Abstract
A library of benzimidazole briged pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine (6a-q) was designed, synthesized and subjected for evaluation for cytotoxic potential. Antiproliferative activity, ranging from 3.1–51.5 μM, was observed against a panel of cancer cell lines which included MCF-7 (breast cancer), A549 (lung cancer), HeLa (cervical cancer) and SiHa (cervical cancer). Among them, 6k, 6l, 6n and 6o have shown significant cytotoxicity and were investigated further to study their probable mechanism of action against MCF-7 cell line. Accumulation of cells at sub-G1 phase was observed in flow cytometric analysis. The detachment of cells from substratum and membrane blebbing seen under bright field microscopy supports the ability of these conjugates to induce apoptosis. Immunostaining and western blot analysis showed EGFR, p-EGFR, STAT3, and p-STAT3 significant downregulation. Western blot analysis demonstrated an elevated level of apoptotic proteins such as p53, p21, Bax, whereas a decrease in the antiapoptotic protein Bcl-2 and procaspase-9, confirming the ability of these conjugates to trigger cell death by apoptosis. EGFR kinase assay confirms the specific activity of conjugates. Molecular docking simulation study disclosed that these molecules fit well in ATP-binding pocket of EGFR. The analysis of docking poses and the atomic interactions of different conjugates rationalize the structural–activity relationship in this series.
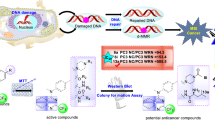
Graphical abstract
Benzimidazole-linked pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine conjugates were synthesized and evaluated for their anticancer potential. All the conjugates have significant anticancer potential. Further mechanistic studies revealed that these conjugates arrest cancer cell growth by EGFR/STAT3 inhibition.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schlessinger J (2000) Cell signaling by receptor tyrosine kinases. Cell 103:211–225. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0092-8674(00)00114-8
Yarden Y, Sliwkowski MX (2001) Untangling the ErbB signalling network. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2:127–137. https://doi.org/10.1038/35052073
Schlessinger J (2004) Common and distinct elements in cellular signaling via EGF and FGF receptors. Science 306:1506–1507. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1105396
Thiel KW, Carpenter G (2007) Epidermal growth factor receptor juxtamembrane region regulates allosteric tyrosine kinase activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci 104:19238–19243. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0703854104
Jura N, Endres NF, Engel K et al (2009) Mechanism for activation of the EGF receptor catalytic domain by the juxtamembrane segment. Cell 137:1293–1307. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2009.04.025
Holbro T, Hynes NE (2004) ErbB receptors: directing key signaling networks throughout life. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 44:195–217. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.pharmtox.44.101802.121440
Speake G, Holloway B, Costello G (2005) Recent developments related to the EGFR as a target for cancer chemotherapy. Curr Opin Pharmacol 5:343–349. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coph.2005.02.007
Olayioye MA, Neve RM, Lane HA, Hynes NE (2000) The ErbB signaling network: receptor heterodimerization in development and cancer. EMBO J 19:3159–3167. https://doi.org/10.1093/emboj/19.13.3159
Temam S, Kawaguchi H, El-Naggar AK et al (2007) Epidermal growth factor receptor copy number alterations correlate with poor clinical outcome in patients with head and neck squamous cancer. J Clin Oncol 25:2164–2170. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2006.06.6605
Tanaka E, Hashimoto Y, Ito T et al (2005) The clinical significance of Aurora-A/STK15/BTAK expression in human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 11:1827–1834. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-04-1627
Kurai M, Shiozawa T, Shih H-C et al (2005) Expression of Aurora kinases A and B in normal, hyperplastic, and malignant human endometrium: Aurora B as a predictor for poor prognosis in endometrial carcinoma. Hum Pathol 36:1281–1288. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.humpath.2005.09.014
Rimawi MF, Shetty PB, Weiss HL et al (2010) Epidermal growth factor receptor expression in breast cancer association with biologic phenotype and clinical outcomes. Cancer 116:1234–1242. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.24816
Salomon DS, Brandt R, Ciardiello F, Normanno N (1995) Epidermal growth factor-related peptides and their receptors in human malignancies. Crit Rev Oncol/Hematol 19:183–232. https://doi.org/10.1016/1040-8428(94)00144-I
Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Murray T, Xu J, Thun MJ (2007) Cancer statistics, 2007. Ca-Cancer J Clin 57:43–66. https://doi.org/10.3322/canjclin.57.1.43
Sharma SV, Bell DW, Settleman J, Haber DA (2007) Epidermal growth factor receptor mutations in lung cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 7:169–181. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc2088
