Abstract
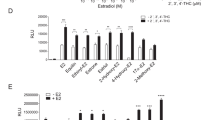
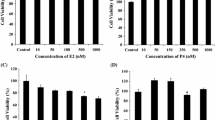
The aim of this study was to elucidate the effects of sex hormones on activity of the ABCG2 promoter in different cell lines. T47D cells and BeWo cells were used as models for ABCG2-expressing cell lines, and luciferase assays using ABCG2 promoter–luciferase constructs were performed. It was shown that progesterone increased the response of the ABCG2 promoter in T47D cells but not in BeWo cells. On the other hand, estradiol had no effect on response of the ABCG2 promoter in either cell line. However, response of the ABCG2 promoter was enhanced by overexpression of ERα in both T47D cells and BeWo cells. T47D cells had higher sensitivity to ERα than did BeWo cells. Furthermore, it was shown that the inductive effect of progesterone on the ABCG2 promoter was inhibited by addition of RU486 or mithramycin A. Therefore, it was thought that the ABCG2 promoter responded to stimulation of the progesterone receptor (PR)-Sp1 pathway in T47D cells. Furthermore, progesterone suppressed the response of the ABCG2 promoter by changing the expression levels of PR-A and PR-B in BeWo cells. These findings suggested that there are differences between cell lines in the regulation mechanism of ABCG2 expression by sex hormone treatment.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schinkel AH, Jonker JW (2003) Mammalian drug efflux transporters of the ATP binding cassette (ABC) family: an overview. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 55:3–29. doi:10.1016/S0169-409X(02)00169-2
Assaraf YG (2006) The role of multidrug resistance efflux transporters in antifolate resistance and folate homeostasis. Drug Resist Updat 9:227–246. doi:10.1016/j.drup.2006.09.001
Latunde-Dada GO, Simpson RJ, McKie AT (2006) Recent advances in mammalian haem transport. Trends Biochem Sci 31:182–188. doi:10.1016/j.tibs.2006.01.005
Scherrmann JM (2005) Expression and function of multidrug resistance transporters at the blood–brain barriers. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol 1:233–246. doi:10.1517/17425255.1.2.233
Young AM, Allen CE, Audus KL (2003) Efflux transporters of the human placenta. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 55:125–132. doi:10.1016/S0169-409X(02)00174-6
Doyle LA, Ross DD (2003) Multidrug resistance mediated by the breast cancer resistance protein BCRP (ABCG2). Oncogene 22:7340–7358. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1206938
Ee PL, Kamalakaran S, Tonetti D, He X, Ross DD, Beck WT (2004) Identification of a novel estrogen response element in the breast cancer resistance protein (ABCG2) gene. Cancer Res 64:1247–1251. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-03-3583
Imai Y, Ishikawa E, Asada S, Sugimoto Y (2005) Estrogen-mediated post transcriptional down-regulation of breast cancer resistance protein/ABCG2. Cancer Res 65:596–604. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-1894
Yasuda S, Itagaki S, Hirano T, Iseki K (2005) Expression level of ABCG2 in the placenta decreases from the mid stage to the end of gestation. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 69:1871–1876. doi:10.1271/bbb.69.1871
Yasuda S, Itagaki S, Hirano T, Iseki K (2006) Effects of sex hormones on regulation of ABCG2 expression in the placental cell line BeWo. J Pharm Pharm Sci 9:133–139
Nakanishi T, Bailey-Dell KJ, Hassel BA, Shiozawa K, Sullivan DM, Turner J, Ross DD (2006) Novel 5′ untranslated region variants of BCRP mRNA are differentially expressed in drug-selected cancer cells and in normal human tissues: implications for drug resistance, tissue-specific expression, and alternative promoter usage. Cancer Res 66:5007–5011. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-4572
Jiang SW, Lloyd RV, Jin L, Eberhardt NL (1997) Estrogen receptor expression and growth-promoting function in human choriocarcinoma cells. DNA Cell Biol 16:969–977
