Abstract
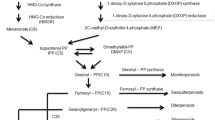
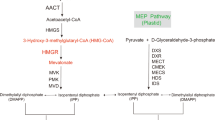
Ginkgo biloba contains terpene triclactones of high pharmaceutical value such as ginkgolides. 1-hydroxy-2-methyl-2-(E)-butenyl-4-diphosphate (HMBPP) reductase (HDR) is proved to be the terminal-acting enzyme in the plastid MEP pathway which provides isoprenoid precursors for the biosynthesis of ginkgolides. The full-length cDNA encoding HDR, designated as GbHDR (Genbank Accession Number DQ364231), was isolated for the first time from G. biloba by RACE method. GbHDR contained a 1,422-bp open reading frame encoding 474 amino acids. The deduced GbHDR protein, showing high identity to HDRs of other plant species, was predicted to possess a chloroplast transit peptide at the N-terminal and four conserved cysteine residues. Two-dimensional structural analysis showed that GbHDR had a similar secondary structure with HDR from Arabidopsis thaliana. Southern blot analysis indicated that GbHDR belonged to a small gene family. Transcription pattern analysis revealed that GbHDR had high transcription in roots, and low in leaves and stems. The cloning of GbHDR gene will enable us to further understand the role of GbHDR involved in terpene triclatones biosynthetic pathway in G. biloba at molecular level.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Braquet P (1988) The ginkgolides from Chinese pharmacopoeia to a new class of pharmacological agents: the antagonists of platelet activating factor. In: Braquet P (ed) Ginkgolides-chemistry, biology, pharmacology and chemical perspectives, vol 1. J. R. Prous Science Publishers, Barcelona, pp 15–34
Braquet P, Spinnewyn B, Braquet M, Bourgain RH, Taylor JE, Etienne A, Drieu K (1985) BN 52021 and related compounds: a new series of highly specific PAF-acether antagonists isolated from Ginkgo biloba. Blood Vessels 16:559–572
Cunningham FX, Gantt E (1998) Genes and enzymes of carotenoid biosynthesis in plants. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 49:557–583
Eisenreich W, Rohdich F, Bacher A (2001) Deoxyxylulose phosphate pathway to terpenoids. Trends Plant Sci 6:78–84
Lichtenthaler HK (1999) The 1-deoxy-d-xylulose 5-phosphate pathway of isoprenoid biosynthesis in plants. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 50:47–66
Rodríguez-Concepción M, Boronat A (2002) Elucidation of the methylerythritol phosphate pathway for isoprenoid biosynthesis in bacteria and plastids. A metabolic milestone achieved through genomics. Plant Physiol 130:1079–1089
Chappell J (1995) Biochemistry and molecular biology of the isoprenoid biosynthetic pathway in plants. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 46:521–547
Eisenreich W, Schwarz M, Cartayrade A, Arigoni D, Zenk MH, Bacher A (1998). The deoxyxylulose phosphate pathway of terpenoid biosynthesis in plants and microorganisms. Chem Biol 5:221–223
Kim SM, Kuzuyama T, Chang YJ, Kim SU (2005) Functional identification of Ginkgo biloba 1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate synthase (DXS) gene by using Escherichia coli disruptants defective in DXS gene. Agr Chem Biotechnol 48:101–104
Gong Y, Liao Z, Guo B, Sun X, Tang K (2006) Molecular cloning and expression profile analysis of Ginkgo biloba DXS gene encoding 1-deoxy-d-xylulose 5-phosphate synthase, the first committed enzyme of the 2-C-methyl-d-erythritol 4-phosphate pathway. Planta Med 72:329–335
Gong Y, Liao Z, Chen M, Zuo K, Guo L, Tan Q, Huang Z, Kai G, Sun X, Tan F, Tang K (2005) Molecular cloning and characterization of a 1-deoxy-d-xylulose 5-phosphate reductoisomerase gene from Ginkgo biloba. DNA Seq 16:111–120
Kim SM, Kuzuyama T, Chang YJ, Song KS, Kim SU (2006) Identification of class 2 1-deoxy-d-xylulose 5-phosphate synthase and 1-deoxy-d-xylulose 5-phosphate reductoisomerase genes from Ginkgo biloba and their transcription in embryo culture with respect to ginkgolide biosynthesis. Planta Med 72:234–240
Kim SM, Kuzuyama T, Chang YJ, Kim SU (2006) Cloning and characterization of 2-C-methyl-D-erythritol 2,4-cyclodiphosphate synthase (MECS) gene from Ginkgo biloba. Plant Cell Rep 25:829–835
