Abstract
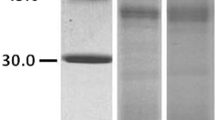
Salsola kali pollen is a common cause of pollinosis during summer and early fall in desert and semi-desert regions. The aim of this study was the identification and characterization of Sal k 3, a new allergen from S. kali pollen. S. kali pollen extract was fractionated by SDS-PAGE and the allergenic profile was determined by IgE-immunoblotting using twelve S. kali allergic patients. Protein identification was carried out by the means of mass spectrometry. Using degenerated primers, two DNA fragments encoding N- and C-terminal domain of Sal k 3 were amplified by PCR, then cloned into the PTZ57R/T vector and sequenced. The open reading frame of Sal k 3 fragments were subcloned in the pET-32b(+) vector, expressed in E. coli, and purified by Ni2+ affinity chromatography. The IgE-binding capacity of rSal k 3 fragments was then studied by IgE-immunoblotting, inhibition assays, and skin prick tests. A 45-kDa allergen was identified as a fragment of the cobalamin-independent methionine synthase (MetE) by mass spectrometry and was detected in the sera of 8/12 (66.6%) of S. kali allergic patients. Moreover, inhibition assays demonstrated that the purified rSal k 3 fragments were similar to their counterparts in the crude extract. Sal k 3 represents a new allergen of S. kali pollen and seems to be an important allergenic compound in S. kali pollen.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Dowaisan A, Fakim N, Khan MR, Arifhodzic N, Panicker R, Hanoon A, Khan I (2004) Salsola pollen as a predominant cause of respiratory allergies in Kuwait. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol 92:262–267
Assarehzadegan MA, Sankian M, Jabberi Azad F, Noorbakhsh R, Varasteh A (2009) Allergy to Salsola kali in a Salsola Incanescens-rich area: role of extensive cross allergenicity. Allergol Int 58:261–266
Colas C, Monzon S, Venturini M, Lezaun A (2006) Double-blind, placebo-controlled study with a modified therapeutic vaccine of Salsola kali (Russian thistle) administered through use of a cluster schedule. J Allergy Clin Immunol 117:810–816
Colas C, Monzon S, Venturini M, Lezaun A, Laclaustra M, Lara S, Fernandez-Caldas E (2005) Correlation between Chenopodiacea/Amaranthacea pollen counts and allergic symptoms in Salsola kali monosensitized patients. J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol 15:254–258
Ezeamuzie CI, Thomson MS, Al-Ali S, Dowaisan A, Khan M, Hijazi Z (2000) Asthma in the desert: spectrum of the sensitizing aeroallergens. Allergy 55:157–162
Suliaman FA, Holmes WF, Kwick S, Khouri F, Ratard R (1997) Pattern of immediate type hypersensitivity reactions in the Eastern Province, Saudi Arabia. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol 78:415–418
Shafiee A, Yunginger JW, Gleich GJ (1981) Isolation and characterization of Russian thistle (Salsola pestifer) pollen allergens. J Allergy Clin Immunol 67:472–481
Carnes J, Fernandez-Caldas E, Marina A, Alonso C, Lahoz C, Colas C, Lezaun A (2003) Immunochemical characterization of Russian thistle (Salsola kali) pollen extracts. Purification of the allergen Sal k 1. Allergy 58:1152–1156
Barderas R, Garcia-Selles J, Salamanca G, Colas C, Barber D, Rodriguez R, Villalba M (2007) A pectin methylesterase as an allergenic marker for the sensitization to Russian thistle (Salsola kali) pollen. Clin Exp Allergy 37:1111–1119
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Sankian M, Varasteh A, Pazouki N, Mahmoudi M (2005) Sequence homology: a poor predictive value for profilins cross-reactivity. Clin Mol Allergy 3:13
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685
Plunkett G (2008) Stability of allergen extracts used in skin testing and immunotherapy. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 16:285–291
