Abstract
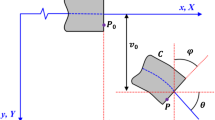
Based on Hamilton’s variational principle, strain gradient theory and Timoshenko curved nanobeam model, governing equations and corresponding boundary conditions are derived. Governing differential equations are transformed into algebraic equations by employing Navier method, thus an analytical solution for size-dependent static bending, free vibration and buckling analysis of curved flexomagnetic nanobeam is established. Influences of opening angle, aspect ratio and scale parameter on bending deformation, free vibration and stability are discussed in detail. Compared and validated with available investigations, a good agreement is found.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ma W, Cross LE (2001) Observation of the flexoelectric effect in relaxor Pb(Mg 1/3Nb2/3)O3 ceramics. Appl Phys Lett 78(19):2920
Ma W, Cross LE (2002) Flexoelectric polarization of barium strontium titanate in the paraelectric state. Appl Phys Lett 81(18):3440
Ma W, Cross LE (2005) Flexoelectric effect in ceramic lead zirconate titanate. Appl Phys Lett 86(7):072905-072905–3
Sharma ND, Maranganti R, Sharma P (2007) On the possibility of piezoelectric nanocomposites without using piezoelectric materials. J Mech Phys Solids 55(11):2328–2350
Ma W (2008) A study of flexoelectric coupling associated internal electric field and stress in thin film ferroelectrics. Phys Status Solidi 245(4):761–768
Majdoub MS, Sharma P, Cagin T (2008) Size-dependent super-piezoelectricity and elasticity in nanostructures due to the flexoelectric effect. Phys Rev B 77(12):125424-1–9
Shen S, Hu S (2010) A theory of flexoelectricity with surface effect for elastic dielectrics. J Mech Phys Solids 58(5):665–677
Zhuang X et al (2020) Computational modeling of flexoelectricity—a review. Energies 13(6):1326
Yudin PV, Tagantsev AK (2013) Fundamentals of flexoelectricity in solids. Nanotechnology 24(43):432001
Zhao X, Zheng S, Li Z (2019) Size-dependent nonlinear bending and vibration of flexoelectric nanobeam based on strain gradient theory. Smart Mater Struct 28(7):075027
Nan Z et al (2020) Size-dependent static bending and free vibration analysis of porous functionally graded piezoelectric nanobeams. Smart Mater Struct 29(4):045025
Chen Q et al (2021) Size-dependent free vibration analysis of functionally graded porous piezoelectric sandwich nanobeam reinforced with graphene platelets with consideration of flexoelectric effect. Smart Mater Struct 30(3):035008
Zhang R, Liang X, Shen S (2015) A Timoshenko dielectric beam model with flexoelectric effect. Meccanica 51(5):1181–1188
Zheng S, Zhao X, Wang H (2019) Theoretical and finite element modeling of piezoelectric nanobeams with surface and flexoelectricity effects. Mech Adv Mater Struct 26(15):1261–1270
Li JY (2000) Magnetoelectroelastic multi-inclusion and inhomogeneity problems and their applications in composite materials. Int J Eng Sci 38:1993–2011
Yang Y, Li X-F (2019) Bending and free vibration of a circular magnetoelectroelastic plate with surface effects. Int J Mech Sci 157–158:858–871
Eliseev EA et al (2009) Spontaneous flexoelectric/flexomagnetic effect in nanoferroics. Phys Rev B 79(16):165433
Lukashev P, Sabirianov RF (2010) Flexomagnetic effect in frustrated triangular magnetic structures. Phys Rev B 82(9):094417
Eliseev EA et al (2011) Linear magnetoelectric coupling and ferroelectricity induced by the flexomagnetic effect in ferroics. Phys Rev B 84(17):174112
Pyatakov AP, Zvezdin AK (2009) Flexomagnetoelectric interaction in multiferroics. Eur Phys J B 71(3):419–427
Kabychenkov AF, Lisovskii FV (2019) Flexomagnetic and flexoantiferromagnetic effects in centrosymmetric antiferromagnetic materials. Tech Phys 64(7):980–983
Sidhardh S, Ray MC (2018) Flexomagnetic response of nanostructures. J Appl Phys 124(24):244101
Zhang N, Zheng S, Chen D (2019) Size-dependent static bending of flexomagnetic nanobeams. J Appl Phys 126(22):223901
Malikan M, Eremeyev VA, Zur KK (2020) Effect of axial porosities on flexomagnetic response of in-plane compressed piezomagnetic nanobeams. Symmetry-Basel 12(12):1935
Malikan M, Eremeyev VA (2020) On nonlinear bending study of a piezo-flexomagnetic nanobeam based on an analytical-numerical solution. Nanomaterials 10(9)
Malikan M, Uglov NS, Eremeyev VA (2020) On instabilities and post-buckling of piezomagnetic and flexomagnetic nanostructures. Int J Eng Sci 157:103395
Malikan M, Eremeyev VA (2020) On the geometrically nonlinear vibration of a piezo‐flexomagnetic nanotube. Math Methods Appl Sci
Malikan M, Wiczenbach T, Eremeyev VA (2021) On thermal stability of piezo-flexomagnetic microbeams considering different temperature distributions. Contin Mech Thermodyn
Malikan M, Eremeyev VA (2021) Effect of surface on the flexomagnetic response of ferroic composite nanostructures; nonlinear bending analysis. Compos Struct 271
Malikan M, Eremeyev VA (2021) Flexomagnetic response of buckled piezomagnetic composite nanoplates. Compos Struct 267
Malikan M, Eremeyev VA (2021) Flexomagneticity in buckled shear deformable hard-magnetic soft structures. Contin Mech Thermodyn
Sladek J et al (2021) A cantilever beam analysis with flexomagnetic effect. Meccanica 56(9):2281–2292
Shi Y et al (2021) Enhanced magnetoelectric response in nanostructures due to flexoelectric and flexomagnetic effects. J Magn Magn Mater 521
Arefi M, Zenkour AM (2017) Influence of magneto-electric environments on size-dependent bending results of three-layer piezomagnetic curved nanobeam based on sinusoidal shear deformation theory. J Sandwich Struct Mater 21(8):2751–2778
Zenkour AM, Arefi M, Alshehri NA (2017) Size-dependent analysis of a sandwich curved nanobeam integrated with piezomagnetic face-sheets. Results Phys 7:2172–2182
Arefi M, Zenkour AM (2018) Size-dependent vibration and electro-magneto-elastic bending responses of sandwich piezomagnetic curved nanobeams. Steel Compos Struct 29(5):579–590
Wu JS, Chiang LK (2003) Out-of-plane responses of a circular curved Timoshenko beam due to a moving load. Int J Solids Struct 40(26):7425–7448
Malekzadeh P, Haghighi MRG, Atashi MM (2010) Out-of-plane free vibration of functionally graded circular curved beams in thermal environment. Compos Struct 92(2):541–552
Thai H-T (2012) A nonlocal beam theory for bending, buckling, and vibration of nanobeams. Int J Eng Sci 52:56–64
Acknowledgements
This research was partially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 11572151), the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, N., Zheng, S. & Chen, D. Size-dependent static bending, free vibration and buckling analysis of curved flexomagnetic nanobeams. Meccanica 57, 1505–1518 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11012-022-01506-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11012-022-01506-8