Abstract
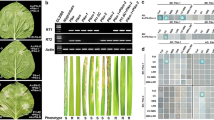
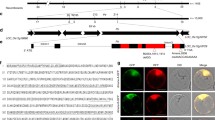
To study similar, but distinct, plant disease resistance (R) specificities exhibited by allelic genes at the rice blast resistance locus Pik/Pikm, we cloned the Pik gene from rice cultivar Kanto51 and compared its molecular features with those of Pikm and of another Pik gene cloned from cv. Kusabue. Like Pikm, Pik is composed of two adjacent NBS-LRR (nucleotide-binding site, leucine-rich repeat) genes: the first gene, Pik1-KA, and the second gene, Pik2-KA. Pik from Kanto51 and Pik from Kusabue were not identical; although the predicted protein sequences of the second genes were identical, the sequences differed by three amino acids within the NBS domain of the first genes. The Pik proteins from Kanto51 and Kusabue differed from Pikm in eight and seven amino acids, respectively. Most of these substituted amino acids were within the coiled-coil (CC) and NBS domains encoded by the first gene. Of these substitutions, all within the CC domain were conserved between the two Pik proteins, whereas all within the NBS domain differed between them. Comparison of the two Pik proteins and Pikm suggests the importance of the CC domain in determining the resistance specificities of Pik and Pikm. This feature contrasts with that of most allelic or homologous NBS-LRR genes characterized to date, in which the major specificity determinant is believed to lie in the highly diverged LRR domain. In addition, our study revealed high evolutionary flexibility in the genome at the Pik locus, which may be relevant to the generation of new R specificities at this locus.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ashikawa I, Hayashi N, Yamane H, Kanamori H, Wu J, Matsumoto T, Ono K, Yano M (2008) Two adjacent nucleotide-binding site-leucine-rich repeat class genes are required to confer Pikm-specific rice blast resistance. Genetics 180:2267–2276
Costanzo S, Jia Y (2010) Sequence variation at the rice blast resistance gene Pi-km locus: implications for the development of allele specific markers. Plant Sci 178:523–530
Eitas TK, Dangl JL (2010) NB-LRR proteins: pairs, pieces, perception, partners, and pathways. Curr Opin Plant Biol 13:472–477
Ellis JG, Lawrence GJ, Luck JE, Dodds PN (1999) Identification of regions in alleles of the flax rust resistance gene L that determine differences in gene-for-gene specificity. Plant Cell 11:495–506
Fuse T, Sasaki T, Yano M (2001) Ti-plasmid vectors useful for functional analysis of rice genes. Plant Biotechnol 18:219–222
Hayashi K, Hashimoto N, Daigen M, Ashikawa I (2004) Development of PCR-based SNP markers for rice blast resistance genes at the Piz locus. Theor Appl Genet 108:1212–1220
Hayashi K, Yoshida H, Ashikawa I (2006) Development of PCR-based allele specific and InDel markers sets for nine rice blast resistance genes. Theor Appl Genet 113:251–260
Kiyosawa S (1968) Inheritance of blast-resistance in some Chinese rice varieties and their derivatives. Jpn J Breed 18:193–204
Kiyosawa S (1978) Identification of blast-resistance genes in some rice varieties. Jpn J Breed 28:287–296
Kiyosawa S, Nomura K (1988) Disease resistance in crop plants and mutational breeding. Gamma Field Symposia No. 27. Institute of Radiation Breeding, NIAR. MAFF, Ibaraki
Lee S-K, Song M-Y, Seo Y-S, Kim H-K, Ko S, Cao P-J, Suh J-P, Yi G, Roh J-H, Lee S, An G, Hahn T-R, Wang G-L, Ronald P, Jeon J-S (2009) Rice Pi5-mediated resistance to Magnaporthe oryzae requires the presence of two CC-NB-LRR genes. Genetics 181:1627–1638
Liu G, Lu G, Zeng L, Wang GL (2002) Two broad-spectrum blast resistance genes, Pi9(t) and Pi2(t), are physically linked on rice chromosome 6. Mol Genet Genomics 267:472–480
Liu J, Wang X, Mitchell T, Hu Y, Liu X, Dai L, Wang G-L (2010) Recent progress and understanding of the molecular mechanisms of the rice-Magnaporthe oryzae interaction. Mol Plant Pathol 11:419–427
Loutre C, Wicker T, Travella S, Galli P, Scofield S, Fahima T, Feuillet C, Keller B (2009) Two different CC-NBS-LRR genes are required for Lr10-mediated leaf rust resistance in tetraploid and hexaploid wheat. Plant J 60:1043–1054
Martin GB, Bogdanove AJ, Sessa G (2003) Understanding the function of plant disease resistance proteins. Annu Rev Plant Biol 54:23–61
