Abstract
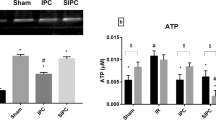
The aim of this study was to characterise the effects of ischemic preconditioning (IP) on heart function parameters (ΔST and ΔT), activities of serum creatine kinase (CK), lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), and levels of serum nitric oxide (NO), malondialdehyde (MDA), and myocardium Caspase-3 mRNA, SOCS-1, SOCS-3, tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) and interleukin-6 (IL-6) expression levels and Apoptosis index in myocardium IR rats. Results showed that ΔST and ΔST values in IP group were markedly lower than those in IR group. Compared with IR group, IP significantly (p < 0.01) decreased serum CK (0.83 ± 0.09 vs 1.36 ± 0.15), LDH (5613 ± 462 vs 7106 ± 492) activities and MDA (11.32 ± 1.05 vs 15.49 ± 1.26) level, increased the serum NO (86.39 ± 7.03 vs 53.77 ± 4.27) level in IR group. The IP induced a significant decreased in myocardium Caspase-3 mRNA (0.303 ± 0.021 vs 0.515 ± 0.022) gene expression (p < 0.01) compared to IR model group. The IP induced a significant decreased in myocardium SOCS-1 (0.241 ± 0.031 vs 0.596 ± 0.036), SOCS-3 (0.258 ± 0.031 vs 0.713 ± 0.057), TNF-α (0.137 ± 0.011 vs 0.427 ± 0.035) and IL-6 (0.314 ± 0.021 vs 0.719 ± 0.064) mRNA gene expression (p < 0.01) compared to IR model group. We conclude that IP is effective in the therapy of heart disease. These findings may have implications for the clinical development of preconditioning-based therapies for ischemic heart disease.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Maxwell SR, Lip GY (1997) Reperfusion injury: a review of the pathophysiology, clinical manifestations and therapeutic options. Int J Cardiol 58(2):95–117
Eltzschig HK, Collard CD (2004) Vascular ischaemia and reperfusion injury. Brit Med Bull 70:71–86
Mathers CD, Loncar D (2006) Projections of global mortality and burden of disease from 2002 to 2030. PLoS Med 3:e442
Buja LM, Vela D (2008) Cardiomyocyte death and renewal in the normal and diseased heart. Cardiovasc Pathol 17:349–374
Murry CE, Jennings RB, Reimer KA (1986) Preconditioning with ischemia: a delay of lethal cell injury in ischemic myocardium. Circulation 74:1124–1136
Ottani F, Galvani M, Ferrini D, Sorbello F, Limonetti P, Pantoli D, Rusticali F (1995) Prodromal angina limits infarct size. A role for ischemic preconditioning. Circulation 91(2):291–297
Yellon DM, Hausenloy DJ (2007) Myocardial reperfusion injury. N Engl J Med 357:1121–1135
Turer AT, Hill JA (2010) Pathogenesis of myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury and rationale for therapy. Am J Cardiol 106:360–368
Yellon DM, Alkhulaifi AM, Pugsley WB (1993) Preconditioning the human myocardium. Lancet 342:276–277
Rossoni G, Manfredi B, Civelli M, Berti F, Razzetti R (2008) Combined simvastatin–manidipine protect against ischemia–reperfusion injury in isolated hearts from normocholesterolemic rats. Eur J Pharmacol 587:224–230
Przyklenk K, Kloner RA (1998) Ischemic preconditioning: exploring the paradox. Prog Cardiovasc Dis 40:517–547
DeFily DV, Chilian WM (1993) Preconditioning protects coronary arteriolar endothelium from ischemia–reperfusion injury. Am J Physiol 265:H700–H706
Richard V, Kaeffer N, Tron C, Thuillez C (1994) Ischemic preconditioning protects against coronary endothelial dysfunction induced by ischemia and reperfusion. Circulation 89:1254–1261
Beresewicz A, Czarnowska E, Maczewski M (1998) Ischemic preconditioning and superoxide dismutase protect against endothelial dysfunction and endothelium glycocalyx disruption in the postischemic guinea-pig hearts. Mol Cell Biochem 186:87–92
Kharbanda RK, Peters M, Walton B, Kattenhorn M, Mullen M, Klein N, Vallance P, Deanfield J, MacAllister R (2001) Ischemic preconditioning prevents endothelial injury and systemic neutrophil activation during ischemia–reperfusion in humans in vivo. Circulation 103:1624–1630
McCord JM (1985) Oxygen-derived free radicals in postischemic tissue injury. New Eng J Med 312:159–163
Giraldez RR, Panda A, Xia Y, Sanders SP, Zweier JL (1997) Decreased nitric-oxide synthase activity causes impaired endothelium-dependent relaxation in the postischemic heart. J Biol Chem 34:21420–21426
Wang L, Cherednichenko G, Hernandez L, Halow J, Camacho SA, Figueredo V, Schaefer S (2001) Preconditioning limits mitochondrial Ca2+ during ischemia in rat hearts: role of KATP channels. Am. J. Physiol Heart Circ. Physiol 280:H2321–H2328
