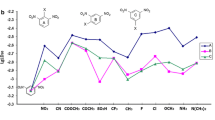
Summary
The toxicological structure-activity relationships are investigated using conceptual DFT based descriptors like global and local electrophilicities. In the present work the usefulness of electrophilicity in predicting toxicity of several polyaromatic hydrocarbons (PAH) is assessed. The toxicity is expressed through biological activity data (pIC50) defined as molar concentration of those chemicals necessary to displace 50% of radiolabeled tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) from the arylhydrocarbon (Ah) receptor. The experimental toxicity values (pIC50) for the electron acceptor toxin like polychlorinated dibenzofurans (PCDF) are taken as dependent variables and the DFT based global descriptor electrophilicity index (ω) is taken as independent variable in the training set. The same model is then tested on a test set of polychlorinated biphenyls (PCB). A good correlation is obtained which vindicates the importance of these descriptors in the QSAR studies on toxins. These toxins act as electron acceptors in the presence of biomolecules whereas aliphatic amines behave as electron donors some of which are also taken into account for the present work. The toxicity values of the aliphatic amines in terms of the 50% inhibitory growth concentration (IGC50) towards ciliate fresh-water protozoa Tetrahymena pyriformis are considered. Since there is no global nucleophilicity we apply local nucleophilicity (ωmax +) as the descriptor in this case of training set. The same regression model is then applied to a test set of amino alcohols. Although the correlation is very good the statistical analysis reflects some cross validation problem. As a further check the amines and amino alcohols are used together to form both the training and the test sets to provide good correlation. It is demonstrated that the toxicity of several toxins (both electron donors and acceptors) in the gas and solution phases can be adequately explained in terms of global and local electrophilicities. Amount of charge transfer between the toxin and the biosystem, simulated as nucleic acid bases and DNA base pairs, indicates the importance of charge transfer in the observed toxicity. The major strength of the present analysis vis-à-vis the existing ones rests on the fact that it requires only one descriptor having a direct relationship with toxicity to provide a better correlation. Importance of using the information from both the toxin and the biosystem is also analyzed.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- DFT:
-
Density Functional Theory
- PCDF:
-
polychlorinated dibenzofuran
- PCB:
-
polychlorinated biphenyl
- PCDD:
-
polychlorinated dibenzo-$p$-dioxin
- QSAR:
-
quantitative structure activity relationship
References
1. Parr, R.G. and Yang, W., Density Functional Theory of Atoms and Molecules (Oxford University Press: New York) (1989).
2. Chermette, H., Chemical reactivity indexes in density functional theory, J. Comp. Chem., 20 (1999) 129–154.
3. Geerlings, P., De Proft, F. and Langenaeker, W., Conceptual Density Functional Theory, Chem. Rev., 103 (2003) 1793–1874.
4. Chattaraj, P.K., Nath, S. and Maiti, B., “Reactivity descriptors” in Computational Medicinal Chemistry and Drug Discovery. Eds., Tollenaere, J., Bultinck, P., Winter, H. D., and Langenaeker, W. (Marcel Dekker: New York), Chapter 11, 2003, pp. 295–322.
5. Karelson, M., “Quantum-Chemical descriptors in QSAR” in Computational medicinal chemistry and drug discovery. Eds., Tollenaere, J., Bultinck, P., Winter, H. D., and Langenaeker, W. (Marcel Dekker: New York), Chapter 11, 2004, pp. 641–668.
6. Parr, R.G., Szentpaly, L.V. and Liu, S., Electrophilicity index, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 121 (1999) 1922–1924.
7. Maynard, A.T. and Covell, D.G., Reactivity of Zinc Finger Cores: Analysis of Protein Packing and Electrostatic Screening, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 123 (2001) 1047–1058.
8. Chattaraj, P.K., Maiti, B. and Sarkar, U., Philicity: A Unified Treatment of Chemical Reactivity and Selectivity, J. Phys. Chem. A., 107 (2003) 4973–4975.
9. Thanikaivelan, P., Subramanian, V., Raghava Rao, J. and Nair, B.U., Application of quantum chemical descriptor in quantitative structure activity and structure property relationship, Chem. Phys. Lett., 323 (2000) 59–70.
10. Parthasarathi, R., Subramanian, V., Roy, D.R. and Chattaraj, P.K., Electrophilicity Index as a Possible Descriptor of Biological Activity, Bioorg. Med. Chem., 12 (2004) 5533–5543.
