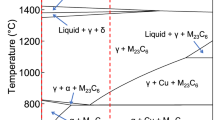
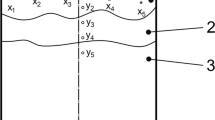
Among many factors influencing steel resistance to hydrogen induced cracking, the sulfur content in the metal and steel modification technology with calcium are of particular importance. In assessing the impact of process parameters on HIC resistance many authors do not consider their effect on production process efficiency and other quality indicators. The combined effect of calcium and rare earth metals on hot-rolled steel quality is described (with respect to steel HIC resistance, and contamination of metal by nonmetallic inclusions) in this paper. Formation of nonmetallic inclusions containing calcium and rare earth metals is described, and nonmetallic inclusions in the metal with different versions of modification are analyzed. The optimum amount of calcium and cerium required for obtaining stable results for HIC resistance in low-carbon micro-alloyed steels while retaining good rolled steel surface quality is determined.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
L. I. Éfron, Materials Science in “Big” Metallurgy. Pipe Steels [in Russian], Metallurgizdat, Moscow (2012).
V. Schwinn, A. Streibelberger, and J. Bauer, Conf. Corrosion’95. NACE Intern., Houston, Texas (1993).
Treatise on Process Metallurgy, Industrial Processes, Vol. 3, Elsevier (2014).
A. Wilson, “Technology for producing clean steel - reasons for improvement of technology for manufacturing high quality steels,” in: High Quality Steel Production, American Soc. For Testing Materials (1999).
Y. Wang, S. Sridhar, and M. Valdez, “Formation of CaS on Al2O3CaO inclusions during solidification of steels,” Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B, 33, No. 4, 625–632 (2002).
Jose Carlos, S. Pires, and Amauri Garcia, “Modification of oxide inclusions formed in steel deoxidized with aluminum by adding calcium,” Trudy Metal. Mater. (2004).
S. K. Choudhary and A. Ghosh, “Thermodynamic evaluation of the formation of two-phase oxysulfide inclusions,” Metallurgiya, 48, No. 2, 95–98 (2009).
T. Liz, “Modification of oxide and sulfide inclusions in steel by treatment with calcium,” Iron and Steel Technol. Conf. (2015).
S. Abraham, R. Bodnar, and J. Raines, “Inclusions engineering and the metallurgy of calcium treatment,” The Iron and Steel Technology Conf. (2014).
E-P. Heikkinen, et al., “A thermodynamic study on the distribution of sulfur between inclusions and molten steel,” 9 th Clean Steel Conf. (2015).
State of the Art and Process Technology in Clean Steelmaking, IISI Committee on Technology (2006).
A. V. Ioffe, T. V. Tetyueva, et al., “Effect of modification by rare earth metals on mechanical and corrosion properties of lowcarbon steels,” Vektor Nauki TGU, No. 4(14) (2010).
E. T. Turkdogan, “Deoxidation and desulfurization of steel in a ladle and nonmetallic inclusions in steels — theoretical bases and practical observations,” in: Clean Steel, Coll. Sci. Work (A. G. Shalimov, editor) [Russian translation], Metallurgiya, Moscow (1987).
NACE TM9284-2011. Standard test method of steel evaluation for pipelines and vessels under pressure for hydrogen cracking resistance.
D. V. Kudashov, E. S. Mursenkov, G. V. Semernin, et al., “Assimilation of extra-furnace treatment and casting technology for pipe grades of steel with specifications for H2S media resistance under casting and rolling module conditions,” Metallurg, No. 8, 48–56 (2017).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Metallurg, Vol. 62, No. 10, pp. 27–35, October, 2018.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mursenkov, E.S., Kudashov, D.V., Kislitsa, V.V. et al. Features of Technology for Pipe Steel Modification with Calcium and Cerium with Specification for Resistance to H2S-MEDIA. Metallurgist 62, 994–1005 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11015-019-00730-0
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11015-019-00730-0