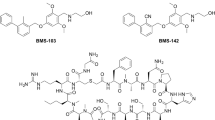
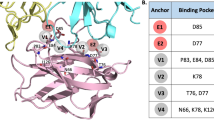
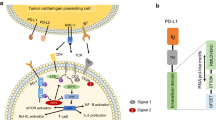
Abstract
Programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1)/programmed cell death protein ligand 1 (PD-L1) plays an important role in negative regulating immunity. The search for effective PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors has been at the cutting-edge of academic and industrial medicinal chemistry, leading to the emergence of 16 clinical candidate drugs and the launch of six monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) drugs. However, due to the unclear mechanism of the interaction between drugs and substances in vivo, the screening of preclinical drugs often takes a long time. In order to shorten the time of drug development as much as possible, the binding mode analysis that can simulate the interaction between drugs and substances in vivo at the molecular level can significantly shorten the drug development process. This paper reviews the mechanism of PD-1/PD-L1 signaling pathway at the molecular level, as well as the research progress and obstacles of inhibitors. Besides, we analyzed the binding mode of recently reported PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors with PD-1 or PD-L1 protein in detail in order to provide ideas for the development of PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors.
Graphical abstract

























Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rattanavirotkul N, Kirschner K, Chandra T (2021) Induction and transmission of oncogene-induced senescence. Cellular Mol Life Sci 78(3):843–852. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-020-03638-0
Teoh JY, Huang J, Ko WY, Lok V, Choi P, Ng CF, Sengupta S, Mostafid H, Kamat AM, Black PC, Shariat S, Babjuk M, Wong MC (2020) Global trends of bladder cancer incidence and mortality, and their associations with tobacco use and gross domestic product per capita. Eur Urol 78(6):893–906. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2020.09.006
Gao P, Lazare C, Cao C, Meng Y, Wu P, Zhi W, Lin S, Wei J, Huang X, Xi L, Chen G, Hu J, Ma D, Wu P (2019) Immune checkpoint inhibitors in the treatment of virus-associated cancers. J Hematol Oncol 12(1):58–67. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13045-019-0743-4
Bai R, Lv Z, Xu D, Cui J (2020) Predictive biomarkers for cancer immunotherapy with immune checkpoint inhibitors. Biomarker Res 8:34–51. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40364-020-00209-0
Nishimura H, Nose M, Hiai H, Minato N, Honjo T (1999) Development of lupus-like autoimmune diseases by disruption of the PD-1 gene encoding an ITIM motif-carrying immunoreceptor. Immunity 11(2):141–151. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1074-7613(00)80089-8
Nishimura H, Okazaki T, Tanaka Y, Nakatani K, Hara M, Matsumori A, Sasayama S, Mizoguchi A, Hiai H, Minato N, Honjo T (2001) Autoimmune dilated cardiomyopathy in PD-1 receptor-deficient mice. Science (New York, N.Y.) 291(5502):319–322. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.291.5502.319
Freeman GJ, Long AJ, Iwai Y, Bourque K, Chernova T, Nishimura H, Fitz LJ, Malenkovich N, Okazaki T, Byrne MC, Horton HF, Fouser L, Carter L, Ling V, Bowman MR, Carreno BM, Collins M, Wood CR, Honjo T (2000) Engagement of the PD-1 immunoinhibitory receptor by a novel B7 family member leads to negative regulation of lymphocyte activation. J Exp Med 192(7):1027–1034. https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.192.7.1027
