Summary
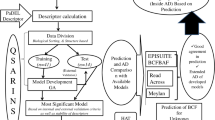
During bioconcentration, chemical pollutants from water are absorbed by aquatic animals via the skin or a respiratory surface, while the entry routes of chemicals during bioaccumulation are both directly from the environment (skin or a respiratory surface) and indirectly from food. The bioconcentration factor (BCF) and the bioaccumulation factor (BAF) for a particular chemical compound are defined as the ratio of the concentration of a chemical inside an organism to the concentration in the surrounding environment. Because the experimental determination of BAF and BCF is time-consuming and expensive, it is efficacious to develop models to provide reliable activity predictions for a large number of chemical compounds. Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) released from industrial activities are persistent pollutants of the environment that produce widespread contamination of water and soil. PCBs can bioaccumulate in the food chain, constituting a potential source of exposure for the general population. To predict the bioconcentration and bioaccumulation factors for PCBs we make use of the biphenyl substitution-reaction network for the sequential substitution of H-atoms by Cl-atoms. Each PCB structure then occurs as a node of this reaction network, which is some sort of super-structure, turning out mathematically to be a partially ordered set (poset). Rather than dealing with the molecular structure via ordinary QSAR we use only this poset, making different quantitative super-structure/activity relationships (QSSAR). Thence we developed cluster expansion and splinoid QSSARs for PCB bioconcentration and bioaccumulation factors. The predictive ability of the BAF and BCF models generated for 20 data sets (representing different conditions and fish species) was evaluated with the leave-one-out cross-validation, which shows that the splinoid QSSAR (r between 0.903 and 0.935) are better than models computed with the cluster expansion (r between 0.745 and 0.887). The splinoid QSSAR models for BAF and BCF yield predictions for the missing PCBs in the investigated data sets.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schüürmann, G. and Klein, W., Advances in bioconcentration prediction, Chemosphere, 17 (1988) 1551–1574.
Feijtel, T., Kloepper-Sams, P., Den Haan, K., Van Egmond, R., Comber, M., Heusel, R., Wierich, P., Ten Berge, W., Gard, A., Wolf, W. and Niessen, H., Integration of bioaccumulation in an environmental risk assessment, Chemosphere, 34 (1997) 2337–2350.
Franke, C., Studinger, G., Berger, G., Böhling, S., Bruckmann, U., Cohors-Fresenborg, D. and Jöhncke, U., The assessment of bioaccumulation, Chemosphere, 29 (1994) 1501–1514.
Turne, L., Choplin, F., Dugard, P., Hermens, J., Jaeckh, R., Marsmann, M. and Roberts, D., Structure-activity relationships in toxicology and ecotoxicology: An assessment, Toxicol. in vitro, 1 (1987) 143– 171.
Carlsen, L. and Walker, J.D., QSARs for prioritizing PBT substances to promote pollution prevention, QSAR Comb. Sci., 22 (2003) 49– 57.
Swanson, G.M., Ratcliffe, H.E. and Fischer, L.J., Human exposure to policlorinated biphenyls (PCBs): A critical assessment of the evidence for adverse health effects, Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol., 21 (1995) 136–150.
Faroon, O., Jones, D. and De Rosa, C., Effects of polychlorinated biphenyls on the nervous system, Toxicol. Ind. Health, 16 (2000) 305–333.
Kamrin, M.A. and Fischer, L.J., Current status of sport fish consumption advisories for PCBs in the Great Lakes, Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol., 29 (1999) 175–181.
Judd, N., Griffith, W.C. and Faustman, E.M., Contribution of PCB exposure from fish consumption to total dioxin-like dietary exposure, Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol., 40 (2004) 125–135.
Ivanciuc, O., Support vector machines prediction of the mechanism of toxic action from hydrophobicity and experimental toxicity against pimephales promelas and tetrahymena pyriformis, Internet Electron. J. Mol. Des., 3 (2004) 800–821, http://www.biochempress.com.
Carlsen, L., A QSAR approach to physico–chemical data for organophosphates with special focus on known and potential nerve agents, Internet Electron. J. Mol. Des., 4 (2005) 355–366, http://www.biochempress.com.
