Abstract
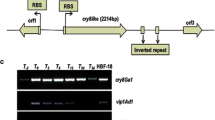
To isolate antimicrobial-related genes from the beet armyworm, Spodoptera exigua, we performed GeneFishing, a polymerase chain reaction (PCR)-based differential display technique. An attacin-like complementary DNA (cDNA) including a 3′-untranslated region was identified from among 18 over-expressed genes in microbial-infected larvae. The full-length attacin cDNA from S. exigua cDNA (Seattacin) was cloned using rapid amplification of cDNA ends PCR. The attacin-like cDNA transcript was 765 nucleotides in length, and the predicted polypeptide was 254 amino acids in length with a calculated molecular mass of 27.6 kDa and an isoelectric point of 6.44. The protein sequence of the attacin-like cDNA showed high identity to that of Trichoplusia ni (61.2%). The amino acid sequence identity of Seattacin to the orthologous proteins in Bombyx mori, Manduca sexta, Heliothis virescens, Hlicoverpa armigera, Hyphantria cunea, Hyalophora cecropia, and Drosophila melanogaster was 61.2, 46.1, 44.5, 42.2, 39.5, 45.1, and 24.0%, respectively. To examine possible immune functions of the attacin-like cDNA, its expression was investigated by reverse transcriptase PCR analysis after challenging S. exigua with microorganisms. The attacin-like cDNA was expressed at high levels 12 h post-infection, and its expression was slightly induced 4–8 h post-infection compared to control larvae inoculated with sterile water. Furthermore, induced Seattacin showed biological activity against several bacteria including Escherichia coli DH5α, Pseudomonas cichorii, Bacillus subtilis, and Listeria monocytogenes. These results suggest that the attacin-like cDNA of S. exigua codes for antimicrobial peptides.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Imler JK, Bulet P (2005) Antimicrobial peptides and activation of immune responses in Drosophila: structures, activities and gene regulation. Chem Immunol Allergy 86:1–21
Kocks C, Cho JH, Nehme N, Ulvila J, Pearson AM, Meister M, Strom C, Conto SL, Hetru C, Stuart LM, Stehle T, Hoffmann JA, Reichhart JM, Ferrandon D, Rämet M, Ezekowitz RA (2005) Eater, a transmembrane protein mediating phagocytosis of bacterial pathogens in Drosophila. Cell 123:11–22
Kurata S, Ariki S, Kawabata S (2006) Recognition of pathogens and activation of immune responses in Drosophila and horseshoe crab innate immunity. Immunobiology 211:237–249
Bulet P, Stocklin R, Menin L (2004) Anti-microbial peptides: from invertebrates to vertebrates. Immunol Rev 198:169–184
De Gregorio E, Spellman PT, Rubin GM, Lemaitre B (2001) Genome-wide analysis of the Drosophila immune response by using oligonucleotide microarrays. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:12590–12595
Zou Z, Evans JD, Lu Z, Zhao P, Williams M, Sumathipala N, Hetru C, Hultmark D, Jiang H (2007) Comparative genomic analysis of the Tribolium immune system. Genome Biol 8:R177
Tanaka H, Ishibashi J, Fujita K, Nakajima Y, Sagisaka A, Tomimoto K, Suzuki N, Yoshiyama M, Kaneko Y, Iwasaki T, Sunagawa T, Yamaji K, Asaoka A, Mita K, Yamakawa M (2008) A genome-wide analysis of genes and gene families involved in innate immunity of Bombyx mori. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 38:1087–1110
Carlsson A, Engström P, Palva ET, Bennich H (1991) Attacin, an antibacterial protein from Hyalophora cecropia, inhibits synthesis of outer membrane proteins in Escherichia coli by interfering with omp gene transcription. Infect Immunol 59:3040–3045
Ando K, Okada M, Natori S (1987) Purification of sarcotoxin II, antibacterial proteins of Sarcophaga peregrina (flesh fly) larvae. Biochemistry 26:226–230
Matsuyama K, Natori S (1988) Purification of three antibacterial proteins from the culture medium of NIH-Sape-4, an embryonic cell line of Sarcophaga peregrina. J Biol Chem 263:17112–17116
Wang L, Yu B, Han G, Chen D (2010) Molecular cloning, expression in Escherichia coli of Attacin A gene from Drosophila and detection of biological activity. Mol Biol Rep 37:2463–2469
Dushay MS, Roethele JB, Chaverri JM, Dulek DE, Syed SK, Kitami T, Eldon ED (2000) Two Attacin antibacterial genes of Drosophila melanogaster. Gene 246:49–57
Lazzaro BP, Clark AG (2001) Evidence for recurrent paralogous gene conversion and exceptional allelic divergence in the Attacin genes of Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics 159:659–671
Geng H, An CJ, Hao YJ, Li DS, Du RQ (2004) Molecular cloning and expression of Attacin from housefly (Musca domestica). Acta Genet Sin 31:1344–1350
Kang DW, Lundström A, Steiner H (1996) Trichoplusia ni attacin A, a differentially displayed insect coding for an antibacterial protein. Gene 174:245–249
Kishimoto K, Fujimoto S, Matsumoto K, Yamano Y, Morishima I (2002) Protein purification, cDNA cloning and gene expression of attacin, an antibacterial protein, from eri-silkworm, Samia cynthia ricini. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 32:881–887
