Summary
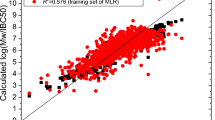
This work introduces a neural network methodology for developing QSTR predictors of toxicity to Vibrio fischeri. The method adopts the Radial Basis Function (RBF) architecture and the fuzzy means training strategy, which is fast and repetitive, in contrast to most traditional training techniques. The data set that was utilized consisted of 39 organic compounds and their corresponding toxicity values to Vibrio fischeri, while lipophilicity, equalized electronegativity and one topological index were used to provide input information to the models. The performance and predictive ability of the RBF model were illustrated through external validation and various statistical tests. The proposed methodology can be used to successfully model toxicity to Vibrio fischerifor a heterogeneous set of compounds.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lu, F.C. and Kacew, S., LU'S BASIC TOXICOLOGY, Taylor & Francis, London, 2002.
Parvez, S., Venkataraman, C. and Mukherji, S., A review on advantages of implementing luminescence inhibition (Vibrio fischeri) for acute toxicity prediction of chemicals, Environ. Int., 32 (2006) 265–268.
Dawson, D.A., Poch, G. and Schultz, T.W., Chemical mixture toxicity testing with Vibrio fischeri: Combined effects of binary mixtures for ten soft electrophiles Ecotox. Environ. Safety (2005) In press.
Karcher, W. and Devillers, J., SAR and QSAR in environmental chemistry and toxicology: Scientific tool or wishful thinking? In: Karcher, W. and Devillers, J. (Eds.). Practical applications of Quantitative Structure-Activity Relationships (QSAR) in environmental chemistry and toxicology. Kluwer, Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1990, pp 1–12.
Nendza, M., Structure-Activity Relationships in Environmental Sciences, Ecotoxicology Series 6, CHAPMAN & HALL, Great Britain, 1998.
Schultz, T.W., Netzeva, T.I. and Cronin, M.T.D., Selection of data sets for QSARs: Analyses of Tetrahymena Toxicity from aromatic compounds, SAR QSAR Environ. Res., 14 (2003) 59–81.
Netzeva, T.I., Schultz, T.W., Aptula, A.O. and Cronin, M.T.D. Partial least squares modelling of the acute toxicity of aliphatic compounds to tetrahymena pyriformis, SAR QSAR Environ. Res., 14 (2003) 265–283.
Warne, M.A., Osborn, D., Lindon, J.C. and Nicholson, J.K., Quantitative Structure-Activity Relationships for halogenated substituted-benzenes to Vibrio fischeri, using atom-based semi-empirical molecular-orbital descriptors, Chemospere, 38 (1999) 3357–3382.
Khadikar, P.V., Mather, K.C., Singh, S., Phadnis, A., Shrivastava, A. and Mandoloi, M., Study on quantitative structure-toxicity relationships of benzene derivatives acting by narcosis, Bioorg. Med. Chem., 10 (2002) 1761–1766.
Roy, K. and Ghosh, G., QSTR with extended topochemical indices. Part 5: Modeling of the acute toxicity of phenylsulfonyl carboxylates to Vibrio fischeri using genetic fuction approximation, Bioorg. Med. Chem., 13 (2005) 1185–1194.
Roy, K. and Ghosh, G., QSTR with extended topochemical atom indices. 4. Modeling of the acute toxicity of phenylsulfonyl carboxylates to Vibrio fischeri using principal component factor analysis and principal component regression analysis, QSAR Comb. Sci., 23 (2004) 526–535.
Melagraki, G., Afantitis, A., Sarimveis, H., Igglessi-Markopoulou, O. and Supuran, C.T., QSAR study on para-substituted aromatic sulfonamides as carbonic anhydrase II inhibitors using topological information indices, Bioorg. Med. Chem., 14 (2006) 1108–1114.
Afantitis, A., Melagraki, G., Sarimveis, H., Koutentis, P. A., Markopoulos, J. and Igglessi-Markopoulou, O., A novel simple QSAR model for the prediction of anti-HIV activity using multiple linear regression analysis, Mol. Diversity, In press (2005).
Hansch, C. and Leo, A., Exploring QSAR: Fundamentals and Applications in Chemistry and Biology. ACS, Washington, DC, 1995.
Debnath, A.K., Quantitative structure – activity relationship (QSAR): A versatile tool in drug design, In: Ghose, A.K. and Viswanadhan, V.N. (Eds.) Combinatorial library design and evaluation: Principles, software tools, and applications in drug discovery, Marcel Dekker, New York, 2001, pp 73–129.
Devillers, J., Neural, Networks in QSAR and Drug Design. Academic Press, London, 1996.
Kaiser, K.L.E., Neural Networks for effect prediction in environmental and health issues using large datasets, Quant. Struct.-Act. Relat., 22 (2003) 185–190.