Seegal, R.F. and Bowers, W.J., Consequences and mechanisms of action of fish-borne toxicants: what we do not know and why, Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol., 12 (2002) 63–68.
Mackay, D. and Fraser, A., Bioaccumulation of persistent organic chemicals: mechanisms and models, Environ. Pollut., 110 (2000) 375–391.
Hope, B., Scatolini, S. and Titus, E., Bioconcentration of chlorinated biphenyls in biota from the North Pacific Ocean, Chemosphere, 36 (1998) 1247–1261.
Voutsas, E., Magoulas, K. and Tassios, D., Prediction of the bioaccumulation of persistent organic pollutants in aquatic food webs, Chemosphere, 48 (2002) 645–651.
Meylan, W.M., Howard, P.H., Boethling, R.S., Aronson, D. Printup, H. and Gouchie, S., Improved method for estimating bioconcentration/bioaccumulation factor from octanol/water partition coefficient, Environ. Toxicol. Chem., 18 (1999) 664–672.
Ivanciuc, O., Aquatic Toxicity Prediction for Polar and Nonpolar Narcotic Pollutants with Support Vector Machines, Internet Electron. J. Mol. Des., 2 (2003) 195–208, http://www.biochempress.com.
Hansch, C. and Leo, A., Exploring QSAR. Fundamentals and applications in chemistry and biology, American Chemical Society, Washington, DC, 1995, pp 580.
Gramatica, P. and Papa, E., QSAR modeling of bioconcentration factor by theoretical molecular descriptors, QSAR Comb. Sci., 22 (2003) 374–385.
Devillers, J., Domine, D., Bintein, S. and Karcher, W., Fish bioconcentration modeling with log P, Toxicol. Methods, 8 (1998) 1–10.
Dearden, J.C. and Shinnawei, N.M., Improved prediction of fish bioconcentration factor of hydrophobic chemicals, SAR QSAR Environ. Res., 15 (2004) 449–455.
Hu, H., Xu, F., Li, B., Cao, J., Dawson, R. and Tao, S., Prediction of the bioconcentration factor of PCBs in fish using the molecular connectivity index and fragment constant models, Water Environ. Res., 77 (2005) 136–150.
Davies, R.P. and Donas, A.J., The prediction of bioconcentration in fish, Water Res., 18 (1984) 1253–1262.
Fatemi, M.H., Jalali-Heravi, M. and Konuze, E., Prediction of bioconcentration factor using genetic algorithm and artificial neural network, Anal. Chim. Acta, 486 (2003) 101–108.
Boon, J.P. and Duinker, J.C., Kinetics of polychlorinated biphenyl (PCB) components in juvenile sole (solea solea) in relation to concentrations in water and to lipid metabolism under conditions of starvation, Aquat. Toxicol., 7 (1985) 119–134.
Renberg, L. and Sundström, G., Prediction of bioconcentration potential of organic compounds using partition coefficients derived from reversed phase thin layer chromatography, Chemosphere, 7 (1979) 449–459.
Harald, J., Geyer, I., Scheunert, I. and Korte, F., Correlation between the bioconcentration potential of organic environmental chemicals in humans and their n-octanol/water partition coefficients, Chemosphere, 16 (1987) 239–252.
Tao, S., Hu, H., Lu, X., Dawson, R.W. and Xu, F., Fragment constant method for prediction of fish bioconcentration factors of non-polar chemicals, Chemosphere, 41 (2000) 1563–1568.
Ivanciuc, O., Artificial neural networks applications. Part 7 - Estimation of bioconcentration factors in fish using solvatochromic parameters, Rev. Roum. Chim., 43 (1998) 347–354.
Dimitrov, S.D., Dimitrova, N.C., Walker, J.D., Veith, G.D. and Mekenyan, O.G., Predicting bioconcentration factors of highly hydrophobic chemicals. Effects of molecular size, Pure Appl. Chem., 74 (2002) 1823–1830.
Dimitrov, S.D., Dimitrova, N.C., Walker, J.D., Veith, G.D. and Mekenyan, O.G., Bioconcentration potential predictions based on molecular attributes – an early warning approach for chemicals found in humans, birds, fish and wildlife, QSAR Comb. Sci., 22 (2003) 58–68.
