Abstract
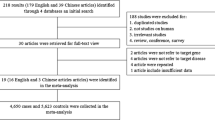
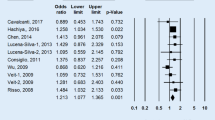
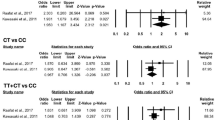
The aim of this study was to summarize results on the association of cytotoxic T-lymphocyte antigen-4 (CTLA-4) promoter exon-1 +49 and 1722T/C polymorphism with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) susceptibility by using the meta-analysis. We searched all the publications about the association between CTLA-4) promoter exon-1 +49 and 1722T/C polymorphism and SLE from PubMed, Elsevier Science Direct, Chinese Biomedical Literature Database (CBM), Chinese National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI), and Wanfang (Chinese). Previous CTLA-4 association studies with SLE, however, have produced inconsistent results. We have performed a meta-analysis to better assess the purported associations. A total of 17 independent studies (to June 2012) testing association between one or more CTLA-4 polymorphisms and SLE were used in this analysis. We have compared allele and genotype frequencies at two polymorphic sites found in exon-1 (at +49) and the promoter region (at −1722). The data demonstrate that the exon-1 +49 polymorphism is associated with SLE susceptibility in Asian population. The overall risk, measured by odds ratio (OR), stratification by ethnicity indicates the exon-1 +49 GG+GA genotype is associated with SLE, at least in Asians (OR = 0.85, 95 % CI = 0.73–0.99, P = 0.04 for GG+GA vs. AA; OR = 0.85, 95 % CI = 0.72–1.00, P = 0.05 for AG vs. AA). Similar trends are found in allele-specific risk estimates and disease association. Overall, there was significant association between the 1722T/C polymorphism and overall SLE risks (OR = 0.78, 95 % CI = 0.63–0.97, P = 0.04 for GG+GA vs. AA, OR = 0.87, 95 % CI = 0.76–0.99, P = 0.04 for G vs. A) in Asian population.In summary, this meta-analysis demonstrates that the CTLA-4 promoter +49A/G and promoter −1722C/T polymorphism may confer susceptibility to SLE, especially in Asian-derived population.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
D’Cruz DP, Khamashta MA, Hughes GR (2007) Systemic lupus erythematosus. Lancet 369(9561):587–596
Flesher DL, Sun X, Behrens TW, Graham RR, Criswell LA (2010) Recent advances in the genetics of systemic lupus erythematosus. Expert Rev Clin Immunol 6(3):461–479
Powell JJ, Van de Water J, Gershwin ME (1999) Evidence for the role of environmental agents in the initiation or progression of autoimmune conditions. Environ Health Perspect 107(Suppl 5):667–672
Sestak AL, Furnrohr BG, Harley JB, Merrill JT, Namjou B (2011) The genetics of systemic lupus erythematosus and implications for targeted therapy. Ann Rheum Dis 70(Suppl 1):i37–i43
Manolio TA, Collins FS, Cox NJ et al (2009) Finding the missing heritability of complex diseases. Nature 461(7265):747–753
Hussain N, Jaffery G, Sabri AN, Hasnain S (2011) HLA association in SLE patients from Lahore-Pakistan. Bosn J Basic Med Sci. 11(1):20–26
Eliopoulos E, Zervou MI, Andreou A, Dimopoulou K, Cosmidis N, Voloudakis G, Mysirlaki H, Vazgiourakis V, Sidiropoulos P, Niewold TB, Boumpas DT (2011) Goulielmos GN Association of the PTPN22 R620W polymorphism with increased risk for SLE in the genetically homogeneous population of Crete. Lupus 20(5):501–506
Aranda F, Wingeyer SP, Muñoz SA, Allievi A, Orden A, Trobo R, Alvarez A, Eimon A, Barreira JC, Schneeberger E, Sarano J, Hofman J, de Larrañaga G (2012) The -2518 A/G polymorphism in the monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 gene is associated with the risk of developing systemic lupus erythematosus in Argentinean patients: a multicenter study. Eur Cytokine Netw 23(1):7–11
Zervou MI, Vazgiourakis VM, Yilmaz N, Kontaki E, Trouw LA, Toes RE, Bicakcigil M, Boumpas DT, Yavuz S, Goulielmos GN (2011) TRAF1/C5, eNOS, C1q, but not STAT4 and PTPN22 gene polymorphisms are associated with genetic susceptibility to systemic lupus erythematosus in Turkey. Hum Immunol 72(12):1210–1213
