Abstract
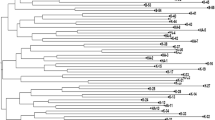
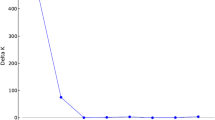
In order to understand the population structure and genetic diversity among a set of 82 rice genotypes collected from different parts of the Asian countries including India were characterized using 39 microsatellite loci. The Population structure analysis suggested that the optimum number of subpopulations was four (K = 4) among the rice genotypes, whereas phylogenetic analysis grouped them into three populations. The results obtained from phylogenetic and STRUCTURE analysis proved to be very powerful for the differentiation of rice genotypes based on their place of origin. The genetic diversity analysis using 39 SSR loci yielded 183 scorable alleles, out of which 182 alleles were observed to be polymorphic with an average of 4.8 alleles per locus. The Polymorphism Information Content (PIC) values for all the polymorphic primers across 82 rice genotypes varied from 0.02 to 0.77, with an average of 0.50. Gene diversity (He) was found to be in the range of 0.02 (RM484) to 0.80 (OSR13) with an average value of 0.55, while heterozygosity (Ho) was observed with an average of 0.07, ranging from 0.01 (RM334) to 0.31 (RM316). The present study resulted in identification of seven highly polymorphic SSR loci viz., OSR13, RM152, RM144, RM536, RM489, RM259 and RM271 based on the parameters like PIC value (≥0.70), gene diversity (≥0.71), and polymorphic alleles (≥6). These seven polymorphic primers can effectively be used in further molecular breeding programs and QTL mapping studies of rice since they exhibited very high polymorphism over other loci. SSR analysis resulted in a more definitive separation of clustering of genotypes indicating a higher level of efficiency of SSR markers for the accurate determination of relationships between accessions.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
ICAR (2011-12) Annual report. Vivekananda Parvatiya Krishi Anusanthan Sansthan, Almora
Juliano BO (1985) Rice chemistry and technology. American Association of Cereal Chemists, Minnesota, p 757
Chaudhary RC, Tran DV (2001) Speciality rices of the world-a prologue. In: Chaudhary RC, Tran DV (eds) Speciality rices of the world: breeding, production and marketing. FAO, Rome; Oxford and IBH Publishing, New Delhi, pp 3–14
Zhang MW, Guo BJ, Chi JW, Wei ZC, Xu ZH, Zhang Y, Zhang RF (2005) Antioxidants and their correlation with total flavonoid and anthocyanin contents in different black rice varieties. Sci Agric Sin 38(7):1324–1331
Cooke RJ (1995) Variety identification of crop plants. In: Skerrit JH, Appels R (eds) New diagnostics in crop science. Biotechnology in Agriculture no. 13. CAB International, Wallingford, pp 33–63
Sun CQ, Wang XK, Li ZC, Yoshimura A, Iwata N (2001) Comparison of the genetic diversity of common wild rice (Oryza rufipogon Griff.) and cultivated rice (O. sativa L.) using RFLP markers. Theor Appl Genet 102(1):157–162
Williams JGK, Kubelik AR, Livak KJ, Rafalski JA, Tingey SV (1991) DNA polymorphisms amplified by arbitrary primers are useful as genetic markers. Nucl Acids Res 18:6531–6535
Gao LZ, Zhang CH, Chang LP, Jia JZ, Qiu ZE, Dong YS (2005) Microsatellite diversity of Oryza sativa with emphasis on indica-japonica divergence. Genet Res 85:1–14
Aggarwal RK, Brar DS, Nandi S, Huang N, Khush GS (1999) Phylogenetic relationships among Oryza species revealed by AFLP markers. Theor Appl Genet 98:1320–1328
Smith JSC, Chin ECL, Shu H, Smith OS, Well SJ, Senior ML, Mitchell SE, Kresovich S, Ziegle J (1997) An evaluation of the utility of SSR loci as molecular markers in maize (Zea mays L.): comparisons with data from RFLPs and pedigree. Theor Appl Genet 95:163–173
Heckenberger M, Bohn M, Ziegle JS, Joe LK, Hauser JD, Hutton M, Melchinger AE (2002) Variation of DNA fingerprints among accessions within maize inbred lines and implications for identification of essentially derived varieties. Mol Breed 10:181–191