Gobas, F.A.P.C., A model for predicting the bioaccumulation of hydrophobic organic chemicals in aquatic food-webs: Application to Lake Ontario, Ecol. Model., 69 (1993) 1–17.
Boon, J.P., Oostingh, I., Van der Meer, J., and Hillebrand, T.M.J., A model for the bioaccumulation of chlorobiphenyl congeners in marine mammals, Eur. J. Pharmacol., Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol., 270 (1994) 237–251.
Walker, C.H., Kinetic models for predicting bioaccumulation of pollutants in ecosystems, Environ. Pollut., 44 (1987) 227–240.
Müller, J.F., Hawker, D.W. and Connell, D.W., Calculation of bioconcentration factors of persistent hydrophobic compounds in the airnegetation system, Chemosphere, 29 (1994) 623–640.
Ivanciuc, O., Bioconcentration factor QSAR with support vector regression and artificial neural networks, Internet Electron. J. Mol. Des., 4 (2005) 000–000, http://www.biochempress.com.
Bruggeman, W.A., Martron, L.B.J.M., Kooiman, D. and Hutzinger, O., Accumulation and elimination of di-, tri-, and tetrachlorobiphenyls by goldfish after dietary and aqueous exposure, Chemosphere, 10 (1981) 811–832.
Ivanciuc, O., Support vector machine identification of the aquatic toxicity mechanism of organic compounds, Internet Electron. J. Mol. Des., 1 (2002) 157–172, http://www.biochempress.com.
Echols, K.R., Gale, R.W., Schwartz, T.R., Huckins, J.N., Williams, L.L.,Meadows, J.C., Morse, D.,Petty, J.D., Orazio, C.E. and Tillitt, D.E., Comparing polychlorinated biphenyl concentrations and patterns in the Saginaw River using sediment caged fish, and semipermeable membrane devices, Environ. Sci. Technol., 34 (2000) 4095–4102.
Geyer, H.J., Scheunert, I., Bruggemann, R., Steinberg, C., Korte, F. and Kettrup, A., QSAR for organic chemical bioconcentration in Daphnia, algae, and mussels, Sci. Total. Environ., 109/110 (1991) 387– 394.
Devillers, J., Bintein, S. and Domine, D., Comparison of BCF models based on log P, Chemosphere, 33 (1996) 1047–1065.
Wei, D., Zhang, A., Wu, C., Han, S. and Wang, L., Progressive study and robustness test of QSAR model based on quantum chemical parameters for predicting BCF of selected polychlorinated organic compound (PCOCs), Chemosphere, 44 (2001) 1421–1428.
Saçan, M.T., Erdem, S.S., Özpinar, G.A. and Balcioglu, I.A., QSPR study on the bioconcentration factors of nonionic organic compounds in fish by characteristic root index and semiempirical molecular descriptors, J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci., 44 (2004) 985–992.
Lu, X., Tao, S., Cao, J. and Dawson, R.W., Prediction of fish bioconcentration factors of nonpolar organic pollutants based on molecular connectivity indices, Chemosphere, 39 (1999) 987–999.
Lu, X., Tao, S., Hu, H. and Dawson, R.W., Estimation of bioconcentration factors of nonionic organic compounds in fish by molecular connectivity indices and polarity correction factors, Chemosphere, 41 (2000) 1675–1688.
Fox, K., Zauke, G.P. and Butte, W., Kinetics of bioconcentration and clearance of 28 polychlorinated biphenyl congeners in Zebrafish (Brachydanio rerio), Ecotox. Environ. Safety, 28 (1994) 99–109.
Burkhard, L.P., Endicott, D.D., Cook, P.M., Sappington, K.G. and Winchester, E.L., Evaluation of two methods for prediction of bioaccumulation factors, Environ. Sci. Technol., 37 (2003) 4626–4634.
Klein, D.J., Similarity and dissimilarity in posets. J. Math. Chem., 18 (1995) 321–348.
Klein, D.J. and Babić, D., Partial orderings in chemistry, J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci., 37 (1997) 656–671.
Klein, D.J., Prolegomenon on partial orderings in Chemistry, MATCH Commun. Math. Comput. Chem., 42 (2000) 7–21.
Klein, D.J. and Bytautas, L., Directed reaction graphs as posets, MATCH Commun. Math. Comput. Chem., 42 (2000) 261–289.
