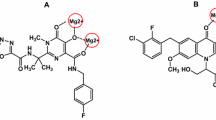
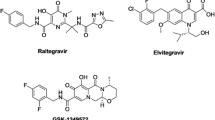
Abstract
The docking studies and comparative molecular field analysis (CoMFA) were performed on highly active molecules of curcumine derivatives against 3′ processing activity of HIV-1 integrase (IN) enzyme. The optimum CoMFA model was selected with statistically significant cross-validated r2 value of 0.815 and non-cross validated r 2 value of 0.99. The common pharmacophore of highly active molecules was used for screening of HIV-1 IN inhibitors. The high contribution of polar interactions in pharmacophore mapping is well supported by docking and CoMFA results. The results of docking, CoMFA, and pharmacophore mapping give structural insights as well as important binding features of curcumine derivatives as HIV-1 IN inhibitors which can provide guidance for the rational design of novel HIV-1 IN inhibitors.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
d’Angelo J, Mouscadet JF, Desmaële D, Zouhiri F, Leh H (2001) HIV-1 integrase: the next target for AIDS therapy?. Pathol Biol 49: 237–246. doi:10.1016/S0369-8114(01)00135-3
Ding J, Das K, Moereels H, Koymans L, Andries K, Janssen PAJ, Hughes SH, Arnold E (1995) Structure of HIV-1 RT/TIBOR 86183 complex reveals similarity in the binding of diverse nonnucleoside inhibitors. Nat Struct Biol 2: 407–415. doi:10.1038/nsb0595-407
Johnson AA, Marchand C, Pommier Y (2004) HIV-1 integrase inhibitors: a decade of research and two drugs in clinical trial. Curr Top Med Chem 4: 1059–1077
The UK collaborative group on HIV drug resistance and UK CHIC study group: (2010) Long-term probability of detecting drug-resistant hiv in treatment-naive patients initiating combination antiretroviral therapy. Clin Infect Dis 50: 1275–1285. doi:10.1086/651684
Harrigan PR (2010) Editorial commentary: HIV drug resistance over the long haul. Clin Infect Dis 50: 1286–1287. doi:10.1086/651685
Pommier Y, Johnson AA, Marchand C (2005) Integrase inhibitors to treat HIV/AIDS. Nat Rev Drug Discov 4: 236–248. doi:10.1038/nrd1660
Richman DD (2001) HIV chemotherapy. Nature 410: 995–1001. doi:10.1038/35073673
Goldgur Y, Craigie R, Cohen GH, Fujiwara T, Yoshinaga T, Fujishita T, Sugimoto H, Endo T, Murai H, Davies DR (1999) Structure of the HIV-1 integrase catalytic domain complexed with an inhibitor: a platform for antiviral drug design. P Natl Acad Sci USA 96: 13040–13043
Zheng R, Jenkins TM, Craigie R (1996) Zinc folds the N-terminal domain of HIV-1 integrase, promotes multimerization, and enhances catalytic activity. P Natl Acad Sci USA 93: 13659–13664
Engelman A, Craigie R (1992) Identification of conserved amino acid residues critical for human immunodeficiency virus type 1 integrase function in vitro. J Virol 66: 6361–6369
Leavitt AD, Shiue L, Varmus HE (1993) Site-directed mutagenesis of HIV-1 integrase demonstrates differential effects on integrase functions in vitro. J Biol Chem 268: 2113–2119
Chiu TK, Davies DR (2004) Structure and function of HIV-1 integrase. Curr Top Med Chem 4: 965–977
Asante-Appiah E, Skalka AM (1997) A metal-induced conformational change and activation of HIV-1 integrase. J Biol Chem 272: 16196–16205. doi:10.1074/jbc.272.26.16196
Drelich M, Wilhelm R, Mous J (1992) Identification of amino acid residues critical for endonuclease and integration activities of HIV-1 IN protein in vitro. Virology 188: 459–468. doi:10.1016/0042-6822(92)90499-F
Bujacz G, Alexandratos J, Wlodawer A, Merkel G, Andrake M, Katz RA, Skalka AM (1997) Binding of different divalent cations to the active site of avian sarcoma virus integrase and their effects on enzymatic activity. J Biol Chem 272: 18161–18168. doi:10.1074/jbc.272.29.18161
Neamati N, Lin Z, Karki RG, Orr A, Cowansage K, Strumberg D, Pais GCG, Voigt JH, Nicklaus MC, Winslow HE (2002) Metal-dependent inhibition of HIV-1 integrase. J Med Chem 45: 5661–5670. doi:10.1021/jm0201417
Grobler JA, Stillmock K, Hu B, Witmer M, Felock P, Espeseth AS, Wolfe A, Egbertson M, Bourgeois M, Melamed J (2002) Diketo acid inhibitor mechanism and HIV-1 integrase: implications for metal binding in the active site of phosphotransferase enzymes. P Natl Acad Sci USA 99: 6661–6666
