Abstract
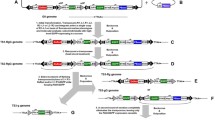
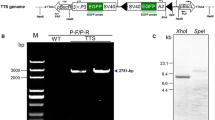
The Streptomyces bacteriophage, φC31, uses a site-specific integrase enzyme to perform efficient recombination. The recombination system uses specific sequences to integrate exogenous DNA from the phage into a host. The sequences are known as the attP site in the phage and the attB site in the host. The system can be used as a genetic manipulation tool. In this study it has been applied to the transformation of cultured BmN cells and the construction of transgenic Bombyx mori individuals. A plasmid, pSK-attB/Pie1-EGFP/Zeo-PASV40, containing a cassette designed to express a egfp-zeocin fusion gene, was co-transfected into cultured BmN cells with a helper plasmid, pSK-Pie1/NLS-Int/NSL. Expression of the egfp-zeocin fusion gene was driven by an ie-1 promoter, downstream of a φC31 attB site. The helper plasmid encoded the φC31 integrase enzyme, which was flanked by two nuclear localization signals. Expression of the egfp-zeocin fusion gene could be observed in transformed cells. The two plasmids were also transferred into silkworm eggs to obtain transgenic silkworms. Successful integration of the fusion gene was indicated by the detection of green fluorescence, which was emitted by the silkworms. Nucleotide sequence analysis demonstrated that the attB site had been cut, to allow recombination between the attB and endogenous pseudo attP sites in the cultured silkworm cells and silkworm individuals.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wimmer EA (2003) Innovations: applications of insect transgenesis. Nat Rev Genet 4:225–232
Shinohara ET, Kaminski JM, Segal DJ, Pelczar P, Kolhe R, Ryan T, Coates CJ, Fraser MJ, Handler AM, Yanagimachi R, Moisyadi S (2007) Active integration: new strategies for transgenesis. Transgenic Res 16:333–339
Venken KJ, Bellen HJ (2007) Transgenesis upgrades for Drosophila melanogaster. Development 134:3571–3584
Vázquez-Manrique RP, Legg JC, Olofsson B, Ly S, Baylis HA (2010) Improved gene targeting in C. elegans using counter-selection and Flp-mediated marker excision. Genomics 95:37–46
Groth AC, Fish M, Nusse R, Calos MP (2004) Construction of transgenic Drosophila by using the site-specific integrase from phage φC31. Genetics 166:1775–1782
Austin S, Ziese M, Sternberg N (1981) A novel role of site-specific recombination in maintenance of bacterial replicons. Cell 25:729–736
Broach JR, Guarascio VR, Jayaram M (1982) Recombination within the yeast plasmid 2mu circle is site-specific. Cell 29:227–234
Kuhstoss S, Rao RN (1991) Analysis of the integration function of the streptomycete bacteriophage φC31. J Mol Biol 222:897–908
Golic KG, Lindquist S (1989) The FLP recombinase of yeast catalyzes site-specific recombination in the Drosophila genome. Cell 59:499–509
Sauer B, McDermott J (2004) DNA recombination with a heterospecific Cre homolog identified from comparison of the pac-c1 regions of P1-related phages. Nucleic Acids Res 32:6086–6095
Thyagarajan B, Olivares EC, Hollis RP, Ginsburg DS, Calos MP (2001) Site-specific genomic integration in mammalian cells mediated by phage φC31 integrase. Mol Cell Biol 21:3926–3934
Chalberg TW, Portlock JL, Olivares EC, Thyagarajan B, Kirby PJ, Hillman RT, Hoelters J, Calos MP (2006) Integration specificity of phage phiC31 integrase in the human genome. J Mol Biol 357:28–48