Latchman Y, Wood CR, Chernova T, Chaudhary D, Borde M, Chernova I, Iwai Y, Long AJ, Brown JA, Nunes R, Greenfield EA, Bourque K, Boussiotis VA, Carter LL, Carreno BM, Malenkovich N, Nishimura H, Okazaki T, Honjo T, Sharpe AH, Freeman GJ (2001) PD-L2 is a second ligand for PD-1 and inhibits T cell activation. Nat Immunol 2(3):261–268. https://doi.org/10.1038/85330
Okazaki T, Honjo T (2007) PD-1 and PD-1 ligands: from discovery to clinical application. Int Immunol 19(7):813–824. https://doi.org/10.1038/85330
Francisco LM, Sage PT, Sharpe AH (2010) The PD-1 pathway in tolerance and autoimmunity. Immunol Rev 236:219–242. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-065X.2010.00923.x
Azuma T, Yao S, Zhu G, Flies AS, Flies SJ, Chen L (2008) B7–H1 is a ubiquitous antiapoptotic receptor on cancer cells. Blood 111(7):3635–3643. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2007-11-123141
Chemnitz JM, Parry RV, Nichols KE, June CH, Riley JL (2004) SHP-1 and SHP-2 associate with immunoreceptor tyrosine-based switch motif of programmed death 1 upon primary human T cell stimulation, but only receptor ligation prevents T cell activation. J Immunol (Baltimore, Md: 1950) 173(2):945–954. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.173.2.945
Sharpe AH, Pauken KE (2018) The diverse functions of the PD1 inhibitory pathway. Nat Rev Immunol 18(3):153–167. https://doi.org/10.1038/nri.2017.108
Hui E, Cheung J, Zhu J, Su X, Taylor MJ, Wallweber HA, Sasmal DK, Huang J, Kim JM, Mellman I, Vale RD (2017) T cell costimulatory receptor CD28 is a primary target for PD-1-mediated inhibition. Science (New York, N.Y.) 355(6332):1428–1433. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aaf1292
Patsoukis N, Brown J, Petkova V, Liu F, Boussiotis LL, V. A. (2012) Selective effects of PD-1 on Akt and Ras pathways regulate molecular components of the cell cycle and inhibit T cell proliferation. Sci Signal 5(230):46–75. https://doi.org/10.1126/scisignal.2002796
Raedler LA (2015) Opdivo (Nivolumab): second PD-1 inhibitor receives FDA approval for unresectable or metastatic melanoma. Am Health Drug Benefits 8:180–183
Poole RM (2014) Pembrolizumab: first global approval. Drugs 74(16):1973–1981. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40265-014-0314-5
Markham A, Duggan S (2018) Cemiplimab: first global approval. Drugs 78(17):1841–1846. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40265-018-1012-5
Inman BA, Longo TA, Ramalingam S, Harrison MR (2017) Atezolizumab: a PD-L1-blocking antibody for bladder cancer. Clin Cancer Res 23(8):1886–1890. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-16-1417
Syed YY (2017) Durvalumab: first global approval. Drugs 77(12):1369–1376. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40265-017-0782-5
Kim ES (2017) Avelumab: first global approval. Drugs 77(8):929–937. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40265-017-0749-6
Lee JY, Lee HT, Shin W, Chae J, Choi J, Kim SH, Lim H, Won Heo T, Park KY, Lee YJ, Ryu SE, Son JY, Lee JU, Heo YS (2016) Structural basis of checkpoint blockade by monoclonal antibodies in cancer immunotherapy. Nat Commun 7:13354–13363. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms13354
Wang X, Ni D, Liu Y, Lu S (2021) Rational design of peptide-based inhibitors disrupting protein-protein interactions. Front Chem 9:682675–682689. https://doi.org/10.3389/fchem.2021.682675
Lin DY, Tanaka Y, Iwasaki M, Gittis AG, Su HP, Mikami B, Okazaki T, Honjo T, Minato N, Garboczi DN (2008) The PD-1/PD-L1 complex resembles the antigen-binding Fv domains of antibodies and T cell receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105(8):3011–3016. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0712278105
Zak KM, Kitel R, Przetocka S, Golik P, Guzik K, Musielak B, Dömling A, Dubin G, Holak TA (2015) Structure of the complex of human programmed death 1, PD-1, and its ligand PD-L1. Structure (London, England: 1993) 23(12):2341–2348. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2015.09.010
