Abstract
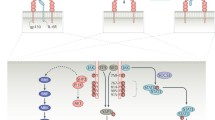
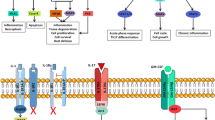
Interleukin-21 (IL-21) is a new member of the type I cytokine superfamily, which binds to a composite receptor that consists of a private receptor (IL-21R) and the common cytokine receptor γ chain. Recently, increasing evidence has shown that IL-21 contributes to the pathogenesis of chronic inflammatory and autoimmune diseases because of its pro-inflammatory and immune-mediated properties. IL-21 induced T-cell activation and pro-inflammatory cytokine secretion in rheumatoid arthritis (RA). IL-21R RNA transcripts were found in synovial tissue samples of patients with RA. In addition, blockade of the IL-21/IL-21R pathway ameliorated disease in animal models of RA and significantly inhibited inflammatory cytokine production in vitro. Moreover, IL-21R deficiency in the K/BxN mouse model of inflammatory arthritis was sufficient to block arthritis initiation completely. All theses findings suggest that IL-21 has important biological effects in autoimmunity that might be a promising therapeutic target for RA. In this review, we discuss the biological features of IL-21 and summarize recent advances in the role of IL-21 in the pathogenesis and treatment of RA.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ji JD, Lee WJ, Kong KA et al (2010) Association of STAT4 polymorphism with rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus: a meta-analysis. Mol Biol Rep 37:141–147
Lipsky PE, van der Heijde DM, St Clair EW et al (2000) Infliximab and methotrexate in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Anti-Tumor Necrosis Factor Trial in Rheumatoid Arthritis with Concomitant Therapy Study Group. N Engl J Med 343:1594–1602
Kay J, Calabrese L (2004) The role of interleukin-1 in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxf) 43(Suppl 3):iii2–iii9
Wolfe F, Michaud K (2004) Lymphoma in rheumatoid arthritis: the effect of methotrexate and anti-tumor necrosis factor therapy in 18,572 patients. Arthritis Rheum 50:1740–1751
Gomez-Reino JJ, Carmona L, Valverde VR et al (2003) Treatment of rheumatoid arthritis with tumor necrosis factor inhibitors may predispose to significant increase in tuberculosis risk: a multicenter active-surveillance report. Arthritis Rheum 48:2122–2127
Miossec P, Korn T, Kuchroo VK (2009) Interleukin-17 and type 17 helper T cells. N Engl J Med 361:888–898
Jungel A, Distler JH, Kurowska-Stolarska M et al (2004) Expression of interleukin-21 receptor, but not interleukin-21, in synovial fibroblasts and synovial macrophages of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 50:1468–1476
Monteleone G, Pallone F, Macdonald TT (2009) Interleukin-21 as a new therapeutic target for immune-mediated diseases. Trends Pharmacol Sci 30:441–447
Parrish-Novak J, Dillon SR, Nelson A et al (2000) Interleukin 21 and its receptor are involved in NK cell expansion and regulation of lymphocyte function. Nature 408:57–63
Jang E, Cho SH, Park H et al (2009) A positive feedback loop of IL-21 signaling provoked by homeostatic CD4+CD25− T cell expansion is essential for the development of arthritis in autoimmune K/BxN mice. J Immunol 182:4649–4656
Spolski R, Leonard WJ (2008) The Yin and Yang of interleukin-21 in allergy, autoimmunity and cancer. Curr Opin Immunol 20:295–301
Hiromura Y, Kishida T, Nakano H et al (2007) IL-21 administration into the nostril alleviates murine allergic rhinitis. J Immunol 179:7157–7165
Ettinger R, Kuchen S, Lipsky PE (2008) Interleukin 21 as a target of intervention in autoimmune disease. Ann Rheum Dis 67(Suppl 3):iii83–iii86
Young DA, Hegen M, Ma HL et al (2007) Blockade of the interleukin-21/interleukin-21 receptor pathway ameliorates disease in animal models of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 56:1152–1163
