Abstract
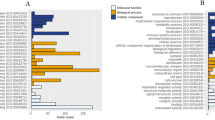
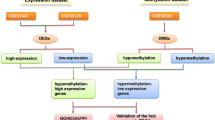
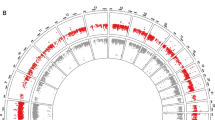
To screen the aberrant methylation genes in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) for Kazakh nationality in Xinjiang, and the aberrant DNA methylation genes pattern provides a clue for deeply study on ESCC mechanism. Illumina Human Methylation 450 K chip was used to screen the genome-wide methylation on six cancer tissues and six adjacent normal tissues of ESCC in Kazakh people. Meanwhile, mRNA library was constructed by scanning the RNA expression on two cancer tissues and two adjacent normal tissues by Hiseq2000. After association study between the methylation profile and expression profile, aberrant DNA methylated genes were screened out and were uploaded to the GoMiner and the KEGG, completing the bioinformatic analysis. There were 227 hypermethylation genes and 6 hypomethylated genes in cancer tissue, mRNA expression varied from 0.0312 to 8,192 in cancer tissues compared with 0.0312–1,024 in adjacent normal tissues. The correlation study indicated that there were 10 loci in 10 down-regulated genes of hypermethylated in negative correlation group. Additionally, there were 11 loci in 10 up-regulated genes in negative group. Using GoMiner to do GO analysis on aberrant DNA methylation genes, RAPGEFL1, TP53AIP1, KIAA1522, DUOXA2 were identified not involved in any biological processes. ALDH1L1 participated in folinic acid catabolism and CAPN1 positively regulated the cell proliferation. And ALDH1L1 involved in one carbon metabolism and CAPN1 participate in the apoptosis process by applying pathway analysis. The aberrant DNA methylation profiles were established and provided a clue for deeply study on ESCC of Kazakh nationality.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhao FJ, Yun MY, Zhang Y, Xu Y (2009) The research progress of esophageal cancer in Xinjiang Kazakh. J Cent Univ Natl (Nat Sci Ed) 18(3):85–90
Chen XC, LJ Pang, Li F (2007) The research progress of esophageal cancer in Xinjiang Kazakh. J Nongken Med 28(5):384–387
Liu L, Zhang JP, Li H, Jiang XF, Chen Y, Li XM, Chen HM, Zhao XX, Li HW (2010) Construction of cdc42 gene and promoter CpG island of Hazak’s esophageal cancer in Eukaryotic Expression Vector. J Xinjiang Med Univ 33(007):735–738
Yu WW, Wang LD, Qi YJ, Du F, Wang ZQ, Gao SS, He X, Fan ZM (2006) Detection of p16 gene deletion and methylation in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma tissue. J Zhengzhou Univ (Med Sci) 41(002):282–284
Lee EJ, Lee BB, Kim JW, Shim YM, Hoseok I, Han J, Cho EY, Park J, Kim DH (2006) Aberrant methylation of fragile histidine triad gene is associated with poor prognosis in early stage esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Eur J Cancer 42(7):972–980
Cong DG, Wang SF (2008) Hypermethylation of promoter region of RAS association domain family gene1A in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and significance thereof. Natl Med J China 87(41):2932–2934
Ge H (2007) The Association between the polymorphisms, the promoter hypermethylation of the CpG island of the p73, PTEN and the carcinogenesis and development of ESCC. Hebei Medical University, Shijiazhuang
Vasavi M, Ponnala S, Gujjari K, Boddu P, Bharatula RS, Prasad R, Ahuja YR, Hasan Q (2006) DNA methylation in esophageal diseases including cancer: special reference to hmlh1 gene promoter status. Tumori 92(2):155–162
Adorj NP, Distler J, Lipscher E, Model F, Müller J, Pelet C, Braun A, Florl AR, Gütig D, Grabs G, Howe A, Kursar M, Lesche R, Leu E, Lewin A, Maier S, Müller V, Otto T, Scholz C, Schulz WA, Seifert HH, Schwope I, Ziebarth H, Berlin K, Piepenbrock C, Olek A (2002) Tumour class prediction and discovery by microarray-based DNA methylation analysis. Nucleic Acids Res 30(5):e21–e27
Lv H (2007) A study on methylation difference between human large cell lung cancer cell lines with different metastatic potential. Sichuan University, Chengdu
Ibanezde C, Dulaimi E, Hoffman AM, Al-Saleem T, Uzzo RG, Cairns P (2006) Identification of novel target genes by an epigenetic reactivation screen of renal cancer. Cancer Res 66(10):5021–5028
Dannenberg L, Edeberg H (2006) Epigenetics of gene expression in human hepatoma cells: expression profiling the response to inhibition of DNA methylation and histone deacetylation. BMC Genomics 7(1):181–187
Oleink NV, Krupenko NI, Krupenko SA (2011) Epigenetic silencing of aldh1l1, a metabolic regulator of cellular proliferation, in cancers. Genes Cancer 2(2):130–139
Hwang PH, Lian L, Zacras AI (2012) Alcohol intake and folate antagonism via cyp2e1 and aldh1: effects on oral carcinogenesis. Med Hypotheses 78(2):197–202
Salehin D, Fromberg I, Haugk C, Dohmen B, Georg T, Bohle RM, Bauerschlag D, Thill M, Friedrich M (2011) Immunhistochemical analysis for expression of calpain 1, calpain 2 and calpastatin in ovarian cancer. Eur J Gynaecol Oncol 32(6):628
Zhang P, Wang SK, Sun GJ (2011) Research progress in association of food and nutrition with esophageal cancer. Tumor 31(8):768–771
Tang HL, Su Q (2008) Association analyses between Ca2+ signal and apoptosis. J Nanhua Univ (Med Sci) 34(5):663–666
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Y., Yin, D., Li, L. et al. Screening aberrant methylation profile in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma for Kazakhs in Xinjiang area of China. Mol Biol Rep 42, 457–464 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-014-3788-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-014-3788-z