Abstract
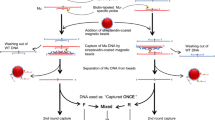
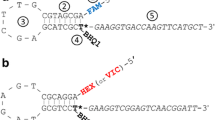
Dot-blot hybridization has been successfully used for the construction of single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP)-based linkage maps, quantitative trait locus analysis, marker-assisted selection, and the identification of species and cultivars. This method is, however, time-consuming, even for a small number of plant samples. We propose a method in which streptavidin-coated magnetic beads replace the nylon membrane for immobilization of the PCR products and are hybridized with allele-specific oligonucleotide probes and a digoxigenin-labeled oligonucleotide hybridized with the allele-specific oligonucleotide probe. After amplification of plant DNA by PCR with the biotinylated primers, those oligonucleotide probes having species-specific or allele-specific sequences were mixed together with the digoxigenin-labeled oligonucleotide and the streptavidin-coated magnetic beads at a temperature suitable for each probe. Species-specific internal transcribed spacer 1 (ITS1) sequences and allele-specific sequences of the hypervariable region I of S-locus receptor kinase (SRK) specifically detected ITS1 sequences and SRK alleles in Brassica species, respectively. SNPs were also successfully analyzed by using allele-specific oligonucleotide probes and competitive oligonucleotides. In the SNP analysis, PCR products were indirectly captured by magnetic beads. SNP alleles of eight cultivars each of Brassica rapa and Raphanus sativus were analyzed using streptavidin-coated magnetic beads. The genotyping results corresponded well with those of dot-blot-SNP analysis. Although allele-specific hybridization using streptavidin-coated magnetic beads is somewhat costly, it is easier and more rapid than dot-blot hybridization. This method is suitable for the analysis of a small number of plant samples with a large number of DNA markers.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bailey AM, Mitchell DJ, Mamjunath KL, Nolasco G, Niblett CL (2002) Identification to the species level of the plant pathogens Phytophthora and Pythium by using unique sequence of the ITS1 region of ribosomal DNA as capture probes for PCR ELISA. FEMS Microbiol 207:153–158
Bonants P, Hagenaar-de WM, Gent-Pelzer MV, Lacourt I, Cooke D, Duncan J (1997) Detection and identification of Phytophthora fragaria Hickman by the polymerase chain reaction. Eur J Plant Pathol 103:345–355
Borrow R, Claus H, Guiver M, Smart L, Jones DM, Kaczmarski EB, Frosch M, Fox AJ (1997) Non-culture diagnosis and serogroup of meningococcal B and C infection by a sialyltransferase (said) PCR ELISA. Epidemiol Infect 118:111–117
Edwards K, Johnstone C, Thompson C (1991) A simple and rapid method for the preparation of plant genomic DNA for PCR analysis. Nucleic Acids Res 19:1349
Fujimoto R, Nishio T (2003) Identification of S haplotypes in Brassica by dot-blot analysis of SP11 alleles. Theor Appl Genet 106:1433–1437
Gibellini D, Zerbini M, Musiani M, Venturoli S, Gentilomi G, Placa ML (1993) Microplate capture hybridization of amplified parvovirus B19 DNA fragment labeled with digoxygenin. Mol Cell Probes 7:453–458
Ishimizu T, Inoue K, Shimonaka M, Saito T, Terai O, Norioka S (1999) PCR-based method for the S-genotypes of Japanese pear cultivars. Theor Appl Genet 98:961–967
Kitashiba H, Zhang SL, Wu J, Shirasawa K, Nishio T (2008) S genotyping and S screening utilizing SFB gene polymorphism in Japanese plum and sweet cherry by dot-blot analysis. Mol Breed 21:339–349
Knight JC, McGuire W, Kortok MM, Kwiatkowski D (1999) Accuracy of genotyping of single nucleotide polymorphisms by PCR-ELISA allele specific oligonucleotide hybridization typing and by amplification refractory mutation system. Clin Chem 45:1860–1863