Brüggemann, R., Schwaiger, J. and Negele, R.D., Applying Hasse diagram technique for the evaluation of toxicological fish tests, Chemosphere, 30 (1995) 1767–1780.
Brüggemann, R. and Bartel, H.G., A theoretical concept to rank environmentally significant chemicals, J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci., 39 (1999) 211–217.
Pudenz, S., Brüggemann, R., Luther, B., Kaune, A. and Kreimes K., An algebraic/graphical tool to compare ecosystems with respect to their pollution V: Cluster analysis and Hasse diagrams, Chemosphere, 40 (2000) 1373–1382.
Brüggemann, R., Pundez, S., Carlsen, L., Sørensen, P.B., Thomsen, M. and Mishra, R.K., The use of Hasse diagrams as a potential approach for inverse QSAR, SAR QSAR Environ. Res., 11 (2001) 473– 487.
Carlsen, L., Sørensen, P.B., Thomsen, M. and Brüggemann R., QSAR's based on partial order ranking, SAR QSAR Environ. Res., 13 (2002) 153–165.
Brüggemann, R., Münzer, B. and Halfon, E., An algebraic/graphical tool to compare ecosystems with respect to their pollution – the German river “Elbe” as an example - I: Hasse-diagrams, Chemosphere, 28 (1994) 863–872.
Lerche, D., Sørensen, P.B., Larsen H.L., Carlsen, L. and Nielsen, O.J., Comparison of the combined monitoring-based and modelling-based priority setting scheme with partial order theory and random linear extensions for ranking of chemical substances, Chemosphere, 49 (2002) 637–649.
Lerche, D. and Sørensen, P.B., Evaluation of the ranking probabilities for partial orders based on random linear extensions, Chemosphere, 53 (2003) 981–992.
Lerche, D., Matsuzaki, S.Y., Sørensen, P.B., Carlsen, L. and Nielsen, O.J., Ranking of chemical substances based on the Japanese pollutant release and transfer register using partial order theory and random linear extensions, Chemosphere, 55 (2004) 1005–1025.
Sørensen, P.B., Mogensen, B.B., Carlsen, L. and Thomsen, M., The influence on partial order ranking from input parameter uncertainty: Definition of a robustness parameter, Chemosphere, 41 (2000) 595–601.
Klein, D.J., Schmalz, T.G. and Bytautas, L., Chemical sub-structural cluster expansions for molecular properties, SAR QSAR Environ. Res., 10 (1999) 131–156.
Ivanciuc, T. and Klein D.J., Parameter-free structure-property correlation via progressive reaction posets for substituted benzenes, J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci., 44 (2004) 610–617.
Ivanciuc, T., Ivanciuc, O. and Klein, D.J., Posetic quantitative superstructure/activity relationships (QSSARs) for chlorobenzenes, J. Chem. Inf. Model., 45 (2005) 870–879.
Došlić, T. and Klein, D.J., Splinoid interpolation on finite posets, J. Comput. Appl. Math., 177 (2005) 175–185.
Klein, D.J., Chemical graph-theoretic cluster expansions, Int. J. Quantum. Chem., Quantum Chem. Symp., 20 (1986) 153–171.
Schmalz, T.G., Živković, T. and Klein, D.J., Cluster expansion of the Hückel molecular energy for acyclics: Applications to pi resonance theory, Math. Chem. Comp., 54 (1987) 173–190.
Ivanciuc, T., Klein, D.J. and Ivanciuc, O., Posetic cluster expansion for substitution – reaction diagrams and its application to cyclobutane, J. Math. Chem. (submitted).
Gillet, V.J., Willett, P. and Bradshaw, J., Identification of biological activity profiles using substructural analysis and genetic algorithms, J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci., 38 (1998) 165–179.
Hawkins, D.M., Basak, S C. and Shi, X., QSAR with few compounds and many features, J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci., 41 (2001) 663–670.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ivanciuc, T., Ivanciuc, O. & Klein, D.J. Modeling the bioconcentration factors and bioaccumulation factors of polychlorinated biphenyls with posetic quantitative super-structure/activity relationships (QSSAR). Mol Divers 10, 133–145 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11030-005-9003-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11030-005-9003-3