Cummings CG, Hamilton AD (2010) Disrupting protein-protein interactions with non-peptidic, small molecule alpha-helix mimetics. Curr Opin Chem Biol 14(3):341–346. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpa.2010.04.001
Hoos A (2016) Development of immuno-oncology drugs—from CTLA4 to PD1 to the next generations. Nat Rev Drug Discovery 15(4):235–247. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrd.2015.35
Konstantinidou M, Zarganes-Tzitzikas T, Magiera-Mularz K, Holak TA, Dömling A (2018) Immune checkpoint PD-1/PD-L1: is there life beyond antibodies? Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 57(18):4840–4848. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201710407
Sharma P, Allison JP (2015) The future of immune checkpoint therapy. Science (New York, NY) 348(6230):56–61. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aaa8172
Ohaegbulam KC, Assal A, Lazar-Molnar E, Yao Y, Zang X (2015) Human cancer immunotherapy with antibodies to the PD-1 and PD-L1 pathway. Trends Mol Med 21(1):24–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molmed.2014.10.009
Naidoo J, Page DB, Li BT, Connell LC, Schindler K, Lacouture ME, Postow MA, Wolchok JD (2015) Toxicities of the anti-PD-1 and anti-PD-L1 immune checkpoint antibodies. Ann oncol 26(12):2375–2391. https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdv383
Scapin G, Yang X, Prosise WW, McCoy M, Reichert P, Johnston JM, Kashi RS, Strickland C (2015) Structure of full-length human anti-PD1 therapeutic IgG4 antibody pembrolizumab. Nat Struct Mol Biol 22(12):953–958. https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.3129
Callahan MK, Postow MA, Wolchok JD (2016) Targeting T cell co-receptors for cancer therapy. Immunity 44(5):1069–1078. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2016.04.023
FDA approves Roche’s cancer immunotherapy TECENTRIQ (atezolizumab) for people with a specific type of metastatic lung cancer. https://www.roche.com/media/releases/med-cor-2016-10-19.htm. Accessed 27 Mar 2022
Lee HT, Lee JY, Lim H, Lee SH, Moon YJ, Pyo HJ, Ryu SE, Shin W, Heo YS (2017) Molecular mechanism of PD-1/PD-L1 blockade via anti-PD-L1 antibodies atezolizumab and durvalumab. Sci Rep 7(1):5532–5543. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-06002-8
Liu K, Tan S, Chai Y, Chen D, Song H, Zhang CW, Shi Y, Liu J, Tan W, Lyu J, Gao S, Yan J, Qi J, Gao GF (2017) Structural basis of anti-PD-L1 monoclonal antibody avelumab for tumor therapy. Cell Res 27(1):151–153. https://doi.org/10.1038/cr.2016.102
Bavencio FDA approval history. https://www.drugs.com/history/bavencio.html. Accessed 27 Mar 2022
Antonia S, Goldberg SB, Balmanoukian A, Chaft JE, Sanborn RE, Gupta A, Narwal R, Steele K, Gu Y, Karakunnel JJ, Rizvi NA (2016) Safety and antitumour activity of durvalumab plus tremelimumab in non-small cell lung cancer: a multicentre, phase 1b study. Lancet Oncol 17(3):299–308. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1470-2045(15)00544-6
Sunshine J, Taube JM (2015) PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors. Curr Opin Pharmacol 23:32–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coph.2015.05.011
AUNP-12—a novel peptide therapeutic targeting PD-1 immune checkpoint pathway for cancer immunotherapy-structure activity relationships & peptide/peptidomimetic analogs. www.differding.com/page/aunp_12_a_novel_peptide_therapeutic_targeting_pd_1_immune_checkpoint_pathway_for_cancer_immunotherapy/f1.html. Accessed 27 Mar 2022
Sasikumar PGN, Ramachandra M, Vadlamani SK, Vemula KR, Satyam LK, Subbarao K, Shrimali KR, Kandepudu S (2011) Immunosuppression modulating compounds. US20110318373, 29 Dec 2011