Sugiyama M, Kuniyoshi H, Kotani E, Taniai K, Kadono-Okuda K, Kato Y, Yamamoto M, Shimabukuro M, Chowdhury S, Xu J, Choi SK, Kataoka H, Suzuki A, Yamakawa M (1995) Characterization of a Bombyx mori cDNA encoding a novel member of the Attacin family of insect antibacterial proteins. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 25:385–392
Zhang B, Wang LM, Ye B, Li SY, Zhao ZJ, Fan Q (2006) Cloning and analysis of cDNA of the Attacin gene from the Chinese oak silkworm, Antheraea pernyi, using RLM-RACE method. Canye Kexue 32:333–339
Capinera JL (2001) Handbook of vegetable pests. Academic Press, San Diego, pp 729–738
Wang Q, Liu Y, He H, Zhao X, Wang J (2010) Immune response of Helicoverpa armigera to different kinds of pathogens. BMC Immunol 11:9
Hancock REW, Brown KL, Mookherjee N (2006) Host defense peptides from invertebrates—emerging antimicrobial strategies. Immunobiology 211:315–322
Raulston JR, Lingren PD (1972) Methods for large-scale rearing of the tobacco budworm. United States Department of Agriculture Product Research Report, vol 145, pp 1–10
Thompson JD, Higgins DG, Gibson TJ (1994) CLUSTAL W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, positions-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res 22:4673–4680
Kyte J, Doolittle RF (1982) A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol 157:105–132
Steinberg DA, Lehrer RI (1997) Designer assays for antimicrobial peptides. Disputing the “one-size-fits-all” theory. Methods Mol Biol 78:169–186
Finn RD, Mistry J, Tate J, Coggill P, Heger A, Pollington JE, Gavin OL, Gunesekaran P, Ceric G, Forslund K, Holm L, Sonnhammer EL, Eddy SR, Bateman A (2010) The Pfam protein families database. Nucleic Acids Res 38:D211–D222 (database issue)
Tamura K, Dudley J, Nei M, Kumar S (2007) MEGA4: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Mol Biol Evol 24:1596–1599
Freitak D, Heckel DG, Vogel H (2009) Bacterial feeding induces changes in immune-related gene expression and has trans-generational impacts in the cabbage looper (Trichoplusia ni). Front Zool 6:7
Jin YH, Jung S, Jin SG, Jung TY, Moon KS, Kim IY (2010) GRIM-19 Expression and function in human Gliomas. J Korean Neurosurg Soc 48:20–30
Bryson K, McGuffin LJ, Marsden RL, Ward JJ, Sodhi JS, Jones DT (2005) Protein structure prediction servers at University College London. Nucl Aci Res 33:W36–W38 (Web server issue)
Jones DT (1999) Protein secondary structure prediction based on position specific scoring matrices. J Mol Biol 292:195–202
Puntervoll P, Linding R, Gemünd C, Chabanis-Davidson S, Mattingsdal M, Cameron S, Martin DMA, Ausiello G, Brannetti B, Costantini A, Ferrè F, Maselli V, Via A, Cesareni G, Diella F, Superti-Furga G, Wyrwicz L, Ramu C, McGuigan C, Gudavalli R, Letunic I, Bork P, Rychlewski L, Küster B, Helmer-Citterich M, Hunter WN, Aasland R, Gibson TJ (2003) ELM server: a new resource for investigating short functional sites in modular eukaryotic proteins. Nucleic Acids Res 31:3625–3630
Park CB, Yi KS, Matsuzaki K, Kim MS, Kim SC (2000) Structure–activity analysis of buforin II, a histone H2A-derived antimicrobial peptide: the proline hinge is responsible for the cell-penetrating ability of buforin II. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:8245–8250
Ganz T (2003) The role of antimicrobial peptides in innate immunity. Integr Comp Biol 43:300–304
Carlsson A, Nystrom T, Cock H, Bennichl H (1998) Attacin—an insect immune protein-binds LPS and triggers the specific inhibition of bacterial outer-membrane protein synthesis. Microbiology 144:2179–2188
Wikipedia contributors (2011) “Listeria monocytogenes” Wikipedia, the Free Encyclopedia Web, 9 May
Damodharan L, Pattabhi V (2004) Hydropathy analysis to correlate structure and function of proteins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 323:996–1002
Engstrom A, Engstrom P, Tao Zj, Carlsson A, Bennich H (1984) Insect immunity. The primary structure of the antibacterial protein attacin F and its relation to two native attacins from Hyalophora cecropia. Eur Mol Biol Org J 9:2065–2070
Sun SC, Lindström I, Lee JY, Faye I (1991) Structure and expression of the attacin genes in Hyalophora cecropia. Eur J BioChem 196:247–254
Tanaka H, Furukawa S, Nakazawa H, Sagisaka A, Yamakawa M (2005) Regulation of gene expression of attacin, an antibacterial protein in the silkworm, Bombyx mori. J Insect Biotech Sericol 74:45–56
Wang L, Yu B, Han G, He J, Chen D (2009) Design expression and characterization of recombinant hybrid peptide Attacin-Thanatin in Escherichia coli. Mol Biol Rep 37:3495–3501
Acknowledgment
This research was supported by National Research Foundation of Korea (Grant Number; 2010-0021231).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bang, K., Park, S., Yoo, J.Y. et al. Characterization and expression of attacin, an antibacterial protein-encoding gene, from the beet armyworm, Spodoptera exigua (Hübner) (Insecta: Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Mol Biol Rep 39, 5151–5159 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-011-1311-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-011-1311-3