygenase-3 (COX-3): filling in the gaps toward a COX continuum? Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99(21):13371–13373
Yamazaki T, Muramoto M, Oe T, Morikawa N, Okitsu O, Nagashima T, Nishimura S, Katayama Y, Kita Y (2006) Diclofenac, a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug, suppresses apoptosis induced by endoplasmic reticulum stresses by inhibiting caspase signaling. Neuropharmacology 50(5):558–567
Yefi R, Ponce DP, Niechi I, Silva E, Cabello P, Rodriguez DA, Marcelain K, Armisen R, Quest AF, Tapia JC (2011) Protein kinase CK2 promotes cancer cell viability via up-regulation of cyclooxygenase-2 expression and enhanced prostaglandin E2 production. J Cell Biochem 112(11):3167–3175
Yin N, Qi X, Tsai S, Lu Y, Basir Z, Oshima K, Thomas JP, Myers CR, Stoner G, Chen G (2016) p38gamma MAPK is required for inflammation-associated colon tumorigenesis. Oncogene 35(8):1039–1048
Zhang, D., M. Mi, F. Jiang, Y. Sun, Y. Li, L. Yang, L. Fan, Q. Li, J. Meng, Z. Yue, L. Liu and Q. Mei (2015). Apple polysaccharide reduces NF-Kb mediated colitis-associated colon carcinogenesis. Nutr Cancer 67(1): 177–190.
Acknowledgements
We are thankful for Gizem Damla Yalçın and Şeyma Yıldırım for their valuable technical support. This project is partly supported by TUBITAK-BIDEB 2209 Program and Istanbul Kultur University, Scientific Projects Support Center.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
We declare that this article does not involve any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors. The research has been performed on commercially available cell lines. All authors read and confirmed the final version of the manuscript.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arisan, E.D., Ergül, Z., Bozdağ, G. et al. Diclofenac induced apoptosis via altering PI3K/Akt/MAPK signaling axis in HCT 116 more efficiently compared to SW480 colon cancer cells. Mol Biol Rep 45, 2175–2184 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-018-4378-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-018-4378-2