Abstract
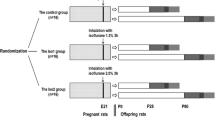
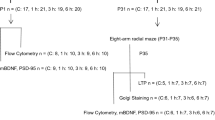
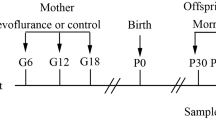
Emerging evidence has demonstrated that exposure to anesthetics early in life caused neurohistopathologic changes and persistent behavioral impairments. In this study, a maternal fetal rat model was developed to study the effects of isoflurane exposure during pregnancy on postnatal memory and learning in the offspring. Pregnant rats at gestational day 14 were either exposed to 1.3% isoflurane in a humidified 100% oxygen carrier gas or simply humidified 100% oxygen without any inhalational anesthetic for 2 h every day before delivery. Four weeks later, spatial learning and memory of the offspring were examined using the Morris Water Maze. The expression levels of GAP-43 and NPY in the hippocampal CA1 region of the pups were determined by immunohistochemistry and RT-PCR. Simultaneously, the ultrastructure changes in synapse of the hippocampus were also observed by transmission electron microscopy (TEM). Isoflurane exposure during pregnancy impaired postnatal spatial memory and learning in the offspring as shown by the longer escape latency and the fewer original platform crossings in the Morris Water Maze test. The number and optical densities of GAP-43 and NPY positive cells, as well as the levels of GAP-43 and NPY mRNA, decreased significantly in the hippocampus of isoflurane-exposed pups. Furthermore, TEM studies showed remarkable changes in synaptic ultrastructure of hippocampus. These results indicate that isoflurane exposure during pregnancy could cause postnatal spatial memory and learning impairments in offspring rats, which may be partially explained by the down-regulation of GAP-43 and NPY in the hippocampal area.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dwyer R, Fee JP, Moore J (1995) Uptake of halothane and isoflurane by mother and baby during caesarean section. Br J Anaesth 74(4):379–383
Jevtovic-Todorovic V, Hartman RE, Izumi Y, Benshoff ND, Dikranian K, Zorumski CF, Olney JW, Wozniak DF (2003) Early exposure to common anesthetic agents causes widespread neurodegeneration in the developing rat brain and persistent learning deficits. J Neurosci 23(3):876–882
Ma D, Williamson P, Januszewski A, Nogaro MC, Hossain M, Ong LP, Shu Y, Franks NP, Maze M (2007) Xenon mitigates isoflurane-induced neuronal apoptosis in the developing rodent brain. Anesthesiology 106(4):746–753
Culley DJ, Baxter MG, Yukhananov R, Crosby G (2004) Long-term impairment of acquisition of a spatial memory task following isoflurane-nitrous oxide anesthesia in rats. Anesthesiology 100(2):309–314
Wilder RT, Flick RP, Sprung J, Katusic SK, Barbaresi WJ, Mickelson C, Gleich SJ, Schroeder DR, Weaver AL, Warner DO (2009) Early exposure to anesthesia and learning disabilities in a population-based birth cohort. Anesthesiology 110(4):796–804
Kalkman CJ, Peelen L, Moons KG, Veenhuizen M, Bruens M, Sinnema G, de Jong TP (2009) Behavior and development in children and age at the time of first anesthetic exposure. Anesthesiology 110(4):805–812
Monk TG, Weldon BC, Garvan CW, Dede DE, van der Aa MT, Heilman KM, Gravenstein JS (2008) Predictors of cognitive dysfunction after major noncardiac surgery. Anesthesiology 108(1):18–30
Oestreicher AB, De Graan PN, Gispen WH, Verhaagen J, Schrama LH (1997) The growth associated protein-43: modulation of cell morphology and communication in the nervous system. Prog Neurobiol 53(6):627–686
Farina V, Gadau S, Lepore G, Manca P, Zedda M (2004) Growth associated protein expression in the frontal and occipital cortices of callosotomized rats. Funct Neurol 19(3):181–184
Chirwa S, Aduonum A, Pizarro J, Reasor J, Kawai Y, Gonzalez M (2005) Dopaminergic DA1 signaling couples growth-associated protein-43 and long-term potentiation in guinea pig hippocampus. Brain Res Bull 64(5):433–440
Caberlotto L, Fuxe K, Hurd YL (2000) Characterization of NPY mRNA expressing cells in the human brain: colocalization with Y2 but not Yl mRNA in the cerebral cortex, hippocampus, amygdala, and striarum. J Chem Neuroanat 20(3–4):327–337
