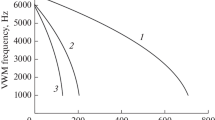
One of the principal problems of modern flow metering, the measurement of flow rate and quantity of wet gas, is considered. This problem is especially critical under production conditions when information about the quantity of the dry component of the gas present in the form of a mixture in a flow of moist gas, is needed. The operating principle and structure of the invariant system used in the measurement of the flow rate of moist gas (except for gases with an abundance of droplet moisture) are presented. The functioning of the invariant system used to measure the flow rate of wet gas is based on the combined application of differential pressure-drop flowmeters and Coriolis flowmeters as well as simultaneous application of the principle of multichanneling and the method of partial flow metering. The results of a test of the proposed invariant system are presented and its metrological characteristics exhibited in measurement of the flowrate of wet gas are estimated. The test results obtained are critical for natural gas extraction, transportation, and storage facilities.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Economides, M. and Wood, D. A., J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng., 1, 1–13 (2009), https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jngse.2009.03.005.
Yorucu, V. and Bahramian, P., J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng., 24, 464–472 (2015), https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JNGSE.2015.04.006.
Reader-Harris, M., Orifice Plates and Venturi Tubes, Springer International Publishing, Switzerland (2015), https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-16880-7.
Xu, Y., Yuan, C., Long, Z., et al., Flow Measur. Instr., 34, 68–75 (2013), https://doi.org/10.1016/j.flowmeasinst.2013.07.014.
Xu, L., Xu, J., Dong, F., and Zhang, T., Flow Measur. Instr., 34, 68–75 (2013), https://doi.org/10.1016/S0955-5986(03)00027-X.
Hua, C. and Geng, Y., Measurement, 45, 763–768 (2012), https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2011.12.013.
Li, J., Wang, J., and Geng, Y., Flow Measur. Instr., 20, 168–173 (2009), https://doi.org/10.1016/j.flowmeasinst.2009.04.002.
Steven, R., Flow Measur. Instr., 12, 361–372 (2002), https://doi.org/10.1016/S0955-5986(02)00003-1.
Steven, R. and Hall, A., Flow Measur. Instr., 20, 141–151 (2009), https://doi.org/10.1016/j.flowmeasinst.2009.07.001.
Lupeau, A., Platet, B., Gajan, P., et al., Flow Measur. Instr., 18, 1–11 (2007), https://doi.org/10.1016/j.flowmeasinst.2006.09.002.
He, D, and Bai, B., Measurement, 58, 61–67 (2014), https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2014.08.014.
He, D, and Bai, B., Flow Measur. Instr., 28, 1–6 (2007), https://doi.org/10.1016/j.flowmeasinst.2012.07.008.
Graham, E. M., Reader-Harris, M., Chinello, G., et al., Flow Measur. Instr.,74, 101757 (2020), https://doi.org/10.1016/j.flowmeasinst.2020.101757.
Pan, Y., Hong, Y., Sun, Q., et al., Flow Measur. Instr., 70, 101636 (2019), https://doi.org/10.1016/j.flowmeasinst.2019.101636.
Xu, L., Zhou, W., Li, X., and Tang, S., IEEE Trans. Instr. Measur., 60, 947–956 (2011), https://doi.org/10.1109/TIM.2010.2045934.
Dayev, Zh. and Yuluyev, V. T., Flow Measur. Instr., 70, 101636 (2019), https://doi.org/10.1016/j.flowmeasinst.2019.101653.
Petrov, B. N., Viktorov, V. A., Lunkin, B. V., et al., Principle of Invariance in Measurement Science, Nauka, Moscow (1976).
Bromberg, E. M. and Kulikovskii, K. L., Test Methods of Increased Degree of Measurement Precision, Energiya, Moscow (1978).
Dayev, Zh. A. and Latyshev, L. N., Flow Measur. Instr., 56, 18–22 (2017), https://doi.org/10.1016/j.flowmeasinst.2017.07.001.
Dayev, Zh. A. and Kayrakbaev, A. K., “Features of the measurement of the flow rate of liquid and gases by differential pressure-drop flowmeters,” Izmer. Tekhn., No. 11, 26–29 (2016).
Dayev, Zh. A., Flow Measur. Instr., 71, 101674 (2020), https://doi.org/10.1016/j.flowmeasinst.2019.101674.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Translated from Izmeritel’naya Tekhnika, No. 6, pp. 13−19, June, 2021.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dayev, Z.A., Shopanova, G.E. & Toksanbaeva, B.A. An Invariant Method of Measuring the Flow Rate of Wet Gas. Meas Tech 64, 445–452 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11018-021-01953-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11018-021-01953-x