Abstract
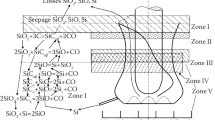
In order to protect the smelting chamber of a crystallizer from the oxidizing effects of the atmosphere, Chelyabinsk Metallurgical Combine (ChMK) has tested the use of thermally expanded graphite (TEG) in electroslag remelting of 70KhGFA-Sh and ShKh15-Sh steel under industrial conditions. The study results showed a substantial reduction in the oxygen content of the test metal, a 30% increase in productivity of the process, and a 30% reduction in the specific electrical power usage.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. P. Yaroshenko, V. N. Radchenko, M. V. Savos’kin, et al., “Intercalated graphite compounds are new materials for electroslag remelting of steel,” Zh. Prikl. Khim. 68, No. 4, 654–657 (1995); Russian J. Appl. Chem. 68, No. 4, 570–573 (1995).
Russian Federation Patent 2058261, IPC C 01 B31/04, Method for Production of Thermally Expanded Graphite (1996).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
__________
Translated from Metallurg, No. 6, pp. 38–40, June, 2008.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Antonov, V.I., Kudrin, A.A., Kostyleva, N.V. et al. Use of thermally expanded graphite for protection of a furnace smelting chamber. Metallurgist 52, 346–349 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11015-008-9057-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11015-008-9057-4