Mazze RI, Rice SA, Baden JM (1985) Halothane, isoflurane, and enflurane MAC in pregnant and nonpregnant female and male mice and rats. Anesthesiology 62(3):339–341
Izquierdo I, Medina JH, Vianna MR, Izquierdo LA, Barros DM (1999) Separate mechanisms for short- and long-term memory. Behav Brain Res 103(1):1–11
Culley DJ, Baxter M, Yukhananov R, Crosby G (2003) The memory effects of general anesthesia persist for weeks in young and aged rats. Anesth Analg 96(4):1004–1009
Yon JH, Daniel-Johnson J, Carter LB, Jevtovic-Todorovic V (2005) Anesthesia induces neuronal cell death in the developing rat brain via the intrinsic and extrinsic apoptotic pathways. Neuroscience 135(3):815–827
Chalon J, Tang CK, Ramanathan S, Eisner M, Katz R, Turndorf H (1981) Exposure to halothane and enflurane affects learning function of murine progeny. Anesth Analg 60(11):794–797
Li Y, Liang G, Wang S, Meng Q, Wang Q, Wei H (2007) Effect of fetal exposure to isoflurane on postnatal memory and learning in rats. Neuropharmacology 53(8):942–950
McClaine RJ, Uemura K, de la Fuente SG, Manson RJ, Booth JV, White WD, Campbell KA, McClaine DJ, Benni PB, Eubanks WS, Reynolds JD (2005) General anesthesia improves fetal cerebral oxygenation without evidence of subsequent neuronal injury. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 25(8):1060–1069
Sametsky EA, Disterhoft JF, Geinisman Y, Nicholson DA (2010) Synaptic strength and postsynaptically silent synapses through advanced aging in rat hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons. Neurobiol Aging 31(5):813–825
Thompson JV, Sullivan RM, Wilson DA (2008) Developmental emergence of fear learning corresponds with changes in amygdala synaptic plasticity. Brain Res 1200:58–65
Gruart A, Munoz MD, Delgado-Garcia JM (2006) Involvement of the CA3–CA1 synapse in the acquisition of associative learning in behaving mice. J Neurosci 26(4):1077–1087
Xiao N, Li SZ, Zhang XP, Chen SY (2008) Effect of ephedrine on neuronal plasticity of hypoxic-ischemic brain damage in neonatal rats. Neurosci Lett 435(2):99–102
Greco B, Carli M (2006) Reduced attention and increased impulsivity in mice lacking NPY Y2 receptors: Relation to anxiolytic-like phenotype. Behav Brain Res 169(2):325–334
Pedrazzini T, Pralong F, Grouzmann E (2003) Neuropeptide Y: the universal soldier. Cell Mol Life Sci 60(2):350–377
Klapstein GJ, Colmers WF (1993) On the sites of presynaptic inhibition by neuropeptide Y in rat hippocampus in vitro. Hippocampus 3(1):103–111
Bacci A, Huguenard JR, Prince DA (2002) Differential modulation of synaptic transmission by neuropeptide Y in rat neocortical neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99(26):17125–17130
Vezzani A, Sperk G, Colmers WF (1999) Neuropeptide Y: emerging evidence for a functional role in seizure modulation. Trends Neurosci 22(1):25–30
Bracci-Laudiero L, Aloe L, Lundeberg T, Theodorsson E, Stenfors C (1999) Altered levels of neuropeptides characterize the brain of lupus prone mice. Neurosci Lett 275(1):57–60
Nakajima M, Inui A, Teranishi A (1994) Effects of pancreatic polypeptide family peptides on feeding and learning behavior in mice. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 268(2):1010–1014
Cleary J, Semotuk M, Levine AS (1994) Effects of neuropeptide Y on short-term memory. Brain Res 653(1–2):210–214
Acknowledgments
We thank Shu Han, M.D., Ph.D. (Associate Professor, Institute of Anatomy and Cell Biology, School of Medicine, Zhejiang University, China) for technical support and thought-provoking discussions. Our work was supported by Medical and Health Research Fund of Health Department of Zhejiang Provincial, China (No. 2010KYA129).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kong, Fj., Tang, Yw., Lou, Af. et al. Effects of isoflurane exposure during pregnancy on postnatal memory and learning in offspring rats. Mol Biol Rep 39, 4849–4855 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-011-1279-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-011-1279-z