Kaiser, K.L.E., The use of neural networks in QSARs for aquatic toxicological endpoints, J. Mol. Str. (Theochem), 622 (2003) 85–95.
Afantitis, A., Melagraki, G., Makridima, K., Alexandridis, A., Sarimveis, H. and Igglessi-Markopoulou, O., Prediction of high-weight polymers glass transition temperature using RBF neural networks, J. Mol. Str. (Theochem), 716 (2005) 193–198.
Melagraki, G., Afantitis, A., Makridima, K., Sarimveis, H. and Igglessi-Markopoulou, O., Prediction of toxicity using a novel RBF neural network training methodology. J. Mol. Model., In press (2005).
Sarimveis, H., Alexandridis. A., Tsekouras G. and Bafas G., A Fast and efficient algorithm for training radial basis function neural networks based on a fuzzy partition of the input space, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 41 (2002) 751–759.
Agrawal, V.K. and Khadikar, P.V., QSAR Study on narcotic mechanism of action and toxicity: A molecular connectivity approach to Vibrio fischeri toxicity testing, Bioorg. Med. Chem., 10 (2002) 3517– 3522.
Zhao, Y.H., Cronin, M.T.D. and Dearden, J.C., Quantitative structure-activity relationships of chemicals acting by non-polar narcosis-theoretical considerations, Quant. Struct.-Act. Relatsh., 17 (1998) 131–138.
Todeschini, R. and Consonni, V., Handbook of Molecular Descriptors, Methods and Principles in Medicinal Chemistry, in Series of Methods and Principles of Medicinal Chemistry Vol. 11. Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2000.
Hall, L.H. and Kier, L.B., Issues in representation of molecular structure. The development of molecular connectivity, J. Mol. Graph. Model., 20 (2001) 4–18.
Newsome, L.D., Johnson, D.E., Lipnick, R.L., Broderius, S.J. and Russom, C.L., A QSAR study of the toxicity of amines to the fathead minnow, Sci. Total Environ., 109 (1991) 537–551.
Khadikar, P.V., Lukovits, I, Agrawal, V.K., Shrivastava, S., Jaiswal, M., Gutman, I., Karmarkar, S. and Shrivastava, A., Equalized electronegativity and topological indices: Application for modeling toxicity of nitrobenzene derivatives. Indian J. Chem., 42A (2003) 1436– 1441.
Zhao, Y.H., Ji, G.D., Cronin, M.T.D. and Dearden, J.C., QSAR study of the toxicity of benzoic acids to Vibrio fischeri, Daphnia magna and carp, Sci. Total Environ., 216 (1998) 205–215.
Cronin, M.T.D. and Schultz, T.W., Structure –toxicity relationships for three mechanisms of action of toxicity to Vibrio fischeri, Ecotox. Environ. Safety, 39 (1998) 65–69.
Darken, C. and Moody, J., Fast adaptive K-means clustering: Some empirical results. IEEE INNS International Joint Conference On Neural Networks, San Diego, CA, USA, June 17–21, 1990, Proceedings Vol. 2, 1990, 233 – 238.
Dunn, J.C., A fuzzy relative of the ISODATA process and its use in detecting compact well-separated clusters, J. Cybernet., 3 (1974) 32–57.
Leonard, J.A. and Kramer, M.A., Radial basis function networks for classifying process faults, IEEE Control Systems. 11 (1991) 31– 38.
Osten, D.W., Selection of oprimal regression models via cross-validation J. Chemom., 2 (1988) 39–48.
Tropsha, A., Gramatica, P. and Gombar, V.K., The importance of being earnest: Validation is the absolute essential for successful application and interpretation of QSPR models. Quant. Comb. Sci., 22 (2003) 69–77.
Golbraikh, A. and Tropsha, A., Beware of q 2!. J. Mol. Graph. Model., 20 (2002) 269–276.
Golbraikh, A. and Tropsha, A., Predictive QSAR modeling based on diversity sampling of experimental datasets for the training and test set selection. Mol. Diversity, 5 (2000) 231–243.
Wold, S. and Eriksson, L., Statistical validation of QSAR results, in: Van de Waterbeemd, H., (Ed.), Chemometrics Methods in Molecular Design, VCH Weinheim (Germany) 1995, pp. 309–318.
Sarimveis, H., Training algorithms and learning abilities of three different types of neural networks, Syst. Anal. Model. Simul., 38 (2000) 555–581.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Melagraki, G., Afantitis, A., Sarimveis, H. et al. A Novel RBF Neural Network Training Methodology to Predict Toxicity to Vibrio Fischeri. Mol Divers 10, 213–221 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11030-005-9008-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11030-005-9008-y