Kusaba M, Nishio T, Satta Y, Hinata K, Ockendon DJ (1997) Striking sequence similarity in inter- and intra-specific comparisons of class I SLG alleles from Brassica oleracea and Brassica campestris: implications for the evolution and recognition mechanism. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:7673–7678
Landgraf A, Reckmann B, Pingoud A (1991) Direct analysis of polymerase chain reaction products using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay techniques. Anal Biochem 198:86–91
Latorra D, Campbell K, Wolter A, Hurley JM (2003) Enhanced allele-specific PCR discrimination in SNP genotyping using 3′ locked nucleic acid (LNA) primers. Hum Mutat 22:79–85
Li F, Kitashiba H, Inaba K, Nishio T (2009) A Brassica rapa linkage map of EST-based SNP markers for identification of candidate genes controlling flowering time and leaf morphological traits. DNA Res 16:311–323
Li F, Hasegawa Y, Saito M, Shirasawa S, Fukushima A, Ito T, Fujii H, Kishitani S, Kitashiba H, Nishio T (2011) Extensive chromosome homoeology among Brassiceae species were revealed by comparative genetic mapping with high-density EST-based SNP markers in Radish (Raphanus sativus L.). DNA Res 18:401–411
Liu G, Cheng Y, Zhao W, Jin Z, Shan H, Xu G (2011) Single-base extension and ELISA-based approach for single-nucleotide polymorphisms genotyping. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 163:573–576
Loffler J, Hebart H, Sepe S, Schumacher U, Klingbiel T, Einsele H (1998) Detection of PCR-amplified fungal DNA by using a PCR-ELISA system. Med Mycol 36:275–279
Michaels SD, Amasino RM (1998) A robust method for detecting single-nucleotide changes as polymorphic markers by PCR. Plant J 14:381–385
Morgante M, Olivieri AM (1993) PCR-amplified microsatellites as markers in plant genetics. Plant J 3:175–182
Munch M, Nielsen LP, Handberg KJ, Jorgensen PH (2001) Detection and subtyping (H5 and H7) of avian type a influenza virus by reverse transcription-PCR and PCR-ELISA. Arch Virol 146:87–97
Murase K, Shiba H, Iwano M, Che FS, Watanabe M, Isogai A, Takayama S (2004) A membrane-anchored protein kinase involved in Brassica self-incompatibility signaling. Science 303:1516–1519
Nishio T, Sakamoto K, Yamaguchi J (1994) PCR-RFLP of S locus for identification of breeding lines in cruciferous vegetables. Plant Cell Rep 13:550–564
Nou IS, Watanabe M, Isogai A, Hinata K (1993) Comparison of S-alleles and S-glycoproteins between two wild populations of Brassica campestris in Turkey and Japan. Sex Plant Reprod 6:79–86
Ockendon DJ (2000) The S-allele collection of Brassica oleracea. Acta Hortic 539:25–30
Oikawa E, Takuno S, Izumita A, Sakamoto K, Hanzawa H, Kitashiba H, Nishio T (2011) Simple and efficient methods for S genotyping and S screening in genus Brassica by dot-blot analysis. Mol Breed 28:1–12
Olmos A, Cambra M, Dasi MA, Candresse T, Esteban O, Gorris MT, Asensio M (1997) Simultaneous detection and typing of plum pox potyvirus (PPV) isolates by heminested-PCR and PCR-ELISA. J Viol Methods 68:127–137
Orita M, Iwahana H, Kanazawa H, Hayashi K, Sekiya T (1989) Detection of polymorphisms of human DNA by gel electrophoresis as single-strand conformation polymorphisms. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86:2766–2770
Sakamoto K, Nishio T (2001) Distribution of S haplotypes in commercial cultivars of Brassica rapa. Plant Breed 120:155–161
Sakamoto K, Kushaba M, Nishio T (2000) Single-seed PCR-RFLP analysis for the identification of S haplotypes in commercial F1 hybrid cultivars of broccoli and cabbage. Plant Cell Rep 19:400–406
Sato K, Nisho T, Kimura R, Kusaba M, Suzuki T, Hatakeyama K, Ockendon DJ, Satta Y (2002) Coevolution of the S-locus genes SRK, SLG and SP11/SCR in Brassica oleracea and B. rapa. Genetics 162:931–940
