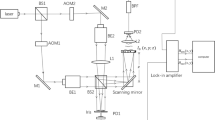
This article discusses optical methods and technologies that can register, transform, store, transmit, and reproduce large arrays of information. Digital holograms recorded using photographic equipment of various types is common carriers of experimentally recorded information. The size of digital hologram files is several tens of megabytes. Hence, for the storage and transmission of holographic data archives via communication channels, holograms should be compressed. Binarization represents one of the options for reducing the hologram size. For binarization, an iterative adaptive method for selecting the weight coefficients of the error diffusion procedure is proposed. The method has been tested on digital holograms that were optically recorded under various conditions. The quality of the measured objects was evaluated through numerical methods of image reconstruction and after displaying digital holograms on a micromirror light modulator. The proposed method can be used for compressing and storing holographic data, measuring the characteristics and shape of micro- and macroobjects, and fast optical image reconstruction using a micromirror light modulator.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
U. Schnars, C. Falldorf, J. Watson, and W. Jüptner, Digital Holography and Wavefront Sensing: Principles, Techniques and Applications, Springer-Verlag (2015), https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-44693-5.
S. A. Shoidin and A. L. Pazoev, Optoelectr. Instrum. Data Proc., 57, No. 1, 80–88 (2021), https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.3103/S8756699021010118.
E. M. Gomez-Valencia, S. Trejos, A. Velez-Zea, et al., J. Opt., 23, No. 7 (2021), https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1088/2040-8986/ac0874.
P A. Cheremkhin and E. A. Kurbatova, Sci. Rep., 9, 7561 (2019), https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-44119-0.
Z. Liu, J. Watson, and A. Allen, IEEE J. Ocean Eng., 43, 83–92 (2018), https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1109/JOE.2017.2690537.
T. J. Naughton, Y. Frauel, B. Javidi, and E. Tajahuerce, Appl. Opt., 41, 4124–4132 (2002), https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1364/AO.41.004124.
K. Min and J. H. Park, Opt. Express, 28, 38140–38154 (2020), https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1364/OE.411312.
P. A. Cheremkhin, E. A. Kurbatova, N. N. Evtikhiev, et al., J. Opt., 23 (2021), https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1088/2040-8986/ac05d1.
N. N. Evtikhiev, V. V. Krasnov, I. P. Ryabcev, et al., Measur. Techn., 64, No. 5, 346–351 (2021), https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1007/s11018-021-01940-2.
I. S. Gibin, V. I. Kozik, and E. S. Nezhevenko, Optoelectr. Instrum. Data Proc., 56, No. 1, 1–9 (2020), https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.3103/S875669902001001X.
P. A. Cheremkhin and E. A. Kurbatova, Opt. Lasers Eng., 115, 119–130 (2019), https://doi.org/10.10167j.optlaseng.2018.11.019.
V. G. Nikitaev, A. N. Pronichev, O. B. Tamrazova, et al., Measur. Techn., 64, 516–521 (2021), https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1007/s11018-021-01962-w.
R. W. Floyd and L. Steinberg, “An adaptive algorithm for spatial gray scale,” Proc. Soc. Inf. Disp., 17, 75–77 (1976).
K. Liu, Z. He, and L. Cao, Chin. Opt. Lett, 9, 050501 (2021), https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.3788/COL202119.050501.
D. E. Knuth, ACM Trans. Grap., 6, No. 4, 245–273 (1987), https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1145/35039.35040.
E. A. Kurbatova, V. G. Rodin, and P. A. Cheremkhin, Optoelectr. Instrum. Data Proc., 56, No. 2, 205–211 (2020), https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.3103/S8756699020020120.
G. Yang, S. Jiao, J. -P. Liu, et al., Appl. Opt, 58, 5547–5555 (2019), https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1364/AO.58.005547.
N. Verrier and M. Atlan, Appl. Opt., 50, H136–H146 (2011), https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1364/AO.50.00H136.
P. A. Cheremkhin, N. N. Evtikhiev, E. A. Kurbatova, et al., J. Imaging, 8, No. 2, 15 (2022), https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging8020015.
Q. Huynh-Thu and M. Ghanbari, Electron. Lett., 44, 800–801 (2008), https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1049/et20080522.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Izmeritel’naya Tekhnika, No. 6, pp. 41–45, June, 2022.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Evtikhiev, N.N., Rodin, V.G., Savchenkova, E.A. et al. Adaptive Iterative Method of Selecting Weight Coefficients for Digital Hologram Binarization Using Error Diffusion. Meas Tech 65, 432–437 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11018-022-02101-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11018-022-02101-9