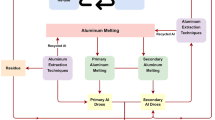
The spent lining of aluminum electrolyzer is one of the most environmentally hazardous wastes of the aluminum industry due to its content of up to 0.2 wt.% cyanide and up to 40 wt.% fluorides. The majority of spent lining is accumulated near aluminum plants in specially equipped landfills, where it can interact with water and air, with formation of toxic compounds and alkaline solutions that could lead to ground water contamination. At the same time, spent lining is of specific value due to presence of fluoride and up to 30 wt.% carbon. Known technology for processing spent lining with preparation of cryolite in operation at some aluminum plants has lost its importance after introduction of dry gas cleaning and a change-over to electrolysis technology using acidic electrolytes. This has led to a substantial reduction of cryolite requirement. Therefore, at present more attention is devoted to technology for producing aluminium fluoride, including from spent lining. This article provides a brief review of known technology for processing aluminum electrolyzer spent lining. Technology is provided for preparing aluminium fluoride product containing fluorine of 55–59 wt.%; thus, there is a reduction in fresh AlF3 consumption of about 4–6 kg/ton Al. Laboratory test results are provided.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Sorl’e and H. A. Oiya, Aluminum Electrolyzer Cathodes, Verso, Krasnoyarsk (2013).
A. A. Savinova, “Problem of utilizing carbon-containing waste of the Krasnoyarsk Aluminum Plant. Search for new ways,” Tekhn.-Ekon. Vestn. Krasnoyarsk. Alum. Zavoda, No. 8, 33–45 (1994).
D. K. Holywell, “Review of methods for utilization, storage, and reduction of spent electrolyzer lining,” Proc. 9th Int. Conf. Aluminum of Siberia 2003, Krasnoyarsk (2003), pp. 4–7.
V. P. Klimenko, Development of Technology for Regenerating Fluorine Salts from Solid Waste of Electrolytic Aluminum Production: Diss. Cand. Techn. Sci., Irkutsk (1972).
V. P. Kulikov and S. P. Istomin, Processing of Aluminum Production Waste, Klassik, Krasnoyarsk (2004).
V. V. Kondrat’ev, “Prospects for processing solid fluorine-containing aluminum electrolyzer waste,” Vestn. IRGTU, 2, No. 1, 36–41 (2007).
N. V. Golovnykh, V. G. Grigor’ev, V. V. Dorofeev, et al., “Use of solid electrolyzer waste in aluminum fluoride production,” Proc. 9th Int. Conf. Aluminum of Siberia 2003, Krasnoyarsk (2003), pp. 29–32.
B. P. Kulikov, P. V. Polyakov, V. E. Zheleznyak, et al., “Preparation of combined modifying addition for ements from aluminum production solid waste,” Proc. 31st Int. Conf. Iksoba and 19th Int. Conf. Aluminum of Siberia, Krasnoyarsk (2013), pp. 854–860.
Cao Xiao-zhou, Shi Yuan-yuan, Zhao Shuang, and Xue Xiang-xin, “Recovery of valuable components from spent pot-lining of aluminium electrolytic reduction cells,” Dongbei daxue xuebao. Ziran kexue ban, J. Northeast. Univ. Natur. Sci., 35. No. 12, 1746–1751 (2014).
T. Johnson and D. Digan, “Plasma treatment of electrolyzer spent refractory lining,” Alum. Int. Today, No. 24, 4–8 (2012).
G. Hamel, R. Breault, G. Charest, et al., “From the ‘low caustic leaching and liming’ process development to the Jonquière spent pot-lining treatment pilot plant start-up, 5 years of process up-scaling, engineering and commissioning,” Light Metals, 921–925 (2009).
B. Meirelles and H. Santos, “Economic and environmental alternative for destination of spent pot lining from primary aluminum production,” Light Metals, 565–570 (2014).
R. K. Patrin and V. Yu. Bazhin, “Spent linings from aluminum cells as a raw material for the metallurgical, chemical, and construction industries,” Metallurgist, 58, No. 7–8, 625–628 (2014).
E. P. Rzhechitskii, V. V. Kondrat’ev, and A. Yu. Tenigin, Technological Solutions for Environmental Protection in Aluminum Production, Izd. IGTU, Irkutsk (2013).
E. P. Rzhechitskii, V. V. Kondrat’ev, et al., Patent 2462418, RF IPC C01F7/50, “Aluminum fl uoride preparation method,” subm. 06.07.2011, publ. 09.27. 2012, Byull., No. 27.
V. V. Kondrat’ev and E. P. Rzhechitskii, “Ecological and economic effi ciency of processing gas cleaning solutions and aluminum production fluorine-containing waste,” Ekol. Prom. Rossii, No. 8, 28–31 (2011).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Metallurg, No. 6, pp. 28–31, June, 2016.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kondrat’ev, V.V., Rzhechitskii, E.P., Shakhrai, S.G. et al. Recycling of Electrolyzer Spent Carbon-Graphite Lining with Aluminum Fluoride Regeneration. Metallurgist 60, 571–575 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11015-016-0333-4
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11015-016-0333-4