Antman EM, Braunwald E (1997) Acute myocardial infarction. In: Braunwald E (ed) Heart disease, a textbook of cardiovascular medicine, 5th edn. WB Saunders & Co, Philadelphia, pp 1184–1188
Kaur H, Parikh V, Sharma A, Singh M (1997) Effect of amiloride a Na+/H+ exchange inhibitor on cardioprotective effect of ischemic preconditioning: possible involvement of resident cardiac mast cells. Pharmacol Res 36:95–102
Ribeiro SP, Villar J, Slutsky AS (1995) Induction of the stress response to prevent organ injury. New Horiz 3:301–311
Benjamin IJ, McMillan DR (1998) Stress (heat shock) proteins: molecular chaperones in cardiovascular biology and disease. Circ Res 83:117–132
De Maio A (1999) Heat shock proteins: facts, thoughts, and dreams. Shock 11:1–12
Morrison AL, Dinges M, Singleton KD, Odoms K, Wong HR, Wischmeyer PE (2006) Glutamine’s protection against cellular injury is dependent on heat shock factor-1. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 290:1625–1632
Schroeder S, Lindemann C, Hoeft A, Putensen C, Decker D, von Ruecker AA, Stuber F (1999) Impaired inducibility of heat shock protein 70 in peripheral blood lymphocytes of patients with severe sepsis. Crit Care Med 27:1080–1084
Villar J, Ribeiro SP, Mullen JB, Kuliszewski M, Post M, Slutsky AS (1994) Induction of the heat shock response reduces mortality rate and organ damage in a sepsis-induced acute lung injury model. Crit Care Med 22:914–921
Yang RC, Wang CI, Chen HW, Chou FP, Lue SI, Hwang KP (1998) Heat shock treatment decreases the mortality of sepsis in rats. Kaohsiung J Med Sci 14:664–672
Pittet JF, Lee H, Morabito D, Howard MB, Welch WJ, Mackersie RC (2002) Serum levels of Hsp 72 measured early after trauma correlate with survival. J Trauma 52:611–617
Jakob U, Gaestel M, Engel K, Buchner J (1993) Small heat shock proteins are molecular chaperones. J Biol Chem 268:1517–1520
Huot J, Houle F, Spitz DR, Landry J (1996) HSP27 phosphorylation- mediated resistance against actin fragmentation and cell death induced by oxidative stress. Cancer Res 56:273–279
Lavoie JN, Hickey E, Weber LA, Landry J (1993) Modulation of actin microfilament dynamics and fluid phase pinocytosis by phosphorylation of heat shock protein 27. J Biol Chem 268:24210–24214
Mehlen P, Mehlen A, Godet J, Arrigo AP (1997) Hsp27 as a switch between differentiation and apoptosis in murine embryonic stem cells. J Biol Chem 272:31657–31665
Mehlen P, Schulze-Osthoff K, Arrigo AP (1996) Small stress proteins as novel regulators of apoptosis. Heat shock protein 27 blocks Fas/APO-1-and staurosporine-induced cell death. J Biol Chem 271:16510–16514
Samali A, Cotter TG (1996) Heat shock proteins increase resistance to apoptosis. Exp Cell Res 223:163–170
Costigan M, Mannion RJ, Kendall G, Lewis SE, Campagna JA, Coggeshall RE, Meridith-Middleton J, Tate S, Woolf CJ (1998) Heat shock protein 27: developmental regulation and expression after peripheral nerve injury. J Neurosci 18:5891–5900
Plumier JC, Hopkins DA, Robertson HA, Currie RW (1997) Constitutive expression of the 27-kDa heat shock protein (Hsp27) in sensory and motor neurons of the rat nervous system. J Comp Neurol 384:409–428
Hopkins DA, Plumier JC, Currie RW (1998) Induction of the 27-kDa heat shock protein (Hsp27) in the rat medulla oblongata after vagus nerve injury. Exp Neurol 153:173–183
Imura T, Shimohama S, Sato M, Nishikawa H, Madono K, Akaike A, Kimura J (1999) Differential expression of small heat shock proteins in reactive astrocytes after focal ischemia: possible role of beta-adrenergic receptor. J Neurosci 19:9768–9779
Han J, Lee JD, Bibbs L, Ulevitch RJ (1994) A MAP kinase targeted by endotoxin and hyperosmolarity in mammalian cells. Science 265(5173):808–811
Lee JC, Laydon JT, McDonnell PC, Gallagher TF, Kumar S, Green D (1994) A protein kinase involved in the regulation of inflammatory cytokine biosynthesis. Nature 372(6508):739–746
Bokemeyer D, Lindemann M, Kramer HJ (1998) Regulation of mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase-1 in vascular smooth muscle cells. Hypertension 32:661–667
Begum N, Ragolia L (2000) High glucose and insulin inhibit VSMC MKP-1 expression by blocking iNos via p38 MAPK activation. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 278:C81–C91