11. Parthasarathi, R., Padmanabhan, J., Subramanian, V., Maiti, B. and Chattaraj, P.K., Chemical Reactivity Profiles of Two Selected Polychlorinated Biphenyls, J. Phys. Chem. A., 107 (2003) 10346–10352.
12. Parthasarathi, R., Padmanabhan, J., Subramanian, V., Maiti, B. and Chattaraj, P.K., Toxicity analysis of 33'44'5 – Pentachloro Biphenyl Through Chemical Reactivity and Selectivity Profiles, Current Sci., 86 (2004) 535–542. Parthasarathi, R., Padmanabhan, J., Subramanian, V., Sarkar, U., Maiti, B. and Chattaraj, P.K., Toxicity Analysis of Benzidine Through Chemical Reactivity and Selectivity Profiles: A DFT approach, Internet Electron J. Mol. Des., 2 (2003) 798–813.
13. Bailey and Love's ‘Short Practice of Surgery’, Russell, R.C.G., Williums, N.S., Bulstrode, C., J.K. (eds.), 23rd Edition (Arnold: London), 2000, pp. 1227–1228.
14. Walker, M.K. and Peterson, R.E., Potencies of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxin, dibenzofuran, and biphenyl congeners, relative to 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin, for producing early life stage mortality in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss), Aquat. Toxicol, 21 (1991) 219–237.
15. Zabel, E.W., Cook, P.M. and Peterson, R.E., Toxic equivalency factors of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxin, dibenzofuran and biphenyl congeners based on early life stage mortality in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss), Aquat. Toxicol., 31 (1995) 315–328.
16. Hutzinger, O., Blumich, M.J., Berg, M.V.D. and Olie, K., Sources and fate of PCDDs and PCDFs: an overview, Chemosphere, 14 (1985) 581–600.
17. Olie, K., Vermeulen, P.L. and Hutzinger, O., Chlorodibenzo-p-dioxins and chlorodibenzofurans are trace components of fly ash and flue gas of some municipal incinerators in the Netherlands, Chemosphere, 6 (1977) 455–459.
18. Marklund, S., Rappe, C., Tsyklind, M. and Egebäck, K.E., Identification of polychlorinated dibenzofurans and dioxins in exhausts from cars run on leaded gasoline, Chemosphere, 16 (1987) 29–36.
19. Lohmann, R. and Jones, K.C., Dioxins and furans in air and deposition: A review of levels, behaviour and processes, Sci. Total Environ., 219 (1998) 53–81.
20. Safe, S.H., Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs): Environmental impact, biochemical and toxic responses, and implications for risk assessment, Crit. Rev. Toxicol., 24 (1994) 87–149.
21. Van den Berg, M., Birnbaum, L., Bosveld, A.T., Brunstrom, B., Cook, P., Feeley, M., Giesy, J.P., Hanberg, A., Hasegawa, R., Kennedy, S.W., Kubiak, T., Larsen, J.C., van Leeuwen, F.X., Liem, A.K., Nolt, C., Peterson, R.E., Poellinger, L., Safe, S., Schrenk, D., Tillitt, D., Tysklind, M., Younes, M., Waern, F. and Zacharewski, T., Toxic equivalency factors (TEFs) for PCBs, PCDDs, PCDFs for humans and wildlife, Environ. Health. Perspet., 106 (1998) 775–792.
22. Oakley, G.G., Devanaboyina, U.S., Robertson, L.W. and Gupta, R.C., Oxidative DNA Damage Induced by Activation of Polychlorinated Biphenyls (PCBs): Implications for PCB-Induced oxidative stress in breast cancer, Chem. Res. Toxicol, 9 (1996) 1285–1292.
23. Erickson, M.D., Analytical Chemistry of PCBs (Butterworth Publishers, Boston) (1986).
24. Silberhorn, E.M., Glauert, H.P. and Robertson, L.W., Carcinogenicity of polyhalogenated biphenyls: PCBs and PBBs, Crit. Rev. Toxicol., 20 (1990) 439–496.
25. Miller, G., Sontum, S. and Crosby, D.G., Electron-acceptor properties of chlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins, Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol, 18 (1977) 611–616.
26. Poland, A., Palen, D., and Glover, E., Tumour promotion by TCDD in skin of HRS/J hairless mice, Nature, 300 (1982) 271–273.
27. Waller, C.L. and McKinney, J.D., Three-dimensional Quantitative Structure-Activity Relationships of Dioxins and Dioxin-like Compounds: Model Validation and Ah Receptor Characterization, Chem. Res. Toxicol. 8 (1995) 847–858.
28. Schultz, T.W., Tetratox: Tetrahymena pyriformis population growth impairment endpoint-a surrogate for fish lethality, Toxicol, Methods, 7 (1997) 289–309.
