Abstract
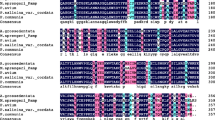
Anthocyanidin synthase (ANS) is a key enzyme of the proanthocyanidin biosynthetic pathway in Arabidopsis. In this study, we report cloning and characterization of an ANS homolog, BjANS, from Brassica juncea. The BjANS cDNA sequence is 1,377 bp long and has a 1,077-bp open reading frame encoding a deduced polypeptide of 358 amino acids with a predicted molecular weight of 40,862 Da and an estimated isoelectric point of 5.18. The putative BjANS protein shows 91–99% amino acid sequence identity with Arabidopsis thaliana, Matthiola incana, B. rapa and B. oleracea ANS proteins. The expression of BjANS was analyzed in yellow- and black-seeded B. juncea accessions to determine its physiological function. RT–PCR analysis showed that BjANS expressed in the seed coats of the black-seeded lines and in embryos of the all lines, but not in the yellow-seeded seed coats. Proanthocyanidins were also detected by histochemical analysis in the seed coat of black-seeded accessions and in embryos of all the lines, but not the yellow-seeded seed coat. Both transcriptional and histochemical analyses confirmed that BjANS was involved in the biosynthesis of proanthocyanidins and in seed coat color formation of B. juncea. Lack of BjANS expression blocked biosynthesis of proanthocyanidins in the yellow seed coat, and therefore seeds appeared yellow because of transparent testa.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abrahams S, Lee E, Walker AR, Tanner GJ, Larkin PJ, Ashton AR (2003) The Arabidopsis TDS4 gene encodes leucoanthocyanidin dioxygenase (LDOX) and is essential for proanthocyanidin synthesis and vacuole development. Plant J 35:624–636
Auger B, Baron C, Lucas MO, Vautrin S, Bergès H, Chalhoub B, Fautrel A, Renard M, Nesi N (2009) Brassica orthologs from BANYULS belong to a small multigene family, which is involved in procyanidin accumulation in the seed. Planta 230:1167–1183
Baudry A, Caboche M, Lepiniec L (2006) TT8 controls its own expression in a feedback regulation involving TTG1 and homologous MYB and bHLH factors, allowing a strong and cell-specific accumulation of flavonoids in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 46:768–779
Chai YR, Lei B, Huang HL, Li JN, Yin JM, Tang ZL, Wang R, Chen L (2009) TRANSPARENT TESTA 12 genes from Brassica napus and parental species: cloning, evolution, and differential involvement in yellow seed trait. Mol Genet Genomics 281:109–123
Debeaujon I, Nesi N, Perez P, Devic M, Grandjean O, Caboche M, Lepiniec L (2003) Proanthocyanidin-accumulating cells in Arabidopsis testa: regulation of differentiation and role in seed development. Plant Cell 15:2514–2531
Dellaporta SL, Wood J, Hicks JB (1983) A plant DNA minipreparation: version II. Plant Mol Biol Rep 1:19–21
Dixon RA, Xie DY, Sharma SB (2005) Proanthocyanidins—a final frontier in flavonoid research? New Phytol 165:9–28
Gollop R, Farhi S, Peri A (2001) Regulation of the leucoanthocyanidin dioxygenase gene expression in Vitis vinifera. Plant Sci 161:579–588
Haughn G, Chaudhury A (2005) Genetic analysis of seed coat development in Arabidopsis. Trends Plant Sci 10:272–277
Lagercrantz U (1998) Comparative mapping between Arabidopsis thaliana and Brassica nigra indicates that Brassica genomes have evolved through extensive genome replication accompanied by chromosome fusions and frequent rearrangements. Genetics 150:1217–1228
Lepiniec L, Debeaujon I, Routaboul JM, Baudry A, Pourcel L, Nesi N, Caboche M (2006) Genetics and biochemistry of seed flavonoids. Annu Rev Plant Biol 57:405–430
Li YG, Tanner G, Larkin P (1996) The DMACA-HCl protocol and the threshold proanthocyanidin content for bloat safety in forage legumes. J Sci Food Agric 70:89–101
Liu XJ, Yuan MZ, Guan CY, Chen SY, Liu SY, Liu ZS (2009) Inheritance, mapping, and origin of yellow-seeded trait in Brassica juncea. Acta Agron Sin 35:839–847
Lysak MA, Cheung K, Kitschke M, Bures P (2007) Ancestral chromosomal blocks are triplicated in Brassiceae species with varying chromosome number and genome size. Plant Physiol 145:402–410
Marles MAS, Gruber MY (2004) Histochemical characterization of unextractable seed coat pigments and quantification of extractable lignin in the Brassicaceae. J Sci Food Agric 84:251–262
