Abstract
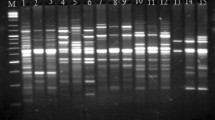
Bagrid catfishes constitute a very important group of fishes having immense commercial importance in south-east countries. The phylogenetic relationships and genome specificity among six species of Bagrid catfishes (Mystus bleekeri, M. cavasius, M. vittatus, M. tengara, M. aor and M. seenghala) were investigated using RAPD markers as discriminating characters for the first time. 511 RAPD fragments were generated using ten decamer primers of arbitrary nucleotide sequences. Amplification reactions resulted in fragments ranging in length between 92 and 2,863 bp, which were assigned to 155 RAPD loci. Clearly resolved and repeatable bands were scored for their presence or absence in a binary matrix. Different RAPD profiles were observed for all the six Mystus species. In the present study three group diagnostic, eleven group exclusive and 18 species-specific markers were generated. Thus six Mystus species can be successfully differentiated on the basis of these 18 species-specific RAPD markers. UPGMA dendrogram constructed on the basis of genetic distance formed two distinct clusters, M. seenghala and M. aor form one separate cluster from other four species i.e., M. tengara, M. cavasius, M. bleekeri and M. vittatus. The inferences drawn from the above study clearly showed their genetic distinctness from the other four Mystus species and supported their inclusion into a separate genus, Sperata.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Talwar PK, Jhingran AG (1991) Inland fisheries of India and adjacent countries, vol 2. Oxford and IBH Publishing Co, New Delhi, India, pp 545–575
Tripathi SD (1996) Present status of breeding and culture of catfishes in South Asia. Aquat Living Resour 9:219–228
Yadev B (2006) Indian Fisheries. In: Fish and fisheries, II edn. Daya Publishing House, Delhi, India, pp 183–190
Jayaram KC (1955) A preliminary review of the genera of the family Bagridae (Pisces:Siluroidea). Proc Natl Inst Sci India 21B(3):120–128
Jayaram KC (1971) Contributions to the study of Bagrid fishes: generic status of Aorichthys Wu (Siluroidea: Bagridae). Proc Zool Soc Calcutta 24(2):149–156
Roberts TR (1994) Systematic revision of Asian Bagrid catfishes of the genus Mystus sensu stricto with a new species from Thailand and Combodia. Ichthyol Explor Freshw 5(3):241–256
Jayaram KC (2002) The fresh water fishes of the Indian region. Narendra publishing House, Delhi, India, pp 220–240
Froese R, Pauly D (2007) Fish base. World Wide Web electronic publication. www.fishbase.org. Version. Accessed Nov 2007
Bartish IV, Garkava LP, Rumpunen K, Nybom H (2000) Phylogentetic relationships and differentiation among and within populations of Chaenomeles Lindl. (Rosaceae) estimated with RAPDs and isozymes. Theor Appl Genet 101:554–561
Callejas C, Ochando MD (2001) Molecular identification (RAPD) of the eight species of the genus Barbus (Cyprinidae) in the Iberian Peninsula. J Fish Biol 59:1589–1599
Mohindra V, Khare P, Lal KK, Peyush P, Singh KS, Barman AS, Lakra WS (2007) Molecular discrimination of five Mahseer species from Indian peninsula using RAPD analysis. Acta Zool Sin 53(4):725–732
Dinesh KR, Lim TM, Chua KL, Chan WK, Phang VPE (1993) RAPD analysis: an efficient method of DNA fingerprinting in fishes. Zool Sci 10:849–855
Johnson SL, Midson CN, Ballinger EW, Postlethwait JH (1994) Identification of RAPD primers that reveal extensive polymorphisms between laboratory strains of zebrafish. Genomics 19:152–156
Foo CL, Dinesh KR, Lim TM, Chan WK, Phang VP (1995) Inheritance of RAPD markers in the guppy fish Poecilia reticulate. Zool Sci 12:535–541
Bielawski JP, Pumo DE (1997) Randomly amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) analysis of Atlantic Coast striped bass. Heredity 78:32–40
Caccone A, Allegrucci G, Fortunato C, Sbordoni V (1997) Genetic differentiation within the European sea bass D. labrax as revealed by 14 RAPD-PCR assays. J Hered 88:316–324
Cunningham CO, Mo TA (1997) Random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) analysis of three Norwegian Gyrodactylus salaris populations Monogenea: Gyrodactylidae. J Parasitol 83:311–314
Barman HK, Barat A, Yadav BM, Banerjee S, Meher PK, Reddy PVGK, Jana RK (2002) Genetic variation between four species of Indian major carps as revealed by random amplified polymorphic DNA assay. Aquaculture 217(1–4):115–123
Bardakci F (2001) Random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) markers. Turk J Biol 25:185–196
Ruzzante DE, Taggart CT, Cook D, Goddard S (1996) Genetic differentiation between inshore and offshore Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua) off Newfoundland: microsatellite DNA variation and antifreeze level. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 53:634–645
Miller MP (1997) Tools for population genetic analysis (TFPGA, 1.3). A windows program for analysis of allozyme and molecular population genetic data. Computer software distributed by the authors. www.marksgeneticsoftware.net/tfpga.htm
Phale SR, Chauhan S, Bhute YV, Baile VV (2009) Detection of genetic variation in the wild populations of Indian major carps using random amplified polymorphic DNA fingerprinting. J Fish Aquat Sci 4(1):63–70
Hadrys H, Balick M, Schierwater B (1992) Applications of random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) in molecular ecology. Mol Ecol 1:55–63
Tianpei M (1991) Anatomy and systematics of Bagridae (Teleostei) and Siluroid phylogeny. Koeltz Scientific Books, Koenigstein, pp 124–137
Acknowledgments
The grant received from the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR, New Delhi, India) in the form of JRF and SRF to the first author for executing this research work is gratefully acknowledged. Authors are also thankful to the Dept of Zoology, Guru Nanak Dev University, Amritsar as well as to National Bureau of Fish Genetic Resources, Lucknow for providing the lab facilities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saini, A., Dua, A., Mohindra, V. et al. Molecular discrimination of six species of Bagrid catfishes from Indus river system using randomly amplified polymorphic DNA markers. Mol Biol Rep 38, 2961–2965 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-010-9960-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-010-9960-1