Cunninghame Graham DS, Wong AK, McHugh NJ, Whittaker JC, Vyse TJ (2006) Evidence for unique association signals in SLE at the CD28-CTLA4-ICOS locus in a family-based study. Hum Mol Genet 15(21):3195–3205
Budarf ML, Goyette P, Boucher G, Lian J, Graham RR, Claudio JO, Hudson T, Gladman D, Clarke AE, Pope JE, Peschken C, Smith CD, Hanly J, Rich E, Boire G, Barr SG, Zummer M, Genes Investigators, Fortin PR, Wither J, Rioux JD (2011) A targeted association study in systemic lupus erythematosus identifies multiple susceptibility alleles. Genes Immun 12(1):51–58
Taha Khalaf A, Song JQ, Gao TT, Yu XP, Lei TC (2011) CTLA-4 gene polymorphism and the risk of systemic lupus erythematosus in the Chinese population. J Biomed Biotechnol 2011:167395 PMCID: PMC3170903
Chua KH, Puah SM, Chew CH, Tan SY, Lian LH (2010) Study of the CTLA-4 gene polymorphisms in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) samples from Malaysia. Ann Hum Biol 37(2):274–280
Lee YH, Kim YR, Ji JD, Sohn J, Song GG (2001) Polymorphisms of the CTLA-4 exon 1 and promoter gene in systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus 10(9):601–605
Ahmed S, Ihara K, Kanemitsu S, Nakashima H, Otsuka T, Tsuzaka K, Takeuchi T, Hara T (2001) Association of CTLA-4 but not CD28 gene polymorphisms with systemic lupus erythematosus in the Japanese population. Rheumatology (Oxford) 40(6):662–667
Gang C, Jiahui Y, Huaizhou W, Qing C, Dongbao Z, Qian S (2009) Defects of mitogen-activated protein kinase in ICOS signaling pathway lead to CD4(+) and CD8(+) T-cell dysfunction in patients with active SLE. Cell Immunol 258(1):83–89
Contin-Bordes C, Lazaro E, Richez C, Jacquemin C, Caubet O, Douchet I, Viallard JF, Moreau JF, Pellegrin JL, Blanco P (2011) Expansion of myelin autoreactive CD8 + T lymphocytes in patients with neuropsychiatric systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann Rheum Dis 70(5):868–871
Smolen JS, Chused TM, Leiserson WN, Reeves JP, Alling D, Steinberg AD (1982) Heterogeneity of immunoregulatory T-cell subsets in systemic lupus erythematosus. Am J Med 72(5):783–790
McInerney MF, Clough JD, Seniztzer D, Cathcart MK (1988) Two distinct subsets of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Immunol Immunopathol 49(1):116–132
Chavele KM, Ehrenstein MR (2011) Regulatory T-cells in systemic lupus erythematosus and rheumatoid arthritis. FEBS Lett 585(23):3603–3610
Gough SC, Walker LS, Sansom DM (2005) CTLA4 gene polymorphism and autoimmunity. Immunol Rev 204:102–115
Schuler PJ, Schilling B, Harasymczuk M, Hoffmann T, Johnson J, Lang S, Whiteside TL (2012) Phenotypic and functional characteristics of ATP-hydrolysing CD4(+) CD39(+) FOXP3(+) and CD4(+) CD39(+) FOXP3(neg) T-cell subsets in patients with cancer. Eur J Immunol 42(7):1876–1885
Anjos S, Nguyen A, Ounissi-Benkalha H, Tessier MC, Polychronakos C (2002) A common autoimmunity predisposing signal peptide variant of the cytotoxic T-lymphocyte antigen 4 results in inefficient glycosylation of the susceptibility allele. J Biol Chem 277(48):46478–46486
Ligers A, Teleshova N, Masterman T, Huang WX, Hillert J (2001) CTLA-4 gene expression is influenced by promoter and exon 1 polymorphisms. Genes Immun 2(3):145–152
Wang XB, Zhao X, Giscombe R, Lefvert AK (2002) A CTLA-4 gene polymorphism at position -318 in the promoter region affects the expression of protein. Genes Immun 3(4):233–234
Lee YH, Harley JB, Nath SK (2005) CTLA-4 polymorphisms and systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE): a meta-analysis. Hum Genet 116(5):361–367
Ulker M, Yazisiz V, Sallakci N, Avci AB, Sanlioglu S, Yegin O, Terzioglu E (2009) CTLA-4 gene polymorphism of exon 1(+49 A/G) in Turkish systemic lupus erythematosus patients. Int J Immunogenet 36(4):245–250
