Abstract
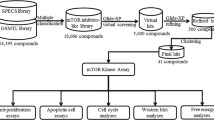
The mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) is an anti-cancer target. In this study, we propose an in silico protocol for identifying mTOR inhibitors from the ZINC natural product database. First, a three-dimensional quantitative structure–activity relationship pharmacophore model was built based on known mTOR inhibitors. The model was validated with an external test set, Fischer’s randomization method, a decoy set and pharmacophore mapping conformation testing. The results showed that the model can predict the mTOR inhibition activity of the tested compounds. Virtual screening was performed based on the best pharmacophore model, and the results were then filtered using a molecular docking approach. In addition, molecular mechanics/generalized born surface area analysis was used to refine the selected candidates. The top 20 natural products were selected as potential mTOR inhibitors, and their structural scaffolds could serve as building blocks in designing drug-like molecules for mTOR inhibition.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yang H, Rudge DG, Koos JD, Vaidialingam B, Yang HJ, Pavletich NP (2013) mTOR kinase structure, mechanism and regulation. Nature 497:217–223. doi:10.1038/nature12122
Meric-Bernstam F, Gonzalez-Angulo AM (2009) Targeting the mTOR signaling network for cancer therapy. J Clin Oncol 27:2278–2287. doi:10.1200/JCO.2008.20.0766
Zeng Z, Sarbassov DD, Samudio IJ, Yee KW, Munsell MF, Jackson CE, Giles FJ, Sabatini DM, Andreeff M, Konopleva M (2007) Rapamycin derivatives reduce mTORC2 signaling and inhibit AKT activation in AML. Blood 109:3509–3512. doi:10.1182/blood-2006-06-030833
Petroulakis E, Mamane Y, Le Bacquer O, Shahbazian D, Sonenberg N (2006) mTOR signaling: implications for cancer and anticancer therapy. Br J Cancer 94:195–199. doi:10.1038/sj.bjc.6602902
Faivre S, Kroemer G, Raymond E (2006) Current development of mTOR inhibitors as anticancer agents. Nat Rev Drug Discov 5:671–688. doi:10.1038/nrd2062
Choo AY, Yoon S-O, Kim SG, Roux PP, Blenis J (2008) Rapamycin differentially inhibits S6Ks and 4E-BP1 to mediate cell-type-specific repression of mRNA translation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:17414–17419. doi:10.1073/pnas.080913610
Borders EB, Bivona C, Medina PJ (2010) Mammalian target of rapamycin: biological function and target for novel anticancer agents. Am J Health Syst Pharm 67:2095–2106. doi:10.2146/ajhp100020
Wang L, Chen L, Liu ZH, Zheng MH (2014) Predicting mTOR inhibitors with a classifier using recursive partitioning and naïve Bayesian approaches. PLoS One 9:e95221. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0095221.eCollection
Carracedo A, Pandolfi PP (2008) The PTEN-PI3K pathway: of feedbacks and cross-talks. Oncogene 27:5527–5541. doi:10.1038/onc.2008.247
Roulin D, Cerantola Y, Dormond-Meuwly A, Demartines N, Dormond O (2010) Targeting mTORC2 inhibits colon cancer cell proliferation in vitro and tumor formation in vivo. Mol Cancer 9:57. doi:10.1186/1476-4598-9-57
Zhang YJ, Duan Y, Zheng XF (2011) Targeting the mTOR kinase domain: the second generation of mTOR inhibitors. Drug Discov Today 16:325–331. doi:10.1016/j.drudis.2011.02.008
Feldman ME, Apsel B, Uotila A, Loewith R, Knight ZA, Ruggero D, Shokat KM (2009) Active-site inhibitors of mTOR target rapamycin-resistant outputs of mTORC1 and mTORC2. PLoS Biol 7:e1000038. doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.1000038
Garcia-Echeverria C (2010) Allosteric and ATP-competitive kinase inhibitors of mTOR for cancer treatment. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 20:4308–4312. doi:10.1016/j.bmcl.2010.05.099
Shen J, Xu X, Cheng F, Liu H, Luo X, Shen J, Chen K, Zhao W, Shen X, Jiang H (2003) Virtual screening on natural products for discovering active compounds and target information. Curr Med Chem 10:2327–2342. doi:10.2174/0929867033456729
Rollinger JM, Stuppner H, Langer T (2008) Virtual screening for the discovery of bioactive natural products. Prog Drug Res 65:211–249. doi:10.1007/978-3-7643-8117-2_6
Kirchmair J, Distinto S, Markt P, Schuster D, Spitzer GM, Liedl KR, Wolber G (2009) How to optimize shape-based virtual screening: choosing the right query and including chemical information. J Chem Inf Model 49:678–692. doi:10.1021/ci8004226
Zhao W, Gu Q, Wang L, Ge H, Li J, Xu J (2011) Three-dimensional pharmacophore modeling of liver-X receptor agonists. J Chem Inf Model 51:2147–2155. doi:10.1021/ci100511v
Sakkiah S, Thangapandian S, John S, Kwon YJ, Lee KW (2010) 3D QSAR pharmacophore based virtual screening and molecular docking for identification of potential HSP90 inhibitors. Eur J Med Chem 45:2132–2140. doi:10.1016/j.ejmech.2010.01.016