Maignan S, Guilloteau JP, Zhou-Liu Q, Clément-Mella C, Mikol V (1998) Crystal structures of the catalytic domain of HIV-1 integrase free and complexed with its metal cofactor: high level of similarity of the active site with other viral integrases. J Mol Biol 282: 359–368. doi:10.1006/jmbi.1998.2002
Goldgur Y, Dyda F, Hickman AB, Jenkins TM, Craigie R, Davies DR (1998) Three new structures of the core domain of HIV-1 integrase: an active site that binds magnesium. P Natl Acad Sci USA 95: 9150–9154
Steitz TA (1998) A mechanism for all polymerases. Nature 391: 231–232. doi:10.1038/34542
Chen X, Tsiang M, Yu F, Hung M, Jones GS, Zeynalzadegan A, Qi X, Jin H, Kim CU, Swaminathan S (2008) Modeling, analysis, and validation of a novel HIV integrase structure provide insights into the binding modes of potent integrase inhibitors. J Mol Biol 380: 504–519. doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2008.04.054
Long YQ, Jiang XH, Dayam R, Sanchez T, Shoemaker R, Sei S, Neamati N (2004) Rational design and synthesis of novel dimeric diketoacid-containing inhibitors of HIV-1 integrase: implication for binding to two metal ions on the active site of integrase. J Med Chem 47: 2561–2573. doi:10.1021/jm030559k
Lubkowski J, Yang F, Alexandratos J, Wlodawer A, Zhao H, Burke TR, Neamati N, Pommier Y, Merkel G, Skalka AM (1998) Structure of the catalytic domain of avian sarcoma virus integrase with a bound HIV-1 integrase-targeted inhibitor. P Natl Acad Sci USA 95: 4831–4836
Kawasuji T, Fuji M, Yoshinaga T, Sato A, Fujiwara T, Kiyama R (2006) A platform for designing HIV integrase inhibitors. Part 2: a two-metal binding model as a potential mechanism of HIV integrase inhibitors. Bioorgan Med Chem 14: 8420–8429. doi:10.1016/j.bmc.2006.08.043
Savarino A (2007) In-silico docking of HIV-1 integrase inhibitors reveals a novel drug type acting on an enzyme/DNA reaction intermediate. Retrovirology 4: 21. doi:10.1186/1742-4690-4-21
Hare S, Gupta SS, Valkov E, Engelman A, Cherepanov P (2010) Retroviral intasome assembly and inhibition of DNA strand transfer. Nature 464: 232–236. doi:10.1038/nature08784
Valkov E, Gupta SS, Hare S, Helander A, Roversi P, McClure M, Cherepanov P (2009) Functional and structural characterization of the integrase from the prototype foamy virus. Nucleic Acids Res 37: 243–255. doi:10.1093/nar/gkn938
Gupta P, Roy N, Garg P (2009) Docking-based 3D-QSAR study of HIV-1 integrase inhibitors. Eur J Med Chem 44: 4276–4287. doi:10.1016/j.ejmech.2009.07.010
Kuo CL, Assefa H, Kamath S, Brzozowski Z, Slawinski J, Saczewski F, Buolamwini JK, Neamati N (2004) Application of CoMFA and CoMSIA 3D-QSAR and docking studies in optimization of mercaptobenzenesulfonamides as HIV-1 integrase inhibitors. J Med Chem 47: 385–399. doi:10.1021/jm030378i
Buolamwini JK, Assefa H (2002) CoMFA and CoMSIA 3D QSAR and docking studies on conformationally-restrained cinnamoyl HIV-1 integrase inhibitors: exploration of a binding mode at the active site. J Med Chem 45: 841–852. doi:10.1021/jm010399h
Vajragupta O, Boonchoong P, Morris GM, Olson AJ (2005) Active site binding modes of curcumin in HIV-1 protease and integrase. Bioorgan Med Chem 15: 3364–3368. doi:10.1016/j.bmcl.2005.05.032
Dayam R, Neamati N (2004) Active site binding modes of the ß-diketoacids: a multi-active site approach in HIV-1 integrase inhibitor design. Bioorg Med Chem 12: 6371–6381. doi:10.1016/j.bmc.2004.09.035
Sechi M, Derudas M, Dallocchio R, Dessi A, Bacchi A, Sannia L, Carta F, Palomba M, Ragab O, Chan C (2004) Design and synthesis of novel Indole [beta]-diketo acid derivatives as HIV-1 integrase inhibitors. J Med Chem 47: 5298–5310. doi:10.1021/jm049944f
Serrao E, Odde S, Ramkumar K, Neamati N (2009) Raltegravir, elvitegravir, and metoogravir: the birth of “me-too” HIV-1 integrase inhibitors. Retrovirology 6: 25. doi:10.1186/1742-4690-6-25
Sotriffer CA, Ni H, McCammon JA (2000) Active site binding modes of HIV-1 integrase inhibitors. J Med Chem 43: 4109–4117. doi:10.1021/jm000194t
Gupta P, Kumar R, Garg P, Singh IP (2010) Active site binding modes of dimeric phloroglucinols for HIV-1 reverse transcriptase, protease and integrase. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 20: 4427–4431. doi:10.1016/j.bmcl.2010.06.057