29. Pearson, R.G., Chemical hardness – Applications from molecules to solids (VCH-Wiley: Weinheim) (1997).
30. Parr, R.G., Donnelly, R.A., Levy, M. and Palke, W.E., Electronegativity: The density functional viewpoint, J. Chem. Phys., 68 (1978) 3801–3807.
31. Parr, R.G. and Yang, W., Density functional approach to the frontier-electron theory of chemical reactivity, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 106 (1984) 4049.
Fukui, K., Role of Frontier Orbitalsin Chemical Reactions, Science, 218(1987) 747–754.
33. Yang, W. and Mortier, W.J., The use of global and local molecular parameters for the analysis of the gas-phase basicity of amines, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 108 (1986) 5708–5711.
34. Lee, C., Yang, W. and Parr, R.G., Local softness and chemical reactivity in the molecules CO, SCN - and H 2 CO, J. Mol. Struct. (Theochem), 163 (1988) 305.
35. Cioslowski, J., Martinov, M. and Mixon, S.T., Atomic Fukui indexes from the topological theory of atoms in molecules applied to Hartree-Fock and correlated electron densities, J. Phys. Chem, 97 (1993) 10948–10951.
36. Parr, R.G. and Pearson, R.G., Absolute hardness: Companion parameter to absolute electronegativity, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 105 (1983) 7512–7516.
37. Sanderson, R. T., An interpretation of bond lengths and a classification of bonds, Science, 114 (1951) 670.
38. Espinosa, A., Frontera, A., García, R., Soler, M.A. and Tárraga, A., Electrophilic behavior of 3-methyl-2-methylthio-1,3,4-thiadiazolium salts: A multimodal theoretical approach, ARKIVOC, (ix) (2005) 415–437.
39. Becke, A.D., Density-functional exchange-energy approximation with correct asymptotic behavior, Phys. Rev. A., 38 (1998) 3098–3100. Hariharan, P. C. and Pople, J. A., Theor. Chim. Acta., 28 (1973) 213.
40. Lee, C., Yang, W. and Parr, R.G., Development of the Colle-Salvetti correlation-energy formula into a functional of the electron density, Phys. Rev. B., 37 (1988) 785–789.
41. Gaussian 03 & Gaussian 98, Revision B.03; Gaussian, Inc.: Pittsburgh, PA.
42. Mulliken, R. S., Electronic Population Analysis on LCAO–MO Molecular Wave Functions,I$, J. Chem. Phys., 23 (1955) 1833–1840.
43. Reed, A.E. and Weinhold, F., Natural bond orbital analysis of near-Hartree-Fock water dimmer, J Chem Phys., 78 (1983) 4066–4073.
44. Reed, A.E., Weinstock, R.B. and Weinhold, F., Natural population analysis, J. Chem. Phys., 83 (1985) 735–746.
45. Hirshfeld, F.L., Bonded-atom fragments for describing molecular charge densities, Theor. Chim. Acta., 44 (1977) 129–138.
46. DMOL3, Accelrys, Inc. San Diego, California.
47. MATLAB, The Math Works (Inc.: Natick, U.S.A), (1999).
48. Pecka, J. and Ponec, R., Simple analytical method for evaluation of statistical importance of correlations in QSAR studies, J. Math. Chem., 27 (2000) 13–22.
49. Basak, S.C., Chertian, J., Natarajan, R.; Private communication.
50. Arulmozhiraja, S. and Morita, M., Structure-activity Relationships for the Toxicity of Polychlorinated Dibenzofurans: Approach through Density Functional Theory-Based Descriptors, Chem. Res. Toxicol., 17 (2004) 348–356.
51. Tysklind, M., Tillitt, D., Eriksson, L., Lundgren, K. and Rappe, C., A toxic equivalency factor scale for polychlorinated dibenzofurans, Fundam. Appl. Toxicol., 22 (1994) 277–285.
52. Roy, D.R., Parthasarathi, R., Maiti, B., Subramanian, V. and Chattaraj, P.K., Electrophilicity as a possible descriptor for toxicity prediction, Bioorg. Med. Chem., 13 (2005) 3405–3412.
53. Hawkins, D.M., Basak, S.C. and Mills, D., Assessing model fit by cross–validation, J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci., 43 (2003) 579–586.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Roy, D.R., Sarkar, U., Chattaraj, P.K. et al. Analyzing Toxicity Through Electrophilicity. Mol Divers 10, 119–131 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11030-005-9009-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11030-005-9009-x