Ohashi H, Matsumori A, Furukawa Y, Ono K, Okada M, Iwasaki A, Miyamoto T, Nakano A, Sasayama S (2000) Role of p38 mitogen activated protein kinase in neointimal hyperplasia after vascular injury. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 20:2521–2526
Soonpaa MH, Field LJ (1998) Survey of studies examining mammalian cardiomyocyte DNA synthesis. Circ Res 83:15–26
Dorn GW 2nd (2009) Apoptotic and non-apoptotic programmed cardiomyocyte death in ventricular remodeling. Cardiovasc Res 15(81):465–473
Olivetti G, Abbi R, Quaini F, Kajstura J, Cheng W, Nitahara JA, Quaini E, Di Loreto C, Beltrami CA, Krajewski S, Reed JC, Anversa P (1997) Apoptosis in the failing human heart. N Engl J Med 336:1131–1141
Graham SH, Chen J (2001) Programmed cell death in cerebral ischemia (review). J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 21:99–109
Namura S, Zhu J, Fink K, Endres M, Srinivasan A, Tomaselli KJ, Yuan J, Moskowitz MA (1998) Activation and cleavage of caspase-3 in apoptosis induced by experimental cerebral ischemia. J Neurosci 18:3659–3668
Zhu C, Wang X, Hagberg H, Blomgren K (2000) Correlation between caspase-3 activation and three different markers of DNA damage in neonatal cerebral hypoxia–ischemia. J Neurochem 75:819–829
Hara H, Friedlander RM, Gagliardini V, Ayata C, Fink K, Huang Z, Shimizu-Sasamata M, Yuan J, Moskowitz MA (1997) Inhibition of interleukin 1beta converting enzyme family proteases reduces ischemic and excitotoxic neuronal damage. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:2007–2012
De Malefyt RW, Abrams J, Bennett B, Figdor CG, de Vries JE (1991) Interleukin 10 (IL-10) inhibits cytokine synthesis by human monocytes: an autoregulatory role of IL-10 produced by monocytes. J Exp Med 174:1209–1220
Meng ZH, Dyer K, Billiar TR, Tweardy DJ (2001) Essential role for IL-6 in postresuscitation inflammation in hemorrhagic shock. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 280:C343–C351
Yamauchi-Takihara K, Ihara Y, Ogata A, Yoshizaki K, Azuma J, Kishimoto T (1995) Hypoxic stress induces cardiac myocyte-derived interleukin-6. Circulation 91:1520–1524
O’Neill PJ, Ayala A, Wang P, Ba ZF, Morrison MH, Schultze AE, Reich SS, Chaudry IH (1994) Role of kupffer cells in interleukin-6 release following trauma-hemorrhage and resuscitation. Shock 1:43–47
Ancey C, Corbi P, Froger J, Delwail A, Wijdenes J, Gascan H, Potreau D, Lecron JC (2002) Secretion of IL-6, IL-11 and LIF by human cardiomyocytes in primary culture. Cytokine 18:199–205
Deten A, Volz HC, Briest W, Zimmer HG (2002) Cardiac cytokine expression is upregulated in the acute phase after myocardial infarction. Experimental studies in rats. Cardiovasc Res 55:329–340
Finkel MS, Oddis CV, Jacob TD, Watkins SC, Hattler BG, Simmons RL (1992) Negative inotropic effects of cytokines on the heart mediated by nitric oxide. Science 257:387–389
Testa M, Yeh M, Lee P, Fanelli R, Loperfido F, Berman JW, LeJemtel TH (1996) Circulating levels of cytokines and their endogenous modulators in patients with mild to severe congestive heart failure due to coronary artery disease or hypertension. J Am Coll Cardiol 28:964–971
Shouda T, Yoshida T, Hanada T, Wakioka T, Oishi M, Miyoshi K, Komiya S, Kosai K, Hanakawa Y, Hashimoto K, Nagata K, Yoshimura A (2001) Induction of the cytokine signal regulator SOCS3/CIS3 as a therapeutic strategy for treating inflammatory arthritis. J Clin Invest 108:1781–1788
Suzuki A, Hanada T, Mitsuyama K, Yoshida T, Kamizono S, Hoshino T, Kubo M, Yamashita A, Okabe M, Takeda K, Akira S, Matsumoto S, Toyonaga A, Sata M, Yoshimura A (2001) CIS3/SOCS3/SSI3 plays a negative regulatory role in STAT3 activation and intestinal inflammation. J Exp Med 193:471–481
Jin X, Zhang Z, Beer-Stolz D, Zimmers TA, Koniaris LG (2007) Interleukin-6 inhibits oxidative injury and necrosis after extreme liver resection. Hepatology 46:802–812
Yoshimura A, Naka T, Kubo M (2007) SOCS proteins, cytokine signalling and immune regulation. Nat Rev Immunol 7:454–465
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, J., Qiao, Z. & Xu, B. Effects of ischemic preconditioning on myocardium Caspase-3, SOCS-1, SOCS-3, TNF-α and IL-6 mRNA expression levels in myocardium IR rats. Mol Biol Rep 40, 5741–5748 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-013-2677-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-013-2677-1