Sasikumar PG, Satyam LK, Shrimali RK, Subbarao K, Ramachandra R, Vadlamani S, Reddy A, Kumar A, Srinivas A, Reddy S, Gopinath S, Samiulla DS, Ramachandra M (2012) Abstract 2850: demonstration of anti-tumor efficacy in multiple preclinical cancer models using a novel peptide inhibitor (Aurigene-012) of the PD1 signaling pathway. Can Res 72(8 Supplement):2850–2850
Miller MM, Mapelli C, Allen MP, Bowsher MS, Boy KM, Gillis EP, Langley DR, Mull E, Poirier MA, Sanghvi N, Sun L, Tenney DJ, Yeung K, Zhu J, Reid PC, Scola PM (2014) Macrocyclic inhibitors of the PD-1/PD-L1 and CD80(B7–1)/PD-L1 protein/protein interactions. US20140294898, 2 Oct 2014
Niesen FH, Berglund H, Vedadi M (2007) The use of differential scanning fluorimetry to detect ligand interactions that promote protein stability. Nat Protoc 2(9):2212–2221. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2007.321
Villar EA, Beglov D, Chennamadhavuni S, Porco JA Jr, Kozakov D, Vajda S, Whitty A (2014) How proteins bind macrocycles. Nat Chem Biol 10(9):723–731. https://doi.org/10.1038/nchembio.1584
Magiera-Mularz K, Skalniak L, Zak KM, Musielak B, Rudzinska-Szostak E, Berlicki Ł, Kocik J, Grudnik P, Sala D, Zarganes-Tzitzikas T, Shaabani S, Dömling A, Dubin G, Holak TA (2017) Bioactive macrocyclic inhibitors of the PD-1/PD-L1 immune checkpoint. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 56(44):13732–13735. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201707707
Sasikumar PGN, Ramachandra M, Naremaddepalli SSS (2013) Compounds as Immunomdulators. US20130237580, 12 Sep 2013
Weinmann H (2016) Cancer immunotherapy: selected targets and small-molecule modulators. ChemMedChem 11(5):450–466. https://doi.org/10.1002/cmdc.201500566
Chen T, Li Q, Liu Z, Chen Y, Feng F, Sun H (2019) Peptide-based and small synthetic molecule inhibitors on PD-1/PD-L1 pathway: a new choice for immunotherapy? Eur J Med Chem 161:378–398. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2018.10.044
Sasikumar PGN, Ramachandra M, Naremaddepalli SSS (2015) Therapeutic immunomodulating compounds. WO2015044900A1, 2 Apr 2015
Wang T, Wu X, Guo C, Zhang K, Xu J, Li Z, Jiang S (2019) Development of inhibitors of the programmed cell death-1/programmed cell death-ligand 1 signaling pathway. J Med Chem 62(4):1715–1730. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.8b00990
Sasikumar PGN, Ramachandra M, Naremaddepalli SSS (2015) 1,2,4-oxadiazole derivatives as immunomodulators. WO2015033299A1, 12 Mar 2015
Sasikumar PGN, Ramachandra M, Naremaddepalli SSS (2015) 1,3,4-oxadiazole and 1,3,4-thiadiazole Derivatives as Immunomodulators. WO2015033301A1, 12 Mar 2015
Sasikumar PGN, Ramachandra M, Naremaddepalli SSS (2016) 3-substituted-1,2,4-oxadiazole and thiadiazole compounds as immunomodulators. WO2016142886A2, 15 Sep 2016
Sasikumar PGN, Ramachandra M, Naremaddepalli SSS (2016) 1,2,4-oxadiazole and thiadiazole compounds as immunomodulators. WO2016142833A1, 15 Sep 2016
Musielak B, Kocik J, Skalniak L, Magiera-Mularz K, Sala D, Czub M, Stec M, Siedlar M, Holak TA, Plewka J (2019) CA-170—a potent small-molecule PD-L1 inhibitor or not? Molecules (Basel, Switzerland) 24(15):2804–2816. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24152804
Prima V, Kaliberova LN, Kaliberov S, Curiel DT, Kusmartsev S (2017) COX2/mPGES1/PGE2 pathway regulates PD-L1 expression in tumor-associated macrophages and myeloid-derived suppressor cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 114(5):1117–1122. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1612920114
Sharpe AH, Butte MJ, Oyama S (2011) Modulators of immunoinhibitory Rreceptor PD-1, and methods of use thereof. WO2011082400A2, 7 Jul 2011
Chupak LS, Zheng X (2015) Compounds useful as immunomodulators. WO2015034820A1, 12 Mar 2015