Waldner C, Rempel O, Schütte F, Yanik M, Solomentsew N, Ryffel GU (2011) Double conditional human embryonic kidney cell line based on FLP and φC31 mediated transgene integration. BMC Res Notes 4:420
Tomita S, Kanda T, Imanishi S, Tamura T (1999) Yeast FLP recombinase-mediated excision in cultured cells and embryos of the silkworm, Bombyx mori (Lepidoptera: Bombycidae). Appl Entomol Zool 34:371–377
Nakayama G, Kawaguchi Y, Koga K, Kusakabe T (2006) Site-specific gene integration in cultured silkworm cells mediated by φC31 integrase. Mol Genet Genomics 275(1):1–8
Duan J, Xu H, Ma S, Guo H, Wang F, Zhao P, Xia Q (2012) Cre-mediated targeted gene activation in the middle silk glands of transgenic silkworms (Bombyx mori). Transgenic Res 22:607–619
Long DP, Zhao AC, Chen XJ, Zhang Y, Lu WJ, Guo Q, Handler AM, Xiang ZH (2012) FLP recombinase-mediated site-specific recombination in silkworm, Bombyx mori. PLoS One 7:e40150
Zhou W, Wang C, Liu B, Cao G, Xue R, Shen W, Gong C (2007) The elementary transgene research of silkworm cells mediated by transposon piggyBac. Acta Sericologica Sin 33:30–35 (in Chinese)
Zhou W, Cao J, Ye A, Cao G, Xue R, Gong C (2008) Cloning and activity analysis of fibroin heavy-chain gene promoter of silkworm, Bombyx mori. Acta Sericologica Sin 34:72–77 (in Chinese)
Xu Y, Gong CL, Xue RY, Shen WD, Cao GL (2006) Expression of a synthesized gene for recombinant human insulin-like growth factor I in E. coli and Bombyx mori. J Changshu Inst Technol 20:72–77 (in Chinese)
Strauss WM (2001) Preparation of genomic DNA from mammalian tissue. In: Ausubel FM, Brent R, Kingston RE, Moore DD, Seidman JG, Smith JA, Struhl K (eds) Curr protocols in molecular biology, Chap 2:Unit2.2. Wiley, New York
Cao GL, Xue RY, He Z, Zheng XJ, Sheng WD, Gong CL (2006) Research on hGM-CSF transgenetic silkworm with piggyBac transposon. Acta Sericologica Sin 32:324–327 (in Chinese)
Zhao Y, Li X, Cao G, Xue R, Gong C (2009) Expression of hIGF-I in the silk glands of transgenic silkworms and in transformed silkworm cells. Sci China C Life Sci 52:1131–1139
Pfeifer TA, Hegedus DD, Grigliatti TA, Theilmann DA (1997) Baculovirus immediate-early promoter-mediated expression of the zeocinTM resistance gene for use as a dominant selectable marker in Dipteran and Lepidopteran insect cell lines. Gene 188:183–190
Gatignol A, Durand H, Tiraby G (1988) Bleomycin resistance conferred by a drug-binding protein. FEBS Lett 230:171–175
Xia Q, Zhou Z, Lu C, Cheng D, Dai F, Li B, Zhao P, Zha X, Cheng T, Chai C, Pan G, Xu J, Liu C, Lin Y, Qian J, Hou Y, Wu Z, Li G, Pan M, Li C, Shen Y, Lan X, Yuan L, Li T, Xu H, Yang G, Wan Y, Zhu Y, Yu M, Shen W, Wu D, Xiang Z, Yu J, Wang J, Li R, Shi J, Li H, Li G, Su J, Wang X, Li G, Zhang Z, Wu Q, Li J, Zhang Q, Wei N, Xu J, Sun H, Dong L, Liu D, Zhao S, Zhao X, Meng Q, Lan F, Huang X, Li Y, Fang L, Li C, Li D, Sun Y, Zhang Z, Yang Z, Huang Y, Xi Y, Qi Q, He D, Huang H, Zhang X, Wang Z, Li W, Cao Y, Yu Y, Yu H, Li J, Ye J, Chen H, Zhou Y, Liu B, Wang J, Ye J, Ji H, Li S, Ni P, Zhang J, Zhang Y, Zheng H, Mao B, Wang W, Ye C, Li S, Wang J, Wong GK, Yang H (2004) A draft sequence for the genome of the domesticated silkworm (Bombyx mori). Science 306:1937–1940
Mita K, Kasahara M, Sasaki S, Nagayasu Y, Yamada T, Kanamori H, Namiki N, Kitagawa M, Yamashita H, Yasukochi Y, Kadono-Okuda K, Yamamoto K, Ajimura M, Ravikumar G, Shimomura M, Nagamura Y, Shin-I T, Abe H, Shimada T, Morishita S, Sasaki T (2004) The genome sequence of silkworm, Bombyx mori. DNA Res 11:27–35