Molina JR, Yang P, Cassivi SD, Schild SE, Adjei AA (2008) Non-small cell lung cancer: epidemiology, risk factors, treatment, and survivorship. Mayo Clin Proc 83:584–594. https://doi.org/10.4065/83.5.584
Wong TW, Lee FY, Yu C et al (2006) Preclinical antitumor activity of BMS-599626, a pan-HER kinase inhibitor that inhibits HER1/HER2 homodimer and heterodimer signaling. Clin Cancer Res 12:6186–6193. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-06-0642
Traxler P, Allegrini PR, Brandt R et al (2004) AEE788 A dual family epidermal growth factor receptor/ErbB2 and vascular endothelial growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor with antitumor and antiangiogenic activity. Cancer Res 64:4931–4941. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-03-3681
Kris MG, Natale RB, Herbst RS et al (2003) Efficacy of gefitinib, an inhibitor of the epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase, in symptomatic patients with non–small cell lung cancer: a randomized trial. JAMA 290:2149–2158. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.290.16.2149
Dowell J, Minna JD, Kirkpatrick P (2005) Erlotinib hydrochloride. Nat Rev Drug Discov 4:13–14. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrd1612
Vasquez RJ, Howell B, Yvon A, Wadsworth P, Cassimeris L (1997) Nanomolar concentrations of nocodazole alter microtubule dynamic instability in vivo and in vitro. Mol Biol Cell 8:973–985. https://doi.org/10.1091/mbc.8.6.973
Heathcote DA, Patel H, Kroll SH et al (2010) A novel pyrazolo [1, 5-a] pyrimidine is a potent inhibitor of cyclin-dependent protein kinases 1, 2, and 9, which demonstrates antitumor effects in human tumor xenografts following oral administration. J Med Chem 53:8508–8522. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmcl.2020.127432
Gao M, Duan L, Luo J et al (2013) Discovery and optimization of 3-(2-(Pyrazolo [1, 5-a] pyrimidin-6-yl) ethynyl) benzamides as novel selective and orally bioavailable discoidin domain receptor 1 (DDR1) inhibitors. J Med Chem 56:3281–3295. https://doi.org/10.1021/jm301824k
Selleri S, Bruni F, Costagli C et al (2005) A novel selective GABAA α1 receptor agonist displaying sedative and anxiolytic-like properties in rodents. J Med Chem 48:6756–6760. https://doi.org/10.1021/jm058002n
Popik P, Kostakis E, Krawczyk M et al (2006) The anxioselective agent 7-(2-chloropyridin-4-yl) pyrazolo-[1, 5-a]-pyrimidin-3-yl](pyridin-2-yl) methanone (DOV 51892) is more efficacious than diazepam at enhancing GABA-gated currents at α1 subunit-containing GABAA receptors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 319:1244–1252. https://doi.org/10.1124/jpet.106.107201
Kamal A, Tamboli JR, Nayak VL, Adil S, Vishnuvardhan M, Ramakrishna S (2013) Synthesis of pyrazolo [1, 5-a] pyrimidine linked aminobenzothiazole conjugates as potential anticancer agents. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 23:3208–3215. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmcl.2013.03.129
McClue SJ, Blake D, Clarke R et al (2002) In vitro and in vivo antitumor properties of the cyclin dependent kinase inhibitor CYC202 (R-roscovitine). Int J Cancer 102:463–468. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.10738
Kamal A, Tamboli JR, Ramaiah MJ et al (2012) Anthranilamide-Pyrazolo [1, 5-a] pyrimidine Conjugates as p53 Activators in Cervical Cancer Cells. ChemMedChem 7:1453–1464. https://doi.org/10.1002/cmdc.201200205
Bagul C, Rao GK, Makani VKK, Tamboli JR, Pal-Bhadra M, Kamal A (2017) Synthesis and biological evaluation of chalcone-linked pyrazolo [1, 5-a] pyrimidines as potential anticancer agents. MedChemComm 8:1810–1816. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7MD00193B
Mullagiri K, Nayak VL, Sunkari S et al (2018) New (3-(1 H-benzo [d] imidazol-2-yl))/(3-(3 H-imidazo [4, 5-b] pyridin-2-yl))-(1 H-indol-5-yl)(3, 4, 5-trimethoxyphenyl) methanone conjugates as tubulin polymerization inhibitors. MedChemComm 9:275–281. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7MD00450H
Donthiboina K, Anchi P, Gurram S et al (2020) Synthesis and biological evaluation of substituted N-(2-(1H-benzo [d] imidazol-2-yl) phenyl) cinnamides as tubulin polymerization inhibitors. Bioorg Chem 103:104191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bioorg.2020.104191
Mani GS, Anchi P, Sunkari S et al (2020) Synthesis of (Z)-3-(arylamino)-1-(3-phenylimidazo [1, 5-a] pyridin-1-yl) prop-2-en-1-ones as potential cytotoxic agents. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 30:127432. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmcl.2020.127432
Ramya PS, Angapelly S, Rani RS et al (2020) Hypervalent iodine (III) catalyzed rapid and efficient access to benzimidazoles, benzothiazoles and quinoxalines: Biological evaluation of some new benzimidazole-imidazo [1, 2-a] pyridine conjugates. Arab J Chem 13:120–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2017.02.007
Korrapati SB, Yedla P, Pillai GG et al (2021) In-silico driven design and development of spirobenzimidazo-quinazolines as potential DNA gyrase inhibitors. Biomed Pharmacother 134:111132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2020.111132
