Abstract
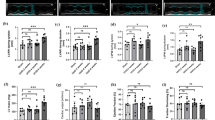
The present study was designed to evaluate whether microRNA-146a and its adapter proteins (TRAF6 and IRAK1) are involved in the pathogenesis of diabetes-induced kidney damage. Male Sprague–Dawley rats were divided into control and diabetic groups (n = 6 in each). Diabetes was induced by injection of streptozotocin (55 mg/kg; i.p.) in 12 h fasted rats. Diabetic kidney damage was diagnosed by renal hypertrophy, thickened glomerular basement membrane, widened filtration slits, mesangial expansion, as well as by elevated levels of blood urea and creatinine in diabetic rats 2 months after induction of diabetes. While the expression of NF-κB mRNA and miR-146a were increased in diabetic kidney compared to the sham controls (p < 0.01 for both comparisons), the mRNA levels of IRAK1 and TRAF6 did not statistically reduce. The NF-κB activity and the concentrations of TNF-α, IL-6 and IL-1β in the kidney of diabetic rats were higher than the kidney of controls (p < 0.05 for TNF-α and NF-κB; p < 0.01 for IL-6 and IL-1β). Our results indicate that the upregulation of miR-146a was not accompanied by downregulation of inflammatory mediators in diabetic kidney. It is possible that a defect in the miR-146a-mediated negative loop provides a situation for sustained activation of NF-κB and its targets to promote cells toward abnormalities.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Luis-Rodríguez D, Martínez-Castelao A, Górriz JL, De-Álvaro F, Navarro-González JF (2012) Pathophysiological role and therapeutic implications of inflammation in diabetic nephropathy. World J Diabetes 15:7–18. doi:10.4239/wjd.v3.i1.7
Zhou X, Wang B, Zhu L, Hao S (2012) A novel improved therapy strategy for diabetic nephropathy: targeting AGEs. Organogenesis 1:18–21. doi:10.4161/org.19332
Palsamy P, Subramanian S (2010) Ameliorative potential of resveratrol on proinflammatory cytokines, hyperglycemia mediated oxidative stress, and pancreatic β-cell dysfunction in streptozotocin-nicotinamide-induced diabetic rats. J Cell Physiol 224:423–432. doi:10.1002/jcp.22138
Palsamy P, Subramanian S (2011) Resveratrol protects diabetic kidney by attenuating hyperglycemia-mediated oxidative stress and renal inflammatory cytokines via Nrf2-Keap1 signaling. Biochim Biophys Acta 1812:719–731. doi:10.1016/j.bbadis.2011.03.008
Sanz AB, Sanchez-Niño MD, Ramos AM, Moreno JA, Santamaria B, Ruiz-Ortega M, Egido J, Ortiz A (2010) NF-kappaB in renal inflammation. J Am Soc Nephrol 21:1254–1262. doi:10.1681/ASN.2010020218
Patel S, Santani D (2009) Role of NF-kappa B in the pathogenesis of diabetes and its associated complications. Pharmacol Rep 61:595–603
Ma X, Becker Buscaglia LE, Barker JR, Li Y (2011) MicroRNAs in NF-kappaB signaling. J Mol Cell Biol 3:159–166. doi:10.1093/jmcb/mjr007
Rusca N, Monticelli S (2011) MiR-146a in immunity and disease. Mol Biol Int 2011:437301. doi:10.4061/2011/437301
Balasubramanyam M, Aravind S, Gokulakrishnan K, Prabu P, Sathishkumar C, Ranjani H, Mohan V (2011) Impaired miR-146a expression links subclinical inflammation and insulin resistance in type 2 diabetes. Mol Cell Biochem 351:197–205. doi:10.1007/s11010-011-0727-3
Feng B, Chen S, McArthur K, Wu Y, Sen S, Ding Q, Feldman RD, Chakrabarti S (2011) miR-146a-Mediated extracellular matrix protein production in chronic diabetes complications. Diabetes 60:2975–2984. doi:10.2337/db11-0478
Wang G, Kwan BC, Lai FM, Chow KM, Li PK, Szeto CC (2011) Elevated levels of miR-146a and miR-155 in kidney biopsy and urine from patients with IgA nephropathy. Dis Markers 1:171–179. doi:10.3233/DMA-2011-0766
Ichii O, Otsuka S, Sasaki N, Namiki Y, Hashimoto Y, Kon Y (2012) Altered expression of microRNA miR-146a correlates with the development of chronic renal inflammation. Kidney Int 81:280–292. doi:10.1038/ki.2011.345
Yar AS, Menevse S, Alp E, Helvacioglu F, Take G (2010) The effects of resveratrol on cyclooxygenase-1 and cyclooxygenase-2 mRNA and protein levels in diabetic rat kidneys. Mol Biol Rep 37:2323–2331. doi:10.1007/s11033-009-9737-6
