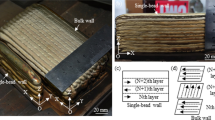
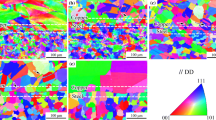
The structure and properties of CuSi3Mn1 (C65500) silicon bronze wire at various processing stages, including the upward continuous casting of a rod having a diameter (∅) of 8 mm and its subsequent multi-stage drawing with intermediate softening annealing up to a diameter of 4 mm, are studied. It has been established that during continuous casting, chemical interactions occur, leading to a hard crust sticking to the inner surface of the graphite die due to the presence of manganese in the alloy, which affects the stability of the casting process. An increase in casting stability is achieved by using a casting regime with an additional periodic dwell, which prevents a long-term hanging of the hardening crust from adhering to the surface of the graphite die. Furthermore, it was established that, following drawing and softening annealing, a significant change in the structure occurs, comprising the formation of twin grains instead of dendrites. The dispersion and the number of twin grains increase with a decrease in the wire diameter during the drawing process. The mechanical and bending tests of a wire of ∅4 mm showed that it complies with the standards, there being a significant plasticity margin. The initial cast rod having an increased diameter can be used in order to obtain a wire of a larger diameter that complies with the standards.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
O. E. Osintsev and V. N. Fedorov, Copper and Copper Alloys. Domestic and Foreign Brands. Handbook [in Russian], Innovatsionnoe Mashinostroenie, Moscow (2016).
J. R. Davis et al. (Eds.), “Copper and copper alloys,” ASM Specialty Handbook, ASM Intern., Mater. Park, OH, Second ed. (2008), pp. 361–363.
V. Korzhyk, V. Khaskin, S. Peleshenko, A. Grynyuk, I. Hos, O. Ganushchak, O. Babych, and D. Strogonov, “Overview of some perspective technical solutions on laser brazing with filler wires,” The 3rd Int. Sci. Pract. Conf. “Innovations and Prospects of World Science,” Perfect Publishing, Vancouver, Canada (2021), pp. 242–253.
N. S. Arsent’eva, E. A. Kazantsev, A. V. Sulitsyn, L. M. Zheleznyak, L. N Marushchak, and O. L. Glukhova, “Technology of production of welding wire from various alloys at the Kamensk-Uralsky Non-Ferrous Metal Processing Plant”, Metallurgist, No. 3, 67–69 (2008).
N. S. Arsent’eva, L. M. Zheleznyak, A. I. Snigirev, E. A. Kazantsev, and N. A. Taskina, “Advanced production of welding wire at the Kamensk-Uralsky Non-Ferrous Metal Processing Plant”, Tsvet. Met., No. 4, 122–126 (2007).
S. A. Tavolzhanskii and I. N. Pashkov, “Features of the continuous casting of small-section billets from copper-based alloys,” Metallurgist, 64, No. 9–10, 1068–1076 (2021).
R. Wilson, A Practical Approach to Continuous Casting of Copper-Based Alloys and Precious Metals, Institute of Materials, IOM Communications Ltd. (2000), p. 260.
E. Bagherian, To Enable the Processing of New Complex High Performance Alloys by Improving the Capacity and Performance of Continuous Casting Equipment, PhD Thesis, School of Science & Engineering, University of Dundee (2017).
S. A. Tavolzhansky and K. F. Koletvinov, “Development and application of a method of upward continuous casting of billets of HMP solders of small assortment”, Tsvet. Met., No. 11, 8588 (2015).
K. F. Koletvinov, S. A. Tavolzhansky, and V. E. Bazhenov, “Research and development of process of continuous-discrete pulling copper alloy billets from melt. State and prospects of development of foundry technologies and equipment in the digital era”, in: Sb. Tr. Vser. Nauch.-prakt. Konf. [in Russian], Universitet Mashinostroeniya, Moscow (2016), pp. 275–284.
E-R. Bagherian, Y. Fan, M. Cooper, B. Frame, and A. Abdolvand, “Effect of melt temperature, cleanout cycle, continuous casting direction (horizontal/vertical) and super-cooler size on tensile strength, elongation percentage and microstructure of continuous cast copper alloys,” Metall. Res. Technol., 113(5), [502] (2016); https://doi.org/10.1051/metal/2016030.
M. B. Gorlovsky and V. N. Merkachev, Handbook of a Wire Drawer, Metallurgiya, Moscow (1993).
M. Kulczyk, S. Przybysz, J. Skiba, and W Pachla, “High strength silicon bronze (C65500) obtained by hydrostatic extrusion,” Arch. Metall. Mater., 57, 859–862 (2012).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Metallurg, Vol. 66, No. 8, pp. 77–82, August, 2022. Russian DOI: https://doi.org/10.52351/00260827_2022_08_77.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Tavolzhanskii, S.A., Vedenkin, E.D., Plisetskaya, I.V. et al. Study of Properties and Structure of Silicon Bronze CuSi3Mn1 (C65500) Wire at Various Stages of Its Production by Continuous Casting and Subsequent Drawing. Metallurgist 66, 962–969 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11015-022-01408-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11015-022-01408-w