Kamal A, Reddy KS, Ahmed SK et al (2006) Anti-tubercular agents. Part 3. Benzothiadiazine as a novel scaffold for anti-Mycobacterium activity. Bioorg Med Chem 14:650–658. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmc.2005.08.063
Pancholia S, Dhameliya TM, Shah P et al (2016) Benzo[d]thiazol-2-yl(piperazin-1-yl) methanones as new anti-mycobacterial chemotypes: Design, synthesis, biological evaluation and 3D-QSAR studies. Eur J Med Chem 116:187–199. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2016.03.060
Mahesh R, Nayak VL, Babu KS et al (2017) Design, Synthesis, and in vitro and in vivo Evaluations of (Z)-3, 4, 5-Trimethoxystyrylbenzenesulfonamides/sulfonates as Highly Potent Tubulin Polymerization Inhibitors. ChemMedChem 12:678–700. https://doi.org/10.1002/cmdc.201600643
Bhagat S, Supriya M, Pathak S, Sriram D, Chakraborti AK (2019) α-Sulfonamidophosphonates as new anti-mycobacterial chemotypes: Design, development of synthetic methodology, and biological evaluation. Bioorg Chem 82:246–252. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bioorg.2018.09.023
Schneider G, Schneider P, Renner S (2006) Scaffold-hopping: how far can you jump? Qsar Comb Sci 25:1162–1171. https://doi.org/10.1002/qsar.200610091
Padmaja P, Rao GK, Indrasena A et al (2015) Synthesis and biological evaluation of novel pyrano [3, 2-c] carbazole derivatives as anti-tumor agents inducing apoptosis via tubulin polymerization inhibition. Org Biomol Chem 13:1404–1414. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4OB02015D
Srinivas C, Ramaiah MJ, Lavanya A et al (2015) Novel etoposide analogue modulates expression of angiogenesis associated micrornas and regulates cell proliferation by targeting STAT3 in breast cancer. PLoS ONE 10:e0142006. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0142006
Carter RE, Sorkin A (1998) Endocytosis of functional epidermal growth factor receptor-green fluorescent protein chimera. J Biol Chem 273:35000–35007. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.273.52.35000
Stamos J, Sliwkowski MX, Eigenbrot C (2002) Structure of the epidermal growth factor receptor kinase domain alone and in complex with a 4-anilinoquinazoline inhibitor. J Biol Chem 277:46265–46272. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M207135200
Madhavi Sastry G, Adzhigirey M, Day T, Annabhimoju R, Sherman W (2013) Protein and ligand preparation: parameters, protocols, and influence on virtual screening enrichments. J Comput Aided Mol Des 27:221–234. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10822-013-9644-8
Frisch MJ, Trucks GW, Schlegel HB, et al. Gaussian 09. Wallingford, CT; 2016.
Morris GM, Goodsell DS, Halliday RS et al (1998) Automated docking using a Lamarckian genetic algorithm and an empirical binding free energy function. J Comput Chem 19:1639–1662. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1096-987X(19981115)19:14
he PyMOL Molecular Graphics System, Version 1.2r3pre, Schrödinger, LLC.
Shrivastava N, Naim MJ, Alam MJ, Nawaz F, Ahmed S, Alam O (2017) Benzimidazole scaffold as anticancer agent: synthetic approaches and structure–activity relationship. Arch Pharm 350:e201700040. https://doi.org/10.1002/ardp.201700040
Kamal A, Shaik AB, Polepalli S et al (2015) Synthesis of arylpyrazole linked benzimidazole conjugates as potential microtubule disruptors. Bioorg Med Chem 23:1082–1095. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmc.2015.01.004
Sharma P, Reddy TS, Thummuri D et al (2016) Synthesis and biological evaluation of new benzimidazole-thiazolidinedione hybrids as potential cytotoxic and apoptosis inducing agents. Eur J Med Chem 124:608–621. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2016.08.029
Padhy GK, Panda J, Behera AK (2019) Synthesis and Characterization of Novel N-Benzylbenzimidazole Linked Pyrimidine Derivatives as Anticancer Agents. Indian J Pharm Educ Res 53:S129–S134. https://doi.org/10.5530/ijper.53.2s.57
Johnson LN (2009) Protein kinase inhibitors: contributions from structure to clinical compounds. Q Rev Biophys 42:1–40. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0033583508004745
Warnault P, Yasri A, Coisy-Quivy M et al (2013) Recent advances in drug design of epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors. Curr Med Chem 20:2043–2067. https://doi.org/10.2174/0929867311320160001
Acknowledgements
The author C.B acknowledges the Department of Pharmaceuticals (Ministry of Chemicals and Fertilizers, Govt. of India) for the financial support & the CSIR-IICT, Hyderabad for providing facilities. K.R.G thanks UGC for his fellowship. This work was financially supported by the CSIR 12th FYP CSC0111 (SMiLE). The authors thank Y. Suresh for the Flow Cytometry and Confocal Microscopy studies.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Bagul, C., Rao, G.K., Veena, I. et al. Benzimidazole-linked pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine conjugates: synthesis and detail evaluation as potential anticancer agents. Mol Divers 27, 1185–1202 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11030-022-10481-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11030-022-10481-x