Wang H, Zhou L, Gupta A, Vethanayagam RR, Zhang Y, Unadkat JD, Mao Q (2006) Regulation of BCRP/ABCG2 expression by progesterone and 17beta-estradiol in human placental BeWo cells. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 290:E798–E807. doi:10.1152/ajpendo.00397.2005
Hubler TR, Denny WB, Valentine DL, Cheung-Flynn J, Smith DF, Scammell JG (2003) The FK506-binding immunophilin FKBP51 is transcriptionally regulated by progestin and attenuates progestin responsiveness. Endocrinology 144:2380–2387. doi:10.1210/en.2003-0092
Leonhardt SA, Edwards DP (2002) Mechanism of action of progesterone antagonists. Exp Biol Med 227:969–980
Owen GI, Richer JK, Tung L, Takimoto G, Horwitz KB (1998) Progesterone regulates transcription of the p21(WAF1) cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor gene through Sp1 and CBP/p300. J Biol Chem 273:10696–10701. doi:10.1074/jbc.273.17.10696
Bamberger AM, Bamberger CM, Gellersen B, Schulte HM (1996) Modulation of AP-1 activity by the human progesterone receptor in endometrial adenocarcinoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:6169–6174. doi:10.1073/pnas.93.12.6169
Krikun G, Schatz F, Mackman N, Guller S, Demopoulos R, Lockwood CJ (2000) Regulation of tissue factor gene expression in human endometrium by transcription factors Sp1 and Sp3. Mol Endocrinol 14:393–400. doi:10.1210/me.14.3.393
Cheng YH, Imir A, Suzuki T, Fenkci V, Yilmaz B, Sasano H, Bulun SE (2006) SP1 and SP3 mediate progesterone-dependent induction of the 17beta hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 2 gene in human endometrium. Biol Reprod 75:605–614. doi:10.1095/biolreprod.106.051912
Bierhaus A, Zhang Y, Quehenberger P, Luther T, Haase M, Muller M, Mackman N, Ziegler R, Nawroth PP (1997) The dietary pigment curcumin reduces endothelial tissue factor gene expression by inhibiting binding of AP-1 to the DNA and activation of NF-kappa B. Thromb Haemost 77:772–782
Surh YJ, Han SS, Keum YS, Seo HJ, Lee SS (2000) Inhibitory effects of curcumin and capsaicin on phorbol ester-induced activation of eukaryotic transcription factors, NF-kappaB and AP-1. Biofactors 12:107–112
Rama S, Petrusz P, Rao AJ (2004) Hormonal regulation of human trophoblast differentiation: a possible role for 17beta-estradiol and GnRH. Mol Cell Endocrinol 218:79–94. doi:10.1016/j.mce.2003.12.016
Conneely OM, Mulac-Jericevic B, DeMayo F, Lydon JP, O’Malley BW (2002) Reproductive functions of progesterone receptors. Recent Prog Horm Res 57:339–355. doi:10.1210/rp.57.1.339
Doyle LA, Yang W, Abruzzo LV, Krogmann T, Gao Y, Rishi AK, Ross DD (1998) A multidrug resistance transporter from human MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:15665–15670. doi:10.1073/pnas.95.26.15665
Bailey-Dell KJ, Hassel B, Doyle LA, Ross DD (2001) Promoter characterization and genomic organization of the human breast cancer resistance protein (ATP-binding cassette transporter G2) gene. Biochim Biophys Acta 1520:234–241
Hall JM, McDonnell DP (2005) Coregulators in nuclear estrogen receptor action: from concept to therapeutic targeting. Mol Interv 5:343–357. doi:10.1124/mi.5.6.7
Schultz JR, Petz LN, Nardulli AM (2005) Cell- and ligand-specific regulation of promoters containing activator protein-1 and Sp1 sites by estrogen receptors alpha and beta. J Biol Chem 280:347–354
Wang H, Lee EW, Zhou L, Leung PC, Ross DD, Unadkat JD, Mao Q (2008) Progesterone receptor (PR) isoforms PRA and PRB differentially regulate expression of the breast cancer resistance protein in human placental choriocarcinoma BeWo cells. Mol Pharmacol 73:845–854. doi:10.1124/mol.107.041087
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yasuda, S., Kobayashi, M., Itagaki, S. et al. Response of the ABCG2 promoter in T47D cells and BeWo cells to sex hormone treatment. Mol Biol Rep 36, 1889–1896 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-008-9395-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-008-9395-0