Abstract
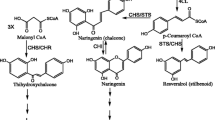
In this study, conserved sequence regions of HMGR, DXR, and CHS (encoding 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA reductase, 1-deoxyxylulose-5-phosphate reductoisomerase and chalcone synthase, respectively) were amplified by reverse transcriptase (RT)-PCR from Eupatorium adenophorum. Quantitative real-time PCR showed that the expression of CHS was related to the level of HHO, an allelochemical isolated from E. adenophorum. Semi-quantitative RT-PCR showed that there was no significant difference in expression of genes among three different tissues, except for CHS. Southern blotting indicated that at least three CHS genes are present in the E. adenophorum genome. A full-length cDNA from CHS genes (named EaCHS1, GenBank ID: FJ913888) was cloned. The 1,455 bp cDNA contained an open reading frame (1,206 bp) encoding a protein of 401 amino acids. Preliminary bioinformatics analysis of EaCHS1 revealed that EaCHS1 was a member of CHS family, the subcellular localization predicted that EaCHS1 was a cytoplasmic protein. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first report of conserved sequences of these genes and of a full-length EaCHS1 gene in E. adenophorum. The results indicated that CHS gene is related to allelopathy of E. adenophorum.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Qiang S (1998) The history and status of the study on Croft on weed (Eupatorium adenophorum Spreng.) a worst worldwide weed. J Wuhan Bot Res 16(4):366–372 (in Chinese)
Baruah NC, Sarma JC, Sarma S, Sharma RP (1994) Seed germination and growth inhibitory cadinenes from Eupatorium adenophorum Spreng. J Chem Ecol 20:1885–1892
Papes M, Peterson AT (2003) Predicting the potential invasive distribution for Eupatorium adenophorum Spreng. J Wuhan Bot Res 21:137–142 (in Chinese)
Duan H, Qiang S, Su XH, Wu HR, Zhu YZ, Liu LL (2004) Genetic diversity of Eupatorium adenophorum determined by AFLP marker. Acta Ecol Sin 25(8):2109–2114 (in Chinese)
Dey S, Sinha B, Kalita J (2005) Effect of Eupatorium adenophorum Spreng leaf extracts on the mustard aphid, Lipaphis erysimi Kalt: a scanning electron microscope study. Microsc Res Tech 66(1):31–36
Chappell J, Wolf F, Proulx J, Cuellar R, Saunders C (1995) Is the reaction catalysed by 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase a rate-limiting step for isoprenoid biosynthesis in plants? Plant Physiol 109(4):1337–1343
Rohmer M (1999) The discovery of a mevalonate-independent pathway for isoprenoid biosynthesis in bacteria, algae and higher plants. Nat Prod Rep 16(5):565–574
Koes RE, Quattrocchio F, Mol JNM (1994) The flavonoid biosynthetic pathway in plants: function and evolution. BioEssays 16:123–132
Ferrer JL, Jez JM, Bowman ME, Dixon RA, Noel JP (1999) Structure of chalcone synthase and the molecular basis of plant polyketide biosynthesis. Nat Struct Biol 6:775–784
Yang GQ, Wan FH, Liu WX, Zhang WX (2006) Physiological effects of allelochemicals from leachates of Ageratina adenophora (Apreng.) on rice seedlings. Allelopathy J 18(2):237–246
Yang GQ, Wan FH, Liu WX, Guo JY (2008) Influence of two allelochemicals from Ageratina adenophora Sprengel on ABA, IAA and ZR contents in roots of upland rice seedlings. Allelopathy J 21(2):253–262
Huang WK, Cheng HM, Guo JY, Gao BD, Wan FH (2007) Cloning, sequence analysis and expression if Escherichia coli of flavonoid 3′-hydroxylase gene of Eupatorium adenophorum sprengel. Plant Physiol Commun 43(5):821–826 (in Chinese)
Murashige T, Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol Plant 15:473–497
Tel-Zur N, Abbo S, Mylaboski D, Mizrahi y (1999) Modified CTAB procedure for DNA isolation from epiphytic cacti of the genera Hylocereus and Selenicereus (Cacataceae). Plant Mol Biol Rep 17:249–254
Kenneth JL, Thomas DS (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real–time quantitative PCR and the 2−△△Ct Method. Methods 25:402–408
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning, a laboratory manual, 2nd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, New York, USA
Shen GA, Pang YZ, Wu WS, Liao ZH, Zhao LX, Sun XF, Tang KX (2006) Cloning and characterization of a root-specific expressing gene encoding 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase from Ginkgo biloba. Mol Biol Rep 33:117–127
Cao XY, Zong ZM, Ju XY, Sun Y, Dai CC, Liu Q, Jiang JH (2010) Molecular cloning, characterization and function analysis of the gene encoding HMG-CoA reductase from Euphorbia Pekinensis Rupr. Mol Biol Rep 37:1559–1567
Schwender J, Müller C, Zeidler J, Lichtenthaler HK (1999) Cloning and heterologous expression of a cDNA encoding 1-deoxy-d-xylulose-5-phosphate reductoisomerase of Arabidopsis thaliana. FEBS Lett 455:140–144
Yang C, Wang ZD, Hollebonea BP, Browna CE, Landriault M (2009) Characteristics of bicyclic sesquiterpanes in crude oils and petroleum products. J Chromatogr A 1216(20):4475–4484
Han YY, Ming F, Wang JW, Wen G, Ye MM, Shen DL (2006) Cloning and characterization of a novel chalcone synthase gene from Phalaenopsis hybrida Orchid flowers. Russ J Plant Physiol 53(2):223–230
Lu X, Zhou W, Gao F (2009) Cloning, characterization and localization of CHS gene from blood orange, Citrus sinensis (L.) Osbeck cv. Ruby. Mol Biol Rep 36:1983–1990
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (30771422) and a 973 Projects grant (2009CB119200) from the Ministry of Science and Technology of China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, H., Pei, X., Wan, F. et al. Molecular cloning of allelopathy related genes and their relation to HHO in Eupatorium adenophorum . Mol Biol Rep 38, 4651–4656 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-010-0599-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-010-0599-8