Petersen A, Suck R, Hagen S, Cromwell O, Fiebig H, Becker WM (2001) Group 13 grass allergens: structural variability between different grass species and analysis of proteolytic stability. J Allergy Clin Immunol 107:856–862
Nelson HS, Ikle D, Buchmeier A (1996) Studies of allergen extract stability: the effects of dilution and mixing. J Allergy Clin Immunol 98:382–388
Nelson HS (1979) The effect of preservatives and dilution on the deterioration of Russian thistle (Salsola pestifer), a pollen extract. J Allergy Clin Immunol 63:417–425
Ferrer JL, Ravanel S, Robert M, Dumas R (2004) Crystal structures of cobalamin-independent methionine synthase complexed with zinc, homocysteine, and methyltetrahydrofolate. J Biol Chem 279:44235–44238
Song J, Zhang H, Liu Z, Ran P (2008) Mango profilin: cloning, expression and cross-reactivity with birch pollen profilin Bet v 2. Mol Biol Rep 35:231–237
Utley CS, Marcell PD, Allen RH, Antony AC, Kolhouse JF (1985) Isolation and characterization of methionine synthetase from human placenta. J Biol Chem 260:13656–13665
Zeh M, Leggewie G, Hoefgen R, Hesse H (2002) Cloning and characterization of a cDNA encoding a cobalamin-independent methionine synthase from potato (Solanum tuberosum L.). Plant Mol Biol 48:255–265
Pejchal R, Ludwig ML (2005) Cobalamin-independent methionine synthase (MetE): a face-to-face double barrel that evolved by gene duplication. PLoS Biol 3:e31
Chardin H, Mayer C, Senechal H, Tepfer M, Desvaux FX, Peltre G (2001) Characterization of high-molecular-mass allergens in oilseed rape pollen. Int Arch Allergy Immunol 125:128–134
Chen Y, Wang H, Wang X, Cao A, Chen P (2006) Cloning and expression of peroxisomal ascorbate peroxidase gene from wheat. Mol Biol Rep 33:207–213
Fan Z, Yue C, Tang Y, Zhang Y (2009) Cloning, sequence analysis and expression of bacterial lipase-coding DNA fragments from environment in Escherichia coli. Mol Biol Rep 36:1515–1519
Dixon DP, Skipsey M, Grundy NM, Edwards R (2005) Stress-induced protein S-glutathionylation in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 138:2233–2244
Bartra J, Mullol J, del Cuvillo A, Davila I, Ferrer M, Jauregui I, Montoro J, Sastre J, Valero A (2007) Air pollution and allergens. J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol 17(Suppl 2):3–8
D’Amato G (2002) Environmental urban factors (air pollution and allergens) and the rising trends in allergic respiratory diseases. Allergy 57(Suppl 72):30–33
Cortegano I, Civantos E, Aceituno E, del Moral A, Lopez E, Lombardero M, del Pozo V, Lahoz C (2004) Cloning and expression of a major allergen from Cupressus arizonica pollen, Cup a 3, a PR-5 protein expressed under polluted environment. Allergy 59:485–490
Armentia A, Lombardero M, Callejo A, Barber D, Martin Gil FJ, Martin-Santos JM, Vega JM, Arranz ML (2002) Is Lolium pollen from an urban environment more allergenic than rural pollen? Allergol Immunopathol (Madr) 30:218–224
Suarez-Cervera M, Castells T, Vega-Maray A, Civantos E, del Pozo V, Fernandez-Gonzalez D, Moreno-Grau S, Moral A, Lopez-Iglesias C, Lahoz C, Seoane-Camba JA (2008) Effects of air pollution on cup a 3 allergen in Cupressus arizonica pollen grains. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol 101:57–66
Pedreschi R, Hertog M, Robben J, Noben J, Nicolai B (2008) Physiological implications of controlled atmosphere storage of ‘Conference’ pears (Pyrus communis L.): a proteomic approach. Posth Biol Tech 50:110–116
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by Research administration of Mashhad University of Medical Sciences.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Assarehzadegan, M.A., Sankian, M., Jabbari, F. et al. Identification of methionine synthase (Sal k 3), as a novel allergen of Salsola kali pollen. Mol Biol Rep 38, 65–73 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-010-0078-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-010-0078-2