Shaabani S, Huizinga HPS, Butera R, Kouchi A, Guzik K, Magiera-Mularz K, Holak TA, Dömling A (2018) A patent review on PD-1/PD-L1 antagonists: small molecules, peptides, and macrocycles (2015–2018). Expert Opin Ther Pat 28(9):665–678. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1612920114
Zak KM, Grudnik P, Guzik K, Zieba BJ, Musielak B, Dömling A, Dubin G, Holak TA (2016) Structural basis for small molecule targeting of the programmed death ligand 1 (PD-L1). Oncotarget 7(21):30323–30335. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.8730
Guzik K, Zak KM, Grudnik P, Magiera K, Musielak B, Törner R, Skalniak L, Dömling A, Dubin G, Holak TA (2017) Small-molecule inhibitors of the programmed cell death-1/programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-1/PD-L1) interaction via transiently induced protein states and dimerization of PD-L1. J Med Chem 60(13):5857–5867. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.7b00293
Chupak LS, Zheng X (2015) Compounds useful as immunomodulators. WO2015160641A2, 22 Oct 2015
Skalniak L, Zak KM, Guzik K, Magiera K, Musielak B, Pachota M, Szelazek B, Kocik J, Grudnik P, Tomala M, Krzanik S, Pyrc K, Dömling A, Dubin G, Holak TA (2017) Small-molecule inhibitors of PD-1/PD-L1 immune checkpoint alleviate the PD-L1-induced exhaustion of T-cells. Oncotarget 8(42):72167–72181. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.20050
Qin M, Cao Q, Zheng S, Tian Y, Zhang H, Xie J, Xie H, Liu Y, Zhao Y, Gong P (2019) Discovery of [1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-a]pyridines as potent inhibitors targeting the programmed cell death-1/programmed cell death-ligand 1 interaction. J Med Chem 62(9):4703–4715. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.9b00312
Qin M, Cao Q, Wu X, Liu C, Zheng S, Xie H, Tian Y, Xie J, Zhao Y, Hou Y, Zhang X, Xu B, Zhang H, Wang X (2020) Discovery of the programmed cell death-1/programmed cell death-ligand 1 interaction inhibitors bearing an indoline scaffold. Eur J Med Chem 186:111856–111868. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2019.111856
Qin M, Meng Y, Yang H, Liu L, Zhang H, Wang S, Liu C, Wu X, Wu D, Tian Y, Hou Y, Zhao Y, Liu Y, Xu C, Wang L (2021) Discovery of 4-arylindolines containing a thiazole moiety as potential antitumor agents inhibiting the programmed cell death-1/programmed cell death-ligand 1 interaction. J Med Chem 64(9):5519–5534. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.0c01958
Cheng B, Ren Y, Niu X, Wang W, Wang S, Tu Y, Liu S, Wang J, Yang D, Liao G, Chen J (2020) Discovery of novel resorcinol dibenzyl ethers targeting the programmed cell death-1/programmed cell death-ligand 1 interaction as potential anticancer agents. J Med Chem 63(15):8338–8358. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.0c00574
Cheng B, Wang W, Niu X, Ren Y, Liu T, Cao H, Wang S, Tu Y, Chen J, Liu S, Yang X, Chen J (2020) Discovery of novel and highly potent resorcinol dibenzyl ether-based PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors with improved drug-like and pharmacokinetic properties for cancer treatment. J Med Chem 63(24):15946–15959. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.0c01684
Cao H, Cheng B, Liu T, Chen J (2021) Synthesis and pharmacological evaluation of novel resorcinol biphenyl ether analogs as small molecule inhibitors of PD-1/PD-L1 with benign toxicity profiles for cancer treatment. Biochem Pharmacol 188:114522–114533. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2021.114522
Yang Y, Wang K, Chen H, Feng Z (2021) Design, synthesis, evaluation, and SAR of 4-phenylindoline derivatives, a novel class of small-molecule inhibitors of the programmed cell death-1/programmed cell death-ligand 1 (PD-1/PD-L1) interaction. Eur J Med Chem 211:113001–113020. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2020.113001