Costi R, Santo RD, Artico M, Massa S, Ragno R, Loddo R, La Colla M, Tramontano E, La Colla P, Pani A (2004) 2, 6-Bis (3, 4, 5-trihydroxybenzylydene) derivatives of cyclohexanone novel potent HIV-1 integrase inhibitors that prevent HIV-1 multiplication in cell-based assays. Bioorg Med Chem 12: 199–215. doi:10.1016/j.bmc.2003.10.005
Deswal S, Roy N (2007) A novel range based QSAR study of human neuropeptide Y (NPY) Y5 receptor inhibitors. Eur J Med Chem 42: 463–470. doi:10.1016/j.ejmech.2006.09.011
Golbraikh A, Tropsha A (2002) Beware of q2!. J Mol Graph Model 20: 269–276
Kramer B, Rarey M, Lengauer T (1999) Evaluation of the FLEXX incremental construction algorithm for protein-ligand docking. Proteins 37: 228–241. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-0134(19991101)37:2<228:AID-PROT8>3.0.CO;2-8
Gasteiger J, Marsili M (1980) Iterative partial equalization of orbital electronegativity—a rapid access to atomic charges. Tetrahedron 36: 3219–3228. doi:10.1016/0040-4020(80)80168-2
Powell MJD (1977) Restart procedures for the conjugate gradient method. Math Program 12: 241–254. doi:10.1007/BF01593790
Carayon K, Leh H, Henry E, Simon F, Mouscadet JF, Deprez E (2010) A cooperative and specific DNA-binding mode of HIV-1 integrase depends on the nature of the metallic cofactor and involves the zinc-containing N-terminal domain. Nucleic Acids Res 38: 3692–3708. doi:10.1093/nar/gkq087
Morris GM, Goodsell DS, Halliday RS, Huey R, Hart WE, Belew RK, Olson AJ (1998) Automated docking using a Lamarckian genetic algorithm and an empirical binding free energy function. J Comput Chem 19: 1639–1662. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1096-987X(19981115)19:14<1639:AID-JCC10>3.0.CO;2-B
Richard DC III, David EP, Jeffrey DB (1988) Comparative molecular field analysis (CoMFA). 1. Effect of shape on binding of steroids to carrier proteins. J Am Chem Soc 110: 5959–5967. doi:10.1021/ja00226a005
Ren JX, Li LL, Zou J, Yang L, Yang JL, Yang SY (2009) Pharmacophore modeling and virtual screening for the discovery of new transforming growth factor- type I receptor (ALK5) inhibitors. Eur J Med Chem 44: 4259–4265. doi:10.1016/j.ejmech.2009.07.008
Schuster D, Maurer EM, Laggner C, Nashev LG, Wilckens T, Langer T, Odermatt A (2006) The discovery of new 11 [beta]-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 inhibitors by common feature pharmacophore modeling and virtual screening. J Med Chem 49: 3454–3466. doi:10.1021/jm0600794
Drake RR, Neamati N, Hong H, Pilon AA, Sunthankar P, Hume SD, Milne GW, Pommier Y (1998) Identification of a nucleotide binding site in HIV-1 integrase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95: 4170–4175
Jenkins TM, Esposito D, Engelman A, Craigie R (1997) Critical contacts between HIV-1 integrase and viral DNA identified by structure-based analysis and photo-crosslinking. EMBO J 16: 6849–6859. doi:10.1093/emboj/16.22.6849
Marchand C, Johnson AA, Karki RG, Pais GCG, Zhang X, Cowansage K, Patel TA, Nicklaus MC, Burke TR, Pommier Y (2003) Metal-dependent inhibition of HIV-1 integrase by ß-diketo acids and resistance of the soluble double-mutant (F185K/C280S). Mol Pharmacol 64: 600–609. doi:10.1124/mol.64.3.600
Barreca ML, Ferro S, Rao A, De Luca L, Zappala M, Monforte AM, Debyser Z, Witvrouw M, Chimirri A (2005) Pharmacophore-based design of HIV-1 integrase strand-transfer inhibitors. J Med Chem 48: 7084–7088. doi:10.1021/jm050549e
Deng J, Lee KW, Sanchez T, Cui M, Neamati N, Briggs JM (2005) Dynamic receptor-based pharmacophore model development and its application in designing novel HIV-1 integrase inhibitors. J Med Chem 48: 1496–1505. doi:10.1021/jm049410e
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic Supplementary Material
The Below is the Electronic Supplementary Material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gupta, P., Garg, P. & Roy, N. Comparative docking and CoMFA analysis of curcumine derivatives as HIV-1 integrase inhibitors. Mol Divers 15, 733–750 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11030-011-9304-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11030-011-9304-7