Marles MAS, Ray H, Gruber MY (2003) New perspectives on proanthocyanidin biochemistry and molecular regulation. Phytochemistry 64:367–383
Nesi N, Lucas MO, Auger B, Lécureuil A, Guerche P, Kronenberger J, Lepiniec L, Debeaujon I, Renard M (2009) The promoter of the Arabidopsis thaliana BAN gene is active in tannin-accumulating cells of the Brassica napus seed coat. Plant Cell Rep 28:601–617
Pelletier MK, Murrell JR, Shirley BW (1997) Characterization of flavonol synthase and leucoanthocyanidin dioxygenase genes in Arabidopsis. Further evidence for differential regulation of “early” and “late” genes. Plant Physiol 113:1437–1445
Rahman MH, Jeoersbo M, Poulsen MH (2001) Development of yellow-seeded Brassica napus of double low quality. Plant Breed 120:473–478
Rashid A, Rakow G, Downey RK (1994) Development of yellow seeded Brassica napus through interspecific crosses. Plant Breed 112:127–134
Schmidt R, Acarkan A, Boivin K (2001) Comparative structural genomics in the Brassicaceae family. Plant Physiol Biochem 39:253–262
Sharma SB, Dixon RA (2005) Metabolic engineering of proanthocyanidins by ectopic expression of transcription factors in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 44:62–75
Solfanelli C, Poggi A, Loreti E, Alpi A, Perata P (2006) Sucrose-specific induction of the anthocyanin biosynthetic pathway in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 140:637–646
Von Wettstein D (2007) From analysis of mutants to genetic engineering. Annu Rev Plant Biol 58:1–19
Wei YL, Li JN, Lu J, Tang Z, Pu DC, Chai YR (2007) Molecular cloning of Brassica napus TRANSPARENT TESTA 2 gene family encoding potential MYB regulatory proteins of proanthocyanidin biosynthesis. Mol Biol Rep 34:105–120
Wilmouth R, Turnbull J, Welford R, Clifton I, Prescott A, Schofield C (2002) Structure and mechanism of anthocyanidin synthase from Arabidopsis thaliana. Structure 10:93–103
Winkel-Shirley B (2001) It takes a garden. How work on diverse plant species has contributed to an understanding of flavonoid metabolism. Plant Physiol 127:1399–1404
Xie DY, Sharma SB, Paiva NL, Ferreira D, Dixon RA (2003) Role of anthocyanidin reductase, encoded by BANYULS in plant flavonoid biosynthesis. Science 299:396–399
Xu BB, Li JN, Zhang XK, Wang R, Xie LL, Chai YR (2007) Cloning and molecular characterization of a functional flavonoid 3′-hydroxylase gene from Brassica napus. J Plant Physiol 31:350–363
Yan ML (2007) Studies on the molecular mechanism of yellow-seeded formation in Brassica juncea. PhD Dissertation of Hunan Agricultural University, Changsha, China
Yan ML, Liu XJ, Liu ZS, Guan CY, Yuan MZ, Xiong XH (2008) Cloning and expression analysis of the dihydroflavonol 4-reductase gene in Brassica juncea. Acta Agron Sin 34:1–7
Yan ML, Liu ZS, Guan CY, Chen SY, Yuan MZ, Liu XJ (2009) Inheritance and molecular markers for the seed coat color in Brassica juncea. Front Agric China 3:1–6
Acknowledgments
We are acknowledged to Prof. Jinling Meng and Dr. Chaozhi Ma at Huazhong Agricultural University, Dr. Cunkou Qi at Jiangsu Academy of Agricultural Science, Prof. Dianrong Li at Shanxi Hybrid Rapeseed Research Center, Prof. Sheng Zhang at Innner Mongolia Agricultural University, Prof. Wanchang Sun at Gansu Agricultural University, and Prof. Nima Zhuoma at Tibet Autonomous Region Institute of Agricultural Science for providing some of the accessions for this study. This study is financially supported by the National Science Foundation of China (30471098), the Hunan Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (09JJ6059), the Scientific Research Fund of Hunan Provincial Education Department (09B029), the Scientific Research Fund of Pre-State Key Laboratory for Germplasm Innovation and Resource Utilization Of Crops in China (200903).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yan, M., Liu, X., Guan, C. et al. Cloning and expression analysis of an anthocyanidin synthase gene homolog from Brassica juncea . Mol Breeding 28, 313–322 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-010-9483-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-010-9483-4