Sato Y, Fujimoto R, Toriyama K, Nisho T (2003) Commonality of self-recognition specificity of S haplotypes between Brassica oleracea and Brassica rapa. Plant Mol Biol 52:617–626
Sato H, Endo T, Shiokai S, Nishio T, Yamaguchi M (2010) Identification of 205 current rice cultivars in Japan by dot-blot-SNP analysis. Breed Sci 60:447–451
Sato H, Shiokai S, Maeda H, Nakagomi K, Kaji R, Ohta H, Yamaguchi M, Nishio T (2011) Analysis of QTL for lowering cadmium concentration in rice grains from ‘LAC23’. Breed Sci 61:196–200
Shen R, Fan J-B, Campbell D, Chang W, Chen J, Doucet D, Yeakley J, Bibikova M, Garcia EW, McBride CM, Steemers F, Garcia F, Kermani BG, Gunderson K, Oliphant A (2005) High-throughput SNP genotyping on universal bead arrays. Mutat Res 573:70–82
Shiokai S, Shirasawa K, Sato Y, Nishio T (2010) Improvement of the dot-blot-SNP technique for efficient and cost-effective genotyping. Mol Breed 25:179–185
Shirasawa K, Shiokai S, Yamaguchi M, Kishitani S, Nishio T (2006) Dot-blot-SNP analysis for practical plant breeding and cultivar identification in rice. Theor Appl Genet 113:147–155
Shirasawa K, Takeuchi Y, Ebitane T, Suzuki Y (2008) Identification of gene for rice (Oryza sativa) seed lipoxygenase-3 involved in the generation of stale flavor and development of SNP markers for lipoxygenase-3 deficiency. Breed Sci 58:169–176
Shirasawa S, Endo T, Nakagomi K, Yamaguchi M, Nishio T (2012) Delimitation of a QTL region controlling cold tolerance at booting stage of a cultivar, ‘Lijiangxintuanheigu’, in rice, Oryza sativa L. Theor Appl Genet 124:937–946
Tamminen M, Joutsjoki T, Sjoblom M, Jousten M, Palva A, Ryhanen EL, Joutsjoki V (2004) Screening of lactic acid bacteria from fermented vegetables by carbohydrate profiling and PCR-ELISA. Appl Microbiol 39:439–444
Thomas MA, Scott NS (1993) Microsatellite repeats in grapevine reveal DNA polymorphisms when analyzed as sequence-tagged sites (STSs). Theor Appl Genet 86:985–990
Till BJ, Burtner C, Comai L, Henikoff S (2004) Mismatch cleavage by single-strand specific nuclease. Nucleic Acids Res 32:2632–2641
Tonosaki K, Nishio T (2010) Identification of species in tribe Brassiceae by dot-blot hybridization using species-specific ITS1 probes. Plant Cell Rep 10:1179–1186
Udagawa H, Ishimaru Y, Li F, Sato Y, Kitashiba H, Nishio T (2010) Genetic analysis of interspecific incompatibility in Brassica rapa. Theor Appl Genet 121:689–696
Venora G, Blangiforti S, Frediani M, Maggini F, Gelati MT, Castiglione MR (2000) Nuclear DNA contents, rDNA, chromatin organization, and karyotype evolution in Vicia sect. faba. Protoplasma 213:118–125
Wittwer CT, Reed GH, Gundry CN, Vandersteen JG, Pryor RJ (2003) High-resolution genotyping by amplicon melting analysis using LCGreen. Clin Chem 49:853–860
Wu KS, Tanksley SD (1993) Abundance, polymorphism and genetic mapping of microsatellites in rice. Mol Gen Genet 241:225–235
Zhou GH, Shirakura H, Kamahori M, Okano K, Nagai K, Kambara H (2004) A gel-free SNP genotyping method: bioluminometric assay coupled with modified primer extension reactions (BAMPER) directly from double-stranded PCR products. Hum Mutat 24:155–163
Zuniga J, Soto B, Campo H (2008) Using a gel-free PCR-ELISA for the molecular identification of wheat genotypes carrying wheat-rye translocations. Plant Breed 127:15–19
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Program for Promotion of Basic and Applied Researches for Innovations in Bio-oriented Industry (BRAIN).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tonosaki, K., Kudo, J., Kitashiba, H. et al. Allele-specific hybridization using streptavidin-coated magnetic beads for species identification, S genotyping, and SNP analysis in plants. Mol Breeding 31, 419–428 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-012-9799-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-012-9799-3