Sharon EM, Kresovich S, Jester CA, Hernandez CJ, Szewc-McFadden AK (1997) Application of multiplex PCR and fluorescence-based, semi-automated allele sizing technology for genotyping plant genetic resources. Crop Sci 37:617–624
Depeige A, Goubely C, Lenoir A, Cocherel S, Picard G, Raynal M, Grellet F, Delseny M (1995) Identification of the most represented repeated motifs in Arabidopsis thaliana microsatellite loci. Theor Appl Genet 91:160–168
Roder MS, Plaschke J, Konig SU, Borner A, Sorrels ME, Tanksley SD, Ganal MW (1995) Abundance, variability and chromosomal location of microsatellites in wheat. Mol Gen Genet 246:327–333
Senior ML, Heun M (1993) Mapping maize microsatellites and polymerase chain reaction confirmation of the targeted repeats using a CT primer. Genome 36:884–889
Olufowote JO, Xu Y, Chen X, Park WD, Beachel HM, Dilday RH, Goto M, McCouch SR (1997) Comparative evaluation of within-cultivar variation of rice (Oryza sativa L.) using microsatellite and RFLP markers. Genome 40:370–378
Pritchard JK, Stephens M, Donnelly P (2000) Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data. Genetics 155:945–959
Falush D, Stephens M, Pritchard JK (2003) Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data: linked loci and correlated allele frequencies. Genetics 164:1567–1587
Herrera TG, Duque DP, Almeida IP, Núñez GT, Pieters AJ, Martinez CP, Tohme JM (2008) Assessment of genetic diversity in Venezuelan rice cultivars using simple sequence repeats markers. Electron J Biotechnol 11(5)
Agrawal PK, Katiyar AK (2008) Validation of chickpea-STMS markers and DNA fingerprinting in lentil (Lens culinaris subsp. culinaris) cultivars of India. Indian J Genet 68(2):149–156
Rohlf FJ (1997) NTSYS-pc. Numerical taxonomy and multivariate analysis system, version 2.0. State University of New York, New York
Jaccard P (1908) Nouvelles recherches sur la distribuition florale. Bull Soc Vaud Nat 44:223–270
Gawel NJ, Jarret RL (1991) A modified CTAB DNA extraction procedure for Musa and Ipomoea plant. Mol Biol Rep 9:262–266
Tang S, Zhang Y, Zeng L, Luo L, Zhong Y, Geng Y (2010) Assessment of genetic diversity and relationships of upland rice accessions from southwest China using microsatellite markers. Plant Biosyst 144(1):85–92
Narvel JM, Fehr WR, Chu WC, Grant D, Shoemaker RC (2000) Simple sequence repeat diversity among soybean plant introductions and elite genotypes. Crop Sci 40:1452–1458
Liu K, Muse SV (2005) Powermarker: integrated analysis environment for genetic marker data. Bioinformatics 21(9):2128–2129
Siwach P, Jain S, Saini N, Chowdhury VK, Jain RK (2004) Allelic diversity among Basmati and non-Basmati long-grain indica rice varieties using microsatellite markers. J Plant Biochem Biotechnol 13:25–32
Aranzana MJ, Abbasi E, Howard W, Arus P (2010) Genetic variation, population structure and linkage disequilibrium in peach commercial varieties. BMC Genet 11:69
Pritchard JK, Wen W (2003) Documentation for the structure software, version 2. Department of Human Genetics, University of Chicago, Chicago. http://pritch.bsd.uchicago.edu/software
Michael JT, Nicholas RP, Joko PKR, Trijatmiko, Tiur SS, McCouch SusanR (2009) Genetic diversity of isolated populations of Indonesian landraces of Rice (Oryza sativa L.) collected in east Kalimantan on the Island of Borneo. Rice 2:80–92
Xinghua W, Yuan X, Yu H, Wang Y, Qun Xu, Tang S (2009) Temporal changes in SSR allelic diversity of major rice cultivars in China. J Genet Genom 36:363–370
Chakravarthi B, Rambabu N (2006) SSR marker based DNA fingerprinting and diversity study in rice (Oryza sativa. L). Afr J Biotechol 5(9):684–688
Ravi M, Geethanjalil S, Sameeyafarheen F, Maheswaran M (2003) Molecular marker based genetic diversity analysis in rice (Oryza sativa L.) using RAPD and SSR markers. Euphytica 133:243–252
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Babu, B.K., Meena, V., Agarwal, V. et al. Population structure and genetic diversity analysis of Indian and exotic rice (Oryza sativa L.) accessions using SSR markers. Mol Biol Rep 41, 4329–4339 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-014-3304-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-014-3304-5