Kimkong I, Nakkuntod J, Sae-Ngow S, Snabboon T, Avihingsanon Y, Hirankarn N (2011) Association between CTLA-4 polymorphisms and the susceptibility to systemic lupus erythematosus and Graves’ disease in Thai population. Asian Pac J Allergy Immunol 29(3):229–235
Xu AP, Yin PD, Su XY (2004) Association of CTLA-4 promoter -1722 polymorphism with systemic lupus erythematosus in Chinese. Di Yi Jun Yi Da Xue Xue Bao 24(10):1107–1112
Takeuchi F, Kuwata S, Mori M (2005) CTLA-4 −1661A/G and −1772T/C dimorphisms in Japanese patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Rheumatol 32(10):2062
Egger M, Davey SG, Schneider M, Minder C (1997) Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ 315(109):629–634
Matsushita M, Tsuchiya N, Shiota M, Komata T, Matsuta K, Zama K, Oka T, Juji T, Yamane A, Tokunaga K (1999) Lack of a strong association of CTLA-4 exon 1 polymorphism with the susceptibility to rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus in Japanese: an association study using a novel variation screening method. Tissue Antigens 54(6):578–584
Heward J, Gordon C, Allahabadia A, Barnett AH, Franklyn JA, Gough SC (1999) The A-G polymorphism in exon 1 of the CTLA-4 gene is not associated with systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann Rheum Dis 58(3):193–195
Pullmann R Jr, Lukác J, Skerenová M, Rovensky J, Hybenová J, Melus V, Celec S, Pullmann R, Hyrdel R (1999) Cytotoxic T-lymphocyte antigen 4 (CTLA-4) dimorphism in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Exp Rheumatol 17(6):725–729
D’Alfonso S, Rampi M, Bocchio D, Colombo G, Scorza-Smeraldi R, Momigliano-Richardi P (2000) Systemic lupus erythematosus candidate genes in the Italian population: evidence for a significant association with interleukin-10. Arthritis Rheum 43(1):120–128
Liu MF, Wang CR, Lin LC, Wu CR (2001) CTLA-4 gene polymorphism in promoter and exon-1 regions in Chinese patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus 10(9):647–649
Hudson LL, Rocca K, Song YW, Pandey JP (2002) CTLA-4 gene polymorphisms in systemic lupus erythematosus: a highly significant association with a determinant in the promoter region. Hum Genet 111(4–5):452–455
Aguilar F, Torres B, Sánchez-Román J, Núñez-Roldán A, González-Escribano MF (2003) CTLA4 polymorphism in Spanish patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Hum Immunol 64(10):936–940
Takeuchi F, Kawasugi K, Nabeta H, Mori M, Tanimoto K (2003) CTLA-4 dimorphisms in Japanese patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Exp Rheumatol 21(4):527–528
Barreto M, Santos E, Ferreira R, Fesel C, Fontes MF, Pereira C, Martins B, Andreia R, Viana JF, Crespo F, Vasconcelos C, Ferreira C, Vicente AM (2004) Evidence for CTLA4 as a susceptibility gene for systemic lupus erythematosus. Eur J Hum Genet 12(8):620–626
George C, Tsokos MD (2011) Systemic lupus erythematosus. N Engl J Med 365:2110–2121
Mak A, Cheung MW, Chiew HJ, Liu Y, Ho RC (2012) Global trend of survival and damage of systemic lupus erythematosus: meta-analysis and meta-regression of observational studies from the 1950 to 2000 s. Semin Arthritis Rheum 41(6):830–839
Lee YH, Lee HS, Choi SJ, Ji JD, Song GG (2012) Associations between eNOS polymorphisms and susceptibility to systemic lupus erythematosus: a meta-analysis. Inflamm Res 61(2):135–141
Egger M, Smith GD (1997) Meta-analysis. Potentials and promise. BMJ 315(7119):1371–1374
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grant from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (30830089). This work was supported by grants from the Anhui Province universities Key Project of Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (KJ2008A015).
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhai, JX., Zou, LW., Zhang, ZX. et al. CTLA-4 polymorphisms and systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE): a meta-analysis. Mol Biol Rep 40, 5213–5223 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-012-2125-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-012-2125-7