Abstract
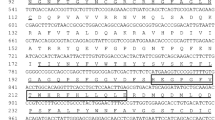
Peptidylarginine deiminase (PADI)-like cDNA sequence was isolated from rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). It consists of a 111-bp 5′-untranslated region, a 731-bp 3′-UTR, and a 2,010-bp open reading frame encoding a protein of 669 amino acids. In the presence of calcium ions, PADI enzymes catalyze the post-translational modification reaction generating citrulline residues. Mammalian PADI enzymes are involved in a number of regulatory processes during cell differentiation and development such as skin keratinization, myelin maturation, and histone deimination. Though five PADI isotypes have been isolated from mammals, in bony fish only one PADI enzyme is present, which contains conserved amino acid residues responsible for catalysis and calcium ion-binding. Sequence identity of piscine PADI protein sequences available at gene databases exceeds 67%. Phylogenetic analyses revealed that not only piscine, but also amphibian and avian PADI-like proteins share most identical amino acid residues with mammalian PADI2. mRNA level of trout PADI-like gene is high in skin, fin, gills, brain, and spleen of rainbow trout. Quantitative Real-Time RT-PCR revealed that PADI gene is differentially expressed in liver, trunk kidney, and spleen of two trout strains, the freshwater-cultured STEELHEAD trout and the brackish water strain BORN.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vossenaar ER, Zendman AJ, van Venrooij WJ, Pruijn GJ (2003) PADI, a growing family of citrullinating enzymes: genes, features and involvement in disease. Bioessays 25:1106–1118
van Venrooij WJ, Pruijn GJ (2000) Citrullination: a small change for a protein with great consequences for rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res 2:249–251
Hung HC, Lin CY, Liao YF, Hsu PC, Tsay GJ, Liu GY (2007) The functional haplotype of peptidylarginine deiminase IV (S55G, A82V and A112G) associated with susceptibility to rheumatoid arthritis dominates apoptosis of acute T leukemia Jurkat cells. Apoptosis 12:475–487
Chavanas S, Mechin MC, Takahara H, Kawada A, Nachat R, Serre G, Simon M (2004) Comparative analysis of the mouse and human peptidylarginine deiminase gene clusters reveals highly conserved non-coding segments and a new human gene PADI6. Gene 330:19–27
Nachat R, Mechin MC, Takahara H, Chavanas S, Charveron M, Serre G, Simon M (2005) Peptidylarginine deiminase isoforms 1–3 are expressed in the epidermis and involved in the deimination of K1 and filaggrin. J Invest Dermatol 124:384–393
von Schalburg KR, Cooper GA, Leong J, Robb A, Lieph R, Rise ML, Davidson WS, Koop BF (2008) Expansion of the genomics research on Atlantic salmon Salmo salar L. project (GRASP) microarray tools. J Fish Biol 72:2051–2070
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)). Methods 25:402–408
Larkin MA, Blackshields G, Brown NP, Chenna R, McGettigan PA, McWilliam H, Valentin F, Wallace IM, Wilm A, Lopez R, Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Higgins DG (2007) Clustal W and Clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics 23:2947–2948
Wilkins MR, Gasteiger E, Bairoch A, Sanchez JC, Williams KL, Appel RD, Hochstrasser DF (1999) Protein identification and analysis tools in the ExPASy server. Methods Mol Biol 112:531–552
Bendtsen JD, Nielsen H, von HG, Brunak S (2004) Improved prediction of signal peptides: SignalP 3.0. J Mol Biol 340:783–795
Kumar S, Tamura K, Nei M (2004) MEGA3: integrated software for molecular evolutionary genetics analysis and sequence alignment. Brief Bioinform 5:150–163
Ji HF, Zhang HY (2008) Bioinformatic identification of the most ancient copper protein architecture. J Biomol Struct Dyn 26:197–201
Bork P, Holm L, Sander C (1994) The immunoglobulin fold. Structural classification, sequence patterns and common core. J Mol Biol 242:309–320
Arita K, Hashimoto H, Shimizu T, Nakashima K, Yamada M, Sato M (2004) Structural basis for Ca(2+)-induced activation of human PADI4. Nat Struct Mol Biol 11:777–783
Rebl A, Siegl E, Kollner B, Fischer U, Seyfert HM (2007) Characterization of twin toll-like receptors from rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss): evolutionary relationship and induced expression by Aeromonas salmonicida salmonicida. Dev Comp Immunol 31:499–510
Rebl A, Hoyheim B, Fischer U, Kollner B, Siegl E, Seyfert HM (2008) Tollip, a negative regulator of TLR-signalling, is encoded by twin genes in salmonid fish. Fish Shellfish Immunol 25:153–162
Yamakoshi A, Ono H, Nishijyo T, Shiraiwa M, Takahara H (1998) Cloning of cDNA encoding a novel isoform (type IV) of peptidylarginine deiminase from rat epidermis. Biochim Biophys Acta 1386:227–232
Rus’D AA, Ikejiri Y, Ono H, Yonekawa T, Shiraiwa M, Kawada A, Takahara H (1999) Molecular cloning of cDNAs of mouse peptidylarginine deiminase type I, type III and type IV, and the expression pattern of type I in mouse. Eur J Biochem 259:660–669
Watanabe K, Akiyama K, Hikichi K, Ohtsuka R, Okuyama A, Senshu T (1988) Combined biochemical and immunochemical comparison of peptidylarginine deiminases present in various tissues. Biochim Biophys Acta 966:375–383
Moscarello MA, Pritzker L, Mastronardi FG, Wood DD (2002) Peptidylarginine deiminase: a candidate factor in demyelinating disease. J Neurochem 81:335–343
Proost P, Loos T, Mortier A, Schutyser E, Gouwy M, Noppen S, Dillen C, Ronsse I, Conings R, Struyf S, Opdenakker G, Maudgal PC, Van DJ (2008) Citrullination of CXCL8 by peptidylarginine deiminase alters receptor usage, prevents proteolysis, and dampens tissue inflammation. J Exp Med 205:2085–2097
Loos T, Mortier A, Gouwy M, Ronsse I, Put W, Lenaerts JP, Van DJ, Proost P (2008) Citrullination of CXCL10 and CXCL11 by peptidylarginine deiminase: a naturally occurring posttranslational modification of chemokines and new dimension of immunoregulation. Blood 112:2648–2656
Acknowledgments
This work was funded by the Exzellenzförderprogramm Mecklenburg-Vorpommern (AU 08 026 entitled “DIREFO”). The authors wish to acknowledge B. F. Koop and W. Davidson for providing the cGRASP chip (http://web.uvic.ca/grasp/). We are grateful to J. Vogt, B. Schöpel, and I. Hennings for excellent technical assistance and to L. Speck and M. Fuchs for sequencing.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rebl, A., Köllner, B., Anders, E. et al. Peptidylarginine deiminase gene is differentially expressed in freshwater and brackish water rainbow trout. Mol Biol Rep 37, 2333–2339 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-009-9738-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-009-9738-5