Walker EH, Pacold ME, Perisic O, Stephens L, Hawkins PT, Wymann MP, Williams RL (2000) Structural determinants of phosphoinositide 3-kinase inhibition by wortmannin, LY294002, quercetin, myricetin, and staurosporine. Mol Cell 6:909–919. doi:10.1016/S1097-2765(05)00089-4
Zask A, Verheijen JC, Curran K, Kaplan J, Richard DJ, Nowak P, Malwitz DJ, Brooijmans N, Bard J, Svenson K, Lucas J, Toral-Barza L, Zhang WG, Hollander I, Gibbons JJ, Abraham RT, Ayral-Kaloustian S, Mansour TS, Yu K (2009) ATP-competitive inhibitors of the mammalian target of rapamycin: design and synthesis of highly potent and selective pyrazolopyrimidines. J Med Chem 52:5013–5016. doi:10.1021/jm900851f
Zask A, Kaplan J, Verheijen JC, Richard DJ, Curran K, Brooijmans N, Bennett EM, Toral-Barza L, Hollander I, Ayral-Kaloustian S, Yu K (2009) Morpholine derivatives greatly enhance the selectivity of mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) inhibitors. J Med Chem 52:7942–7945. doi:10.1021/jm901415x
Menear KA, Gomez S, Malagu K, Bailey C, Blackburn K, Cockcroft X-L, Ewen S, Fundo A, Gall AL, Hermann G (2009) Identification and optimisation of novel and selective small molecular weight kinase inhibitors of mTOR. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 19:5898–5901. doi:10.1016/j.bmcl.2009.08.069
Li H, Sutter J, Hoffmann R (2000) HypoGen: an automated system for generating 3D predictive pharmacophore models. Pharmacophore Percept Dev Use Drug Des 2:171
Liu T, Lin Y, Wen X, Jorissen RN, Gilson MK (2007) BindingDB: a web-accessible database of experimentally determined protein-ligand binding affinities. Nucleic Acids Res 35:D198–D201. doi:10.1093/nar/gkl999
Apsel B, Blair JA, Gonzalez B, Nazif TM, Feldman ME, Aizenstein B, Hoffman R, Williams RL, Shokat KM, Knight ZA (2008) Targeted polypharmacology: discovery of dual inhibitors of tyrosine and phosphoinositide kinases. Nat Chem Biol 4:691–699. doi:10.1038/nchembio.117
Klein S, Levitzki A (2009) Targeting the EGFR and the PKB pathway in cancer. Curr Opin Cell Biol 21:185–193. doi:10.1016/j.ceb.2008.12.006
Fan Q-W, Knight ZA, Goldenberg DD, Yu W, Mostov KE, Stokoe D, Shokat KM, Weiss WA (2006) A dual PI3 kinase/mTOR inhibitor reveals emergent efficacy in glioma. Cancer Cell 9:341–349. doi:10.1016/j.ccr.2006.03.029
Nagarajan S, Choo H, Cho YS, Oh K-S, Lee BH, Shin KJ, Pae AN (2010) IKK \(\beta \) inhibitors identification part II: ligand and structure-based virtual screening. Bioorg Med Chem 18:3951–3960. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2010.04.030
Tanneeru K, Guruprasad L (2012) Ligand-based 3-D pharmacophore generation and molecular docking of mTOR kinase inhibitors. J Mol Model 18:1611–1624. doi:10.1007/s00894-011-1184-3
Cheng H, Bagrodia S, Bailey S, Edwards M, Hoffman J, Hu Q, Kania R, Knighton DR, Marx MA, Ninkovic S, Sun S, Zhang E (2010) Discovery of the highly potent PI3K/mTOR dual inhibitor PF-04691502 through structure based drug design. Med Chem Commun 1:139–144. doi:10.1039/c0md00072h
Ge H, Wang Y, Li C, Chen N, Xie Y, Xu M, He Y, Gu X, Wu R, Gu Q, Zeng L, Xu J (2013) Molecular dynamics-based virtual screening: accelerating the drug discovery process by high-performance computing. J Chem Inf Model 53:2757–2764. doi:10.1021/ci400391s
Barakat KH, Jordheim LP, Perez-Pineiro R, Wishart D, Dumontet C, Tuszynski JA (2012) Virtual screening and biological evaluation of inhibitors targeting the XPA–ERCC1 interaction. PLoS One 7:e51329. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0051329
Mukherjee P, Shah F, Desai P, Avery M (2011) Inhibitors of SARS-3CLpro: virtual screening, biological evaluation, and molecular dynamics simulation studies. J Chem Inf Model 51:1376–1392. doi:10.1021/ci1004916
Shen J, Tan C, Zhang Y, Li X, Li W, Huang J, Shen X, Tang Y (2010) Discovery of potent ligands for estrogen receptor beta by structure-based virtual screening. J Med Chem 53:5361–5365. doi:10.1021/jm100369g
Acknowledgments
This work was partly supported by a Grant from the National High Technology Research and Development Program of China (863 Program; No. 2012AA020307), Guangdong Recruitment Program of Creative Research Groups, the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 81001372, 81173470), and the Special Funding Program for the National Supercomputer Center in Guangzhou (2012Y2-00048/2013Y2-00045, 201200000037).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, L., Wang, L., Gu, Q. et al. An in silico protocol for identifying mTOR inhibitors from natural products. Mol Divers 18, 841–852 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11030-014-9543-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11030-014-9543-5