Abstract
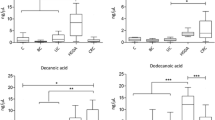
High levels of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) are involved in tumour escape mechanisms. The aim of this study is the evaluation of l-kynurenine of plasma as marker of diagnostic and prognostic in patients with colorectal cancer. The study included 78 patients with colorectal cancer, of whom 15 % were in stage I/II, 30 % in stage III, and 55 % in stage IV, and was compared with a control group of 70 healthy subjects. The receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis showed an area under the curve of 0.917, with a specificity of 100 % and with a sensitivity to detect cancer of the colon of 85.2 %, taking 1.83 μM as a cut-off point. The overall survival analysis also indicated that patients with low levels of l-kynurenine in plasma increased survival rate after 45 months of follow-up (P = 0.032). These results show that the plasma levels of l-kynurenine could be a good biomarker to differentiate individuals with colorectal cancer from healthy individuals.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Karsa LV, Lignini TA, Patnick J, Lambert R, Sauvaget C (2010) The dimensions of the CRC problem. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol 24:381–396
Duffy MJ, van Dalen A, Haglund C, Hansson L, Klapdor R, Lamerz R, Nilsson O, Sturgeon C, Topolcan O (2003) Clinical utility of biochemical markers in colorectal cancer: European group on tumor markers (EGTM) guidelines. Eur J Cancer 39:718–727
Carpelan-Holmstrom M, Louhimo J, Stenman UA, Alfthan H, Jarvinen H, Haglund C (2004) Estimating the probability of cancer with several tumor markers in patients with colorectal disease. Oncology 66:296–302
Basbug M, Arikanoglu Z, Bulbuller N, Cetinkaya Z, Aygen E, Akbulut S, Satici O (2011) Prognostic value of preoperative CEA and CA 19-9 levels in patients with colorectal cancer. Hepatogastroenterology 58:400–405
Tjalsma H (2010) Identification of biomarkers for colorectal cancer through proteomics-based approaches. Expert Rev Proteomics 7:879–895
Babel I, Barderas R, Díaz-Uriarte R, Martínez-Torrecuadrada JL, Sánchez-Carbayo M, Casal JI (2009) Identification of tumor-associated autoantigens for the diagnosis of colorectal cancer in serum using high density protein microarrays. Mol Cell Proteomics 8:2382–2395
Silk AW, Schoen RE, Potter DM, Finn OJ (2009) Humoral immune response to abnormal MUC1 in subjects with colorectal adenoma and cancer. Mol Immunol 47:52–56
Ran Y, Hu H, Zhou Z, Yu L, Sun L, Pan J, Liu J, Yang Z (2008) Profiling tumor-associated autoantibodies for the detection of colon cancer. Clin Cancer Res 14:2696–2700
Duffy MJ, van Dalen A, Haglund C, Hansson L, Holinski-Feder E, Klapdor R, Lamerz R, Peltomaki P, Sturgeon C, Topolcan O (2007) Tumor markers in colorectal cancer: European group on tumor markers (EGTM) guidelines for clinical use. Eur J Cancer 43:1348–1360
Ninomiya S, Hara T, Tsurumi H, Hoshi M, Kanemura N, Goto N, Kasahara S, Shimizu M, Ito H, Saito K, Hirose Y, Yamada T, Takahashi T, Seishima M, Takami T, Moriwaki H (2011) Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase in tumor tissue indicates prognosis in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma treated with R-CHOP. Ann Hematol 90:409–416
Nonaka H, Saga Y, Fujiwara H, Akimoto H, Yamada A, Kagawa S, Takei Y, Machida S, Takikawa O, Suzuki M (2011) Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase promotes peritoneal dissemination of ovarian cancer through inhibition of natural killer cell function and angiogenesis promotion. Int J Oncol 38:113–120
Inaba T, Ino K, Kajiyama H, Shibata K, Yamamoto E, Kondo S, Umezu T, Nawa A, Takikawa O, Kikkawa F (2010) Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase expression predicts impaired survival of invasive cervical cancer patients treated with radical hysterectomy. Gynecol Oncol 117:423–428
Ino K, Yamamoto E, Shibata K, Kajiyama H, Yoshida N, Terauchi M, Nawa A, Nagasaka T, Takikawa O, Kikkawa F (2008) Inverse correlation between tumoral indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase expression and tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in endometrial cancer: its association with disease progression and survival. Clin Cancer Res 14:2310–2317