Arora MK, Reddy K, Balakumar P (2010) The low dose combination of fenofibrate and rosiglitazone halts the progression of diabetes-induced experimental nephropathy. Eur J Pharmacol 636:137–144. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2010.03.002
Tikoo K, Singh K, Kabra D, Sharma V, Gaikwad A (2008) Change in histone H3 phosphorylation, MAP kinase p38, SIR 2 and p53 expression by resveratrol in preventing streptozotocin induced type I diabetic nephropathy. Free Radic Res 42:397–404. doi:10.1080/10715760801998646
Lässer C, Eldh M, Lötvall J (2012) Isolation and characterization of RNA-containing exosomes. J Vis Exp 59:e3037. doi:10.3791/3037
Biyashev D, Veliceasa D, Topczewski J, Topczewska JM, Mizgirev I, Vinokour E, Reddi AL, Licht JD, Revskoy SY, Volpert OV (2012) miR-27b controls venous specification and tip cell fate. Blood 119:2679–2687. doi:10.1182/blood-2011-07-370635
Fink T, Lund P, Pilgaard L, Rasmussen JG, Duroux M, Zachar V (2008) Instability of standard PCR reference genes in adipose-derived stem cells during propagation, differentiation and hypoxic exposure. BMC Mol Biol 9:98. doi:10.1186/1471-2199-9-98
Peltier HJ, Latham GJ (2008) Normalization of microRNA expression levels in quantitative RT-PCR assays: identification of suitable reference RNA targets in normal and cancerous human solid tissues. RNA 14:844–852. doi:10.1261/rna.939908
Wu CC, Sytwu HK, Lin YF (2012) Cytokines in diabetic nephropathy. Adv Clin Chem 56:55–74. doi:10.1016/B978-0-12-394317-0.00014-5
Leung KK, Leung PS (2008) Effects of hyperglycemia on angiotensin II receptor type 1 expression and insulin secretion in an INS-1E pancreatic beta-cell line. JOP 9:290–299
Willemsen JM, Westerink JW, Dallinga-Thie GM, van Zonneveld AJ, Gaillard CA, Rabelink TJ, de Koning EJ (2007) Angiotensin II type 1 receptor blockade improves hyperglycemia-induced endothelial dysfunction and reduces proinflammatory cytokine release from leukocytes. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 49:6–12. doi:10.1097/FJC.0b013e31802b31a7
Thomson SC, Deng A, Bao D, Satriano J, Blantz RC, Vallon V (2001) Ornithine decarboxylase, kidney size, and the tubular hypothesis of glomerular hyperfiltration in experimental diabetes. J Clin Invest 107:217–224. doi:10.1172/JCI10963
Lovis P, Roggli E, Laybutt DR, Gattesco S, Yang JY, Widmann C, Abderrahmani A, Regazzi R (2008) Alterations in microRNA expression contribute to fatty acid-induced pancreatic beta-cell dysfunction. Diabetes 57:2728–2736. doi:10.2337/db07-1252
Zilahi E, Tarr T, Papp G, Griger Z, Sipka S, Zeher M (2012) Increased microRNA-146a/b, TRAF6 gene and decreased IRAK1 gene expressions in the peripheral mononuclear cells of patients with Sjögren’s syndrome. Immunol Lett 141:165–168. doi:10.1016/j.imlet.2011.09.006
Liu Z, Xiao B, Tang B, Li B, Li N, Zhu E, Guo G, Gu J, Zhuang Y, Liu X, Ding H, Zhao X, Guo H, Mao X, Zou Q (2010) Up-regulated microRNA-146a negatively modulate Helicobacter pylori-induced inflammatory response in human gastric epithelial cells. Microbes Infect 12:854–863. doi:10.1016/j.micinf.2010.06.002
Roggli E, Britan A, Gattesco S, Lin-Marq N, Abderrahmani A, Meda P, Regazzi R (2010) Involvement of microRNAs in the cytotoxic effects exerted by proinflammatory cytokines on pancreatic beta-cells. Diabetes 59:978–986. doi:10.2337/db09-0881
Acknowledgments
The Grant of this study was supported by Neurosciences Research Center, Tabriz University of Medical Sciences, Tabriz, Iran. Our data in this work were derived from the thesis of Ms. Nasibeh Yousefzadeh for a Master of Science degree in physiology (thesis serial number: 90/2-1/1).
Conflict of interest
The authors have declared that there is no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alipour, M.R., Khamaneh, A.M., Yousefzadeh, N. et al. Upregulation of microRNA-146a was not accompanied by downregulation of pro-inflammatory markers in diabetic kidney. Mol Biol Rep 40, 6477–6483 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-013-2763-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-013-2763-4