Abstract
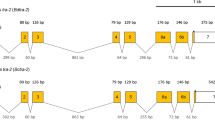
RBP1 is an important splicing factor involved in alternative splicing of the pre-mRNA of Drosophila sex-determining gene dsx. In this work, the Bombyx mori homologue of the rbp1 gene, Bmrbp1, was cloned. The pre-mRNA of Bmrbp1 gene is alternatively spliced to produce four mature mRNAs, named Bmrbp1-PA, Bmrbp1-PB, Bmrbp1-PC and Bmrbp1-PD, with nucleotide lengths of 799 nt, 1,316 nt, 894 nt and 724 nt, coding for 142 aa, 159 aa, 91 aa and 117 aa, respectively. BmRBP1-PA and BmRBP1-PD contain a N terminal RNA recognization motif (RRM) and a C terminal arginine/serine-rich domain, while BmRBP1-PB and BmRBP1-PC only share a RRM. Amino acid sequence alignments showed that BmRBP1 is conserved with its homologues in other insects and with other SR family proteins. The RT-PCR showed that Bmrbp1-PA was strongly expressed in all examined tissues and development stages, but Bmrbp1-PB was weakly expressed in these tissues and stages. The expression of both Bmrbp1-PA and Bmrbp1-PB showed no obvious sex difference. While the Bmrbp1-PC and Bmrbp1-PD were beyond detection by RT-PCR very likely due to their tissue/stage specificity. These results suggested that Bmrbp1 should be a member of SR family splicing factors, whether it is involved in the sex-specific splicing of Bmdsx pre-mRNA needs further research.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Breitbart RE, Andreadis A, Nadal-Ginard B (1987) Alternative splicing: a ubiquitous mechanism for the generation of multiple protein isoforms from single genes. Annu Rev Biochem 56:467–495. doi:10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.002343
Andreadis A, Gallego ME, Nadal-Ginard B (1987) Generation of protein isoform diversity by alternative splicing: mechanistic and biological implications. Annu Rev Cell Biol 3:207–242. doi:10.1146/annurev.cb.03.110187.001231
Norton PA (1994) Alternative pre-mRNA splicing: factors involved in splice site selection. J Cell Sci 107(Pt 1):1–7
Smith CW, Valcárcel J (2000) Alternative pre-mRNA splicing: the logic of combinatorial control. Trends Biochem Sci 25(8):381–388. doi:10.1016/S0968-0004(00)01604-2
Manley JL, Tacke R (1996) SR proteins and splicing control. Genes Dev 10(13):1569–1579. doi:10.1101/gad.10.13.1569
Zahler AM, Lane WS, Stolk JA et al (1992) SR proteins: a conserved family of pre-mRNA splicing factors. Genes Dev 6:837–847. doi:10.1101/gad.6.5.837
Blencowe BJ, Bowman JA, McCracken S, Rosonina E (1999) SR-related proteins and the processing of messenger RNA precursors. Biochem Cell Biol 77(4):277–291
Graveley BR (2000) Sorting out the complexity of SR protein functions. RNA 6(9):1197–1211
Bourgeois CF, Lejeune F, Stévenin J (2004) Broad specificity of SR (serine/arginine) proteins in the regulation of alternative splicing of pre-messenger RNA. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol 78:37–88. doi:10.1016/S0079-6603(04)78002-2
Wu JY, Maniatis T (1993) Specific interactions between proteins implicated in splice site selection and regulated alternative splicing. Cell 75(6):1061–1070
Ca′ceres JF, Krainer AR (1992) Functional analysis of pre-mRNA splicing factor SF2/ASF structural domains. EMBO J 12:4715–4726
Birney E, Kumar S, Krainer AR (1993) Analysis of the RNA-recognition motif and RS and RGG domains: conservation in metazoan pre-mRNA splicing factors. Nucleic Acids Res 21(25):5803–5816
Fu XD (1995) The superfamily of arginine/serine-rich splicing factors. RNA 1:663–680
Heinrichs V, Baker BS (1995) The Drosophila SR protein RBP1 contributes to the regulation of doublesex alternative splicing by recognizing RBP1 RNA target sequences. EMBO J 14(16):3987–4000
Heinrichs V, Baker BS (1997) In vivo analysis of the functional domains of the Drosophila splicing regulator RBP1. Proc Natl Acad Sci 94(1):115–120
Lynch KW, Maniatis T (1996) Assembly of specific SR protein complexes on distinct regulatory elements of the Drosophila doublesex splicing enhancer. Genes Dev 10(16):2089–2101. doi:10.1101/gad.10.16.2089
Graveley BR, Hertel KJ, Maniatis T (1999) SR proteins are ‘locators’ of the RNA splicing machinery. Curr Biol 9(1):R6–R7. doi:10.1016/S0960-9822(99)80032-3
Ohbayashi F, Suzuki MG, Mita K et al (2001) A homologue of the Drosophila doublesex gene is transcribed into sex-specific mRNA isoforms in the silkworm, Bombyx mori. Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol 128(1):145–158. doi:10.1016/S1096-4959(00)00304-3
Suzuki MG, Funaguma S, Kanda T et al (2003) Analysis of the biological functions of a doublesex homologue in Bombyx mori. Dev Genes Evol 213(7):345–354. doi:10.1007/s00427-003-0334-8
Suzuki MG, Funaguma S, Kanda T et al (2005) Role of the male BmDSX protein in the sexual differentiation of Bombyx mori. Evol Dev 7(1):58–68. doi:10.1111/j.1525-142X.2005.05007.x
Ohbayashi F, Suzuki MG, Shimada T (2002) Sex determination in Bombyx mori. Curr Sci 83(4):466–470
Suzuki MG, Ohbayashi F, Mita K et al (2001) The mechanism of sex-specific splicing at the doublesex gene is different between Drosophila melanogaster and Bombyx mori. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 31(12):1201–1211. doi:10.1016/S0965-1748(01)00067-4
Kohtz JD, Jamison SF, Will CL et al (1994) Protein–protein interactions and 5′-splice-site recognition in mammalian mRNA precursors. Nature 368:119–124. doi:10.1038/368119a0
Tian M, Maniatis T (1993) A splicing enhancer complex controls alternative splicing of doublesex pre-mRNA. Cell 74(1):105–114. doi:10.1016/0092-8674(93)90298-5
Kanopka A, Muhlemann O, Akusjarvi G (1996) Inhibition by SR proteins of splicing of a regulated adenovirus pre-mRNA. Nature 381:535–538. doi:10.1038/381535a0
Nagoshi RN, McKeown M, Burtis KC et al (1988) The control of alternative splicing at genes regulating sexual differentiation in D. melanogaster. Cell 53(2):229–236. doi:10.1016/0092-8674(88)90384-4
Forch P, Valcarcel J (2003) Splicing regulation in Drosophila sex determination. Prog Mol Subcell Biol 31:127–151
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by research grants from the National Basic Research Program of China (No. 2005CB121000) and the Program for Changjiang Scholars and Innovative Research Team in University (No. IRT0750).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Z., Zha, X., He, N. et al. Molecular cloning and expression analysis of Bmrbp1, the Bombyx mori homologue of the Drosophila gene rbp1 . Mol Biol Rep 37, 2525–2531 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-009-9768-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-009-9768-z