Parrish-Novak J, Foster DC, Holly RD et al (2002) Interleukin-21 and the IL-21 receptor: novel effectors of NK and T cell responses. J Leukoc Biol 72:856–863
Brandt K, Bulfone-Paus S, Foster DC et al (2003) Interleukin-21 inhibits dendritic cell activation and maturation. Blood 102:4090–4098
Douagi I, Colucci F, Di Santo JP et al (2002) Identification of the earliest prethymic bipotent T/NK progenitor in murine fetal liver. Blood 99:463–471
Caruso R, Fina D, Peluso I et al (2007) IL-21 is highly produced in Helicobacter pylori-infected gastric mucosa and promotes gelatinases synthesis. J Immunol 178:5957–5965
Andorsky DJ, Timmerman JM (2008) Interleukin-21: biology and application to cancer therapy. Expert Opin Biol Ther 8:1295–1307
Mehta DS, Wurster AL, Grusby MJ (2004) Biology of IL-21 and the IL-21 receptor. Immunol Rev 202:84–95
Collins M, Whitters MJ, Young DA (2003) IL-21 and IL-21 receptor: a new cytokine pathway modulates innate and adaptive immunity. Immunol Res 28:131–140
Mizuguchi M, Asao H, Hara T et al (2009) Transcriptional activation of the interleukin-21 and its receptor genes by human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 tax in human T-cells. J Biol Chem 284:25501–25511
Habib T, Nelson A, Kaushansky K (2003) IL-21: a novel IL-2-family lymphokine that modulates B, T, and natural killer cell responses. J Allergy Clin Immunol 112:1033–1045
Habib T, Senadheera S, Weinberg K et al (2002) The common gamma chain (gamma c) is a required signaling component of the IL-21 receptor and supports IL-21-induced cell proliferation via JAK3. Biochemistry 41:8725–8731
Brandt K, Singh PB, Bulfone-Paus S et al (2007) Interleukin-21: a new modulator of immunity, infection, and cancer. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 18:223–232
Ozaki K, Kikly K, Michalovich D et al (2000) Cloning of a type I cytokine receptor most related to the IL-2 receptor beta chain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:11439–11444
Strengell M, Matikainen S, Siren J et al (2003) IL-21 in synergy with IL-15 or IL-18 enhances IFN-gamma production in human NK and T cells. J Immunol 170:5464–5469
Feldmann M, Maini SR (2008) Role of cytokines in rheumatoid arthritis: an education in pathophysiology and therapeutics. Immunol Rev 223:7–19
Li J, Shen W, Kong K et al (2006) Interleukin-21 induces T-cell activation and proinflammatory cytokine secretion in rheumatoid arthritis. Scand J Immunol 64:515–522
Davis ID, Skak K, Smyth MJ et al (2007) Interleukin-21 signaling: functions in cancer and autoimmunity. Clin Cancer Res 13:6926–6932
Sarkar S, Fox DA (2010) Targeting IL-17 and Th17 cells in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheum Dis Clin N Am 36:345–366
Li X, Yuan FL, Lu WG et al (2010) The role of interleukin-17 in mediating joint destruction in rheumatoid arthritis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 397:131–135
Niu X, He D, Zhang X et al (2010) IL-21 regulates Th17 cells in rheumatoid arthritis. Hum Immunol 71:334–341
Andersson AK, Feldmann M, Brennan FM (2008) Neutralizing IL-21 and IL-15 inhibits pro-inflammatory cytokine production in rheumatoid arthritis. Scand J Immunol 68:103–111
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the China National Science Foundation grants no. 30901526 and no. 30873080.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Feng-Lai Yuan, Wei-Hu are the authors contributed equally to this work and should be considered co-first authors.
Wei-Guo Lu, Fei-Hu Chen are the authors contributed equally to this work and should be considered co-corresponding author.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yuan, FL., Hu, W., Lu, WG. et al. Targeting interleukin-21 in rheumatoid arthritis. Mol Biol Rep 38, 1717–1721 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-010-0285-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-010-0285-x