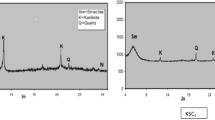
A sorption method is proposed for cleaning industrial effluent with a new nanostructured complex sorbent based on Taganskoe deposit bentonite clay and mineral wool production waste. It is shown that with mechanical activation of bentonite clay together with mineral wool production waste there is an increase in clay particle content with a size less than 1 μm. It is established that for comprehensive and effective cleaning of electrolysis effluent from heavy metal ions a nanostructured complex sorbent (NSCS) is recommended based on bentonite clay from the 11th level and mineral wool production waste with observation of the following optimum conditions: 2:1 ratio of components in NSCS of 11th level bentonite clay : mineral wool production waste; rational mechanical activation scheme with grinding and nanostructuring of complex sorbent starting materials for 15 min; S:L = 1:100 (1 g of paste (in terms of dry substance) to 100 cm3 clean water); sorption time 3 h with constant stirring.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
O. S. Anisimova, A, K, Adryshev, and N. A. Kulenova, Cleaning Nonferrous Metallurgy Enterprise Effluent, VKGTU, Ust-Kamenogorsk (2013).
N. N. Solokhina, R. M. Babusenko, N. Zh. Tumabaev, and K. A. Zhubanov, “Physicochemical properties of bentonite clay of East Kazakhstan,” Izv. MON RK, NAN RK, Ser. Khim., No. 5, 27–31 (1999).
M. M. Kravchenko and E. M. Sapargaliev, Study of Natural Zeolite and Bentonite Properties with the Aim of Use as Sorbents, Catalysts, and for Preparing Materials with Anticorrosion Properties: Research Review, IGN Altai-Sorbent, Ust-Kamenogorsk (1996).
A. K. Adryshev, G. K. Daumova, Yu. V. Lopukhov, and A. A. Khairullina, Patent 29595 RK, IPC B01G20/16, “Method for preparing filter-sorption material,” subm. 05.04.2014, publ. 03.16.2015, Byull., No. 3.
A. K. Adryshev, N. V. Seraya, A. A. Khairullina, and G. K. Daumova, “Ecological aspects of using complex sorbents in effluent cleaning,” Vestn. KazNU im. Al-Farabi, No. 3(45), 54–60 (2015).
A. L. Adryshev, G. K. Daumova, N. V. Seraya, et al., “Use of complex sorbents based on natural alumosilicates and technogenic waste in effluent deep cleaning,” Ekol. Vestn. Rossii, No. 6, 42–45 (2016).
A. K. Adryshev, N. V. Seraya, A. A. Khairullina, and G. K. Daumova, “Use of nanostructured complex sorbents in resolving ecological problems,” Ekosfera, No. 16, 13–16 (2016).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Metallurg, No. 8, pp. 7–13, August, 2017.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mamyachenkov, S.V., Adryshev, A.K., Seraya, N.V. et al. Nanostructured Complex Sorbent for Cleaning Heavy Metal Ions from Industrial Effluent. Metallurgist 61, 615–623 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11015-017-0542-5
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11015-017-0542-5