Messing J, Crea R, Seebung PH (1981) A system for shotgun DNA sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res 9:309–321
Meyers BC, Kaushik S, Nandety RS (2005) Evolving disease resistance genes. Curr Opin Plant Biol 8:129–134
Mondragon-Palomino M, Meyers BC, Michelmore RW, Gaut BS (2002) Patterns of positive selection in the complete NBS-LRR gene family of Arabidopsis thaliana. Genome Res 12:1305–1315
Narusaka M, Shirasu K, Noutoshi Y, Kubo Y, Shiraishi T, Iwabuchi M, Narusaka Y (2009) RRS1 and RPS4 provide a dual resistance-gene system against fungal and bacterial pathogens. Plant J 60:218–226
Noel L, Moores TL, van der Biezen EA, Parniske M, Daniels MJ, Parker JE, Jones JDG (1999) Pronounced interspecific haplotype divergence at the RPP5 complex disease resistance locus of Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 11:2099–2111
Okuyama Y, Kanzaki H, Abe A, Yoshida K, Tamiru M, Saitoh H, Fujibe T, Matsumura H, Shenton M, Galam DC, Undan J, Ito A, Sone T, Terauchi R (2011) A multifaceted genomics approach allows the isolation of the rice Pia-blast resistance gene consisting of two adjacent NBS-LRR protein genes. Plant J 66:467–479. doi:10.1111/j.1365-313X.2011.04502.x
Ravensdale M, Nemri A, Thrall PH, Ellis JG, Dodds PN (2011) Co-evolutionary interactions between host resistance and pathogen effector genes in flax rust disease. Mol Plant Pathol 12:93–102
Rose LE, Bitter-Eddy PD, Langley CH, Holub EB, Michelmore RW, Beynon JL (2004) The maintenance of extreme amino acid diversity at the disease resistance gene, RPP13, in Arabidopsis thaliana. Genetics 166:1517–1527
Sakata K, Nagamura Y, Numa H, Antonio BA, Nagasaki H, Idonuma A, Watanabe W, Shimizu Y, Horiuchi I, Matsumoto T, Sasaki T, Higo K (2002) RiceGAAS: an automated annotation system and database for rice genome sequence. Nucleic Acid Res 30:98–102
Sinapidou E, Williams K, Nott L, Bahkt S, Tor M et al (2004) Two TIR:NB:LRR genes are required to specify resistance to Peronospora parasitica isolate Cala2 in Arabidopsis. Plant J 38:898–909
Smith SM, Pryor AJ, Hulbert SH (2004) Allelic and haplotypic diversity at the Rp1 rust resistance locus of maize. Genetics 167:1939–1947
Takken FLW, Albrecht M, Tameling WIL (2006) Resistance proteins: molecular switches of plant defense. Curr Opin Plant Biol 9:383–390
Tsunematsu H, Yanoria MJT, Ebron LA, Hayashi N, Ando I, Kato H, Imbe T, Khush GS (2000) Development of monogenic lines of rice for blast resistance. Breed Sci 50:229–234
Wang L, Xu XK, Lin F, Pan QH (2009) Characterization of rice blast resistance genes in the Pik cluster and fine mapping of the Pik-p locus. Phytopathology 99:900–905
Yahiaoui N, Kaur N, Keller B (2009) Independent evolution of functional Pm3 resistance genes in wild tetraploid wheat and domesticated bread wheat. Plant J 57:846–856
Yuan B, Zhai C, Wang W, Zeng X, Xu X, Hu H, Lin F, Wang L, Pan Q (2011) The Pik-p resistance to Magnaporthe oryzae in rice is mediated by a pair of closely linked CC-NBS-LRR genes. Theor Appl Genet 122:1017–1028
Zhai C, Lin F, Dong Z, He X, Yuan B, Zeng X, Wang L, Pan Q (2011) The isolation and characterization of Pik, a rice blast resistance gene which emerged after rice domestication. New Phytol 189:321–334
Zhou B, Qu S, Liu G, Dolan M, Sakai H, Lu G, Bellizzi M, Wang G-L (2006) The eight amino-acid differences within three leucine-rich repeats between Pi2 and Piz-t resistance proteins determine the resistance specificity to Magnaporthe grisea. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 12:1216–1228
Zhou B, Dolan M, Sakai H, Wang G-L (2007) The genomic dynamics and evolutionary mechanism of the Pi2/9 locus in rice. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 20:63–71
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. M. Yano of the National Institute of Agrobiological Sciences, Japan, for his encouragement during this work. This work was supported by a grant from the Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries of Japan (Green Technology Project QT-4005).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ashikawa, I., Hayashi, N., Abe, F. et al. Characterization of the rice blast resistance gene Pik cloned from Kanto51. Mol Breeding 30, 485–494 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-011-9638-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-011-9638-y