The International Silkworm Genome Consortium (2008) The genome of a lepidopteran model insect, the silkworm Bombyx mori. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 38:1036–1045
Xia Q, Guo Y, Zhang Z, Li D, Xuan Z, Li Z, Dai F, Li Y, Cheng D, Li R, Cheng T, Jiang T, Becquet C, Xu X, Liu C, Zha X, Fan W, Lin Y, Shen Y, Jiang L, Jensen J, Hellmann I, Tang S, Zhao P, Xu H, Yu C, Zhang G, Li J, Cao J, Liu S, He N, Zhou Y, Liu H, Zhao J, Ye C, Du Z, Pan G, Zhao A, Shao H, Zeng W, Wu P, Li C, Pan M, Li J, Yin X, Li D, Wang J, Zheng H, Wang W, Zhang X, Li S, Yang H, Lu C, Nielsen R, Zhou Z, Wang J, Xiang Z, Wang J (2009) Complete resequencing of 40 genomes reveals domestication events and genes in silkworm (Bombyx). Science 326:433–436
Tamura T, Thibert C, Royer C, Kanda T, Abraham E, Kamba M, Komoto N, Thomas JL, Mauchamp B, Chavancy G, Shirk P, Fraser M, Prudhomme JC, Couble P (2000) Germline transformation of the silkworm Bombyx mori L. using a piggyBac transposon derived vector. Nat Biotechnol 18:81–84
Fraser MJ, Ciszczon T, Elick T, Bauser C (1996) Precise excision of TTAA-specific lepidopteran transposons piggyBac (IFP2) and tagalong (TFP3) from the baculovirus genome in cell lines from two species of Lepidoptera. Insect Mol Biol 5:141–151
Li Y, Cao G, Chen H, Jia H, Xue R, Gong C (2010) Expression of the hGM-CSF in the silk glands of germline of gene-targeted silkworm. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 391:1427–1431
Oberstein A, Pare A, Kaplan L, Small S (2005) Site-specific transgenesis by Cre-mediated recombination in Drosophila. Nat Methods 2:583–585
Calos MP (2006) The φC31 integrase system for gene therapy. Curr Gene Ther 6:633–645
Chavez CL, Calos MP (2011) Therapeutic applications of the φC31 integrase system. Curr Gene Ther 11:375–381
Bischof J, Maeda RK, Hediger M, Karch F, Basler K (2007) An optimized transgenesis system for Drosophila using germ-line-specific φC31 integrases. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:3312–3317
Fish MP, Groth AC, Calos MP, Nusse R (2007) Creating transgenic Drosophila by microinjecting the site-specific φC31 integrase mRNA, a transgene-containing donor plasmid. Nat Protoc 2:2325–2331
Yonemura N, Tamura T, Uchino K, Kobayashi I, Tatematsu K, Iizuka T, Sezutsu H, Muthulakshmi M, Nagaraju J, Kusakabe T (2012) PhiC31 integrase-mediated cassette exchange in silkworm embryos. Mol Genet Genomics 287(9):731–739
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge the financial support of the National Basic Research Program of China (973 Program, 2012CB114600), the Specialized Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education (20113201130002), the Key Fostering Project for Application Research of Soochow University (Q3134991) and a project funded by the Priority Academic Program of Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Yajuan Yin and Guangli Cao have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yin, Y., Cao, G., Xue, R. et al. Construction of transformed, cultured silkworm cells and transgenic silkworm using the site-specific integrase system from phage φC31. Mol Biol Rep 41, 6449–6456 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-014-3527-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-014-3527-5