Polak ME, Borthwick NJ, Gabriel FG, Johnson P, Higgins B, Hurren J, McCormick D, Jager MJ, Cree IA (2007) Mechanisms of local immunosuppression in cutaneous melanoma. Br J Cancer 960:1879–1887
Brandacher G, Perathoner A, Ladurner R, Schneeberger S, Obrist P, Winkler C, Werner ER, Werner-Felmayer G, Weiss HG, Göbel G, Margreiter R, Königsrainer A, Fuchs D, Amberger A (2006) Prognostic value of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase expression in colorectal cancer: effect on tumor-infiltrating T cells. Clin Cancer Res 12:1144–1151
Uyttenhove C, Pilotte L, Théate I, Stroobant V, Colau D, Parmentier N, Boon T, Van den Eynde BJ (2003) Evidence for a tumoral immune resistance mechanism based on tryptophan degradation by indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase. Nat Med 9:1269–1274
Munn DH, Mellor AL (2007) Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase and tumor-induced tolerance. J Clin Invest 117:1147–1154
Gao YF, Peng RQ, Li J, Ding Y, Zhang X, Wu XJ, Pan ZZ, Wan DS, Zeng YX, Zhang XS (2009) The paradoxical patterns of expression of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase in colon cancer. J Transl Med 7:71
Cavia-Saiz M, Muñiz P, De Santiago R, Herreros-Villanueva M, Garcia-Giron C, Lopéz AS, Coma-del Corral MJ (2012) Changes in the levels of thioredoxin and indoleamine-2-3 dioxygenase activity in plasma of patients with colorectal cancer treated with chemotherapy. Biochem Cell Biol 90:173–178
Alegre E, López AS, González A (2005) Tryptophan metabolites interfere with the Ehrlich reaction used for the measurement of kynurenine. Anal Biochem 339:188–189
Singer K, Gottfried E, Kreutz M, Mackensen A (2011) Suppression of T-cell responses by tumor metabolites. Cancer Immunol Immunother 60:425–431
Laimer K, Troester B, Kloss F, Schafer G, Obrist P, Perathoner A, Laimer J, Brandacher G, Rasse M, Margreiter R, Amberger A (2011) Expression and prognostic impact of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase in oral squamous cell carcinomas. Oral Oncol 47:352–357
Pan K, Wang H, Chen MS, Zhang HK, Weng DS, Zhou J, Huang W, Li JJ, Song HF, Xia JC (2008) Expression and prognosis role of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 134:1247–1253
Johnson BA, Baban B, Mellor AL (2009) Targeting the immunoregulatory indoleamine 2,3 dioxygenase pathway in immunotherapy. Immunotherapy 1:645–661
Ciorba MA (2013) Indoleamine 2,3 dioxygenase in intestinal disease. Curr Opin Gastroenterol 29:146–152
Mead R, Duku M, Bhandari P, Cree IA (2011) Circulating tumour markers can define patients with normal colons, benign polyps, and cancers. Br J Cancer 105:239–245
Zhu CB, Wang CX, Zhang X, Zhang J, Li W (2011) Serum sHLA-G levels: a useful indicator in distinguishing colorectal cancer from benign colorectal diseases. Int J Cancer 128:617–622
Yoshikawa T, Hara T, Tsurumi H, Goto N, Hoshi M, Kitagawa J, Kanemura N, Kasahara S, Ito H, Takemura M, Saito K, Seishima M, Takami T, Moriwaki H (2010) Serum concentration of l-kynurenine predicts the clinical outcome of patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma treated with R-CHOP. Eur J Haematol 84:304–309
Seval Kul (2010) The use of survival analysis for clinical pathways. Int J Care Pathw 14:23–26
Acknowledgments
Authors wish to thank to the Banca Civica for their financial support through of the Research Projects of 2010. This work was supported by a grant FIS CA07/00292 from Instituto de Salud Carlos III.
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interest to report.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cavia-Saiz, M., Muñiz Rodríguez, P., Llorente Ayala, B. et al. The role of plasma IDO activity as a diagnostic marker of patients with colorectal cancer. Mol Biol Rep 41, 2275–2279 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-014-3080-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-014-3080-2