Chen H, Wang K, Yang Y, Huang X, Dai X, Feng Z (2021) Design, synthesis, and structure-activity relationship of programmed cell death-1/programmed cell death-ligand 1 interaction inhibitors bearing a benzo[d]isothiazole scaffold. Eur J Med Chem 217:113377–113394. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2021.113377
Dai X, Wang K, Chen H, Huang X, Feng Z (2021) Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of 1-methyl-1H-pyrazolo[4,3-b]pyridine derivatives as novel small-molecule inhibitors targeting the PD-1/PD-L1 interaction. Bioorg Chem 114:105034–105050. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105034
Guo J, Luo L, Wang Z, Hu N, Wang W, Xie F, Liang E, Yan X, Xiao J, Li S (2020) Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of linear aliphatic amine-linked triaryl derivatives as potent small-molecule inhibitors of the programmed cell death-1/programmed cell death-ligand 1 interaction with promising antitumor effects in vivo. J Med Chem 63(22):13825–13850. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.0c01329
OuYang Y, Gao J, Zhao L, Lu J, Zhong H, Tang H, Jin S, Yue L, Li Y, Guo W, Xu Q, Lai Y (2021) Design, synthesis, and evaluation of o-(biphenyl-3-ylmethoxy)nitrophenyl derivatives as PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors with potent anticancer efficacy in vivo. J Med Chem 64(11):7646–7666. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.1c00370
Liu L, Yao Z, Wang S, Xie T, Wu G, Zhang H, Zhang P, Wu Y, Yuan H, Sun H (2021) Syntheses, biological evaluations, and mechanistic studies of benzo[c][1,2,5]oxadiazole derivatives as potent PD-L1 inhibitors with in vivo antitumor activity. J Med Chem 64(12):8391–8409. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.1c00392
Wang T, Cai S, Wang M, Zhang W, Zhang K, Chen D, Li Z, Jiang S (2021) Novel biphenyl pyridines as potent small-molecule inhibitors targeting the programmed cell death-1/programmed cell death-ligand 1 interaction. J Med Chem 64(11):7390–7403. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.1c00010
Zhang H, Xia Y, Yu C, Du H, Liu J, Li H, Huang S, Zhu Q, Xu Y, Zou Y (2021) Discovery of novel small-molecule inhibitors of PD-1/PD-L1 interaction via structural simplification strategy. Molecules (Basel, Switzerland) 26(11):3347–3369. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.1c00010
Muszak D, Surmiak E, Plewka J, Magiera-Mularz K, Kocik-Krol J, Musielak B, Sala D, Kitel R, Stec M, Weglarczyk K, Siedlar M, Dömling A, Skalniak L, Holak TA (2021) Terphenyl-based small-molecule inhibitors of programmed cell death-1/programmed death-ligand 1 protein-protein interaction. J Med Chem 64(15):11614–11636. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.1c00957
Cutsem EV, Prenen H, Delafontaine B, Spencer K, Mitchell T, Burris H, Kotecki N, Kristeleit R, Pinato D, Sahebjam S, Graham D, Karasic T, Daniel J, O’Hayer K, Geschwindt R, Piha-Paul S et al (2021) 529 Phase 1 study of INCB086550, an oral PD-L1 inhibitor, in immune-checkpoint naive patients with advanced solid tumors. J Immunother Cancer 9(Suppl 2):A559–A560
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
QZ, FX, and YJ ran the statistics analysis; XL and ZJ started the project and wrote the paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, X., Zeng, Q., Xu, F. et al. Progress in programmed cell death-1/programmed cell death-ligand 1 pathway inhibitors and binding mode analysis. Mol Divers 27, 1935–1955 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11030-022-10509-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11030-022-10509-2