Liao Z, Chen M, Gong Y, Guo L, Tan Q, Feng X, Sun X, Tan F, Tang K (2004) A new geranylgeranyl diphosphate synthase gene from Ginkgo biloba, which intermediates the biosynthesis of the key precursor for ginkgolides. DNA Seq 15:153–158
Schepmann HG, Pang J, Matsuda SPT (2001) Cloning and characterization of Ginkgo biloba levopimaradiene synthase, which catalyzed the first committed step in the ginkgolide biosynthesis. Arch Biochem Biophys 392:263–269
Adam P, Hecht S, Eisenreich W, Kaiser J, Grawert T, Arigoni D, Bacher A, Rohdich F (2002) Biosynthesis of terpenes: studies on 1-hydroxy-2-methyl-2-(E)-butenyl-4- diphosphate reductase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:12108–12113
Altincicek B, Duin EC, Reichenberg A, Hedderich R, Kollas AK, Hintz M, Wagner S, Wiesner J, Beck E, Jomaa H (2002) LytB protein catalyzes the terminal step of the 2-C-methyl-d-erythritol-4-phosphate pathway of isoprenoid biosynthesis. FEBS Lett 532:437–440
Rohdich F, Hecht S, Gartner K, Adam P, Krieger C, Amslinger S, Arigoni D, Bacher A, Eisenreich W (2002) Studies on the nonmevalonate terpene biosynthetic pathway: metabolic role of IspH (LytB) protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:1158–1163
Wolff M, Seemann M, Tse Sum Bui B, Frapart Y, Tritsch D, Estrabot AG, Rodríguez-Concepción M, Boronat A, Marquet A, Rohmer M (2003) Isoprenoid biosynthesis via the methylerythritol phosphate pathway: the (E)-4-hydroxy-3-methylbut-2-enyl diphosphate reductase (LytB/IspH) from Escherichia coli is a [4Fe–4S] protein. FEBS Lett 541:115–120
Cunningham FX Jr, Lafond TP, Gantt E (2000) Evidence of a role for LytB in the nonmevalonate pathway of isoprenoid biosynthesis. J Bacteriol 182:5841–5848
Botella-Pavía P, Besumbes O, Phillips MA, Carretero-Paulet L, Boronat A, Rodríguez-Concepción M (2004) Regulation of carotenoid biosynthesis in plants: evidence for a key role of hydroxymethylbutenyl diphosphate reductase in controlling the supply of plastidial isoprenoid precursors. Plant J 40:188–199
Jiang L, Cai LH (2000) A method for extracting DNA of Ginkgo biloba. Plant Physiol Commun 36:340–342
Jaakola L, Pirttila AM, Halonen M, Hohtola A (2001) Isolation of high quality RNA from bilberry (Vaccinium myrtillus L.) fruit. Mol Biotechnol 19:201–203
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4:406–425
Thompson JD, Higgins DG, Gibson TJ (1994) Clustal W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res 22:4673–4680
Felsenstein J (1985) Confidence limits on phylogenies: an approach using the bootstrap. Evolution 39:783–791
Seemann M, Bui BT, Wolff M, Tritsch D, Campos N, Boronat A, Marquet A, Rohmer M (2002) Isoprenoid biosynthesis through the methylerythritol phosphate pathway: the (E)-4-hydroxy-3-methylbut-2-enyl diphosphate synthase (GcpE) is a [4Fe–4S] protein. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 41:4337–4339
Emanuelsson O, Nielsen H, Brunak S, von Heijne G (2000) Predicting subcellular localization of proteins based on their N-terminal amino acid sequence. J Mol Biol 300:1005–1016
Combet C, Blanchet C, Geourjon C, Deléage G (2000) NPS@: network protein sequence analysis. TIBS 25:147–150
Cartayrade A, Neau E, Sohier C, Balz JP, Carde JP, Walter J (1997) Ginkgolide and bilobalide biosynthesis in Ginkgo biloba: I. Studies of synthesis, translocation and accumulation of ginkgolides and bilobalide. Plant Physiol Biochem 35:859–868
Guevara-García A, San Román C, Arroyo A, Cortés ME, de la Luz Gutiérrez-Nava M, León P (2005) Characterization of the Arabidopsis clb6 mutant illustrates the importance of posttranscriptional regulation of the methyl-d-erythritol 4-phosphate pathway. Plant Cell 17:628–643
Hsieh M, Goodman H (2005) The arabidopsis IspH homolog is involved in the plastid nonmevalonate pathway of isoprenoid biosynthesis. Plant Physiol 138:641–653
Acknowledgements
This work was funded by China Ministry of Education, and Shanghai Science and Technology Committee.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, J., Wu, W., Cao, S. et al. Molecular cloning and characterization of 1-hydroxy-2-methyl-2-(E)-butenyl-4-diphosphate reductase gene from Ginkgo biloba . Mol Biol Rep